1 The cardiovascular system
ANATOMY AT A GLANCE
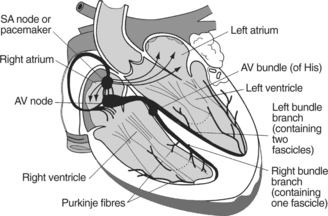
The basic structure of the heart together with the electrical conducting system is shown in Figure 1.1.
PHYSIOLOGY YOU NEED TO KNOW
 Diastole is the resting period during which the two ventricles fill with blood draining under gravity from the atria. During diastole, the right atrium is filled with venous blood from the systemic circulation and the left atrium is filled with oxygenated blood returning from the lungs.
Diastole is the resting period during which the two ventricles fill with blood draining under gravity from the atria. During diastole, the right atrium is filled with venous blood from the systemic circulation and the left atrium is filled with oxygenated blood returning from the lungs. Systole corresponds to the powerful contraction of the ventricular muscle which simultaneously sends blood from the right ventricle via the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and from the left ventricle via the aorta around the systemic circulation. The term ‘atrial systole’ is used to describe contraction of the atria at the end of diastole. This ensures that the ventricles are filled to maximum capacity before systole.
Systole corresponds to the powerful contraction of the ventricular muscle which simultaneously sends blood from the right ventricle via the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and from the left ventricle via the aorta around the systemic circulation. The term ‘atrial systole’ is used to describe contraction of the atria at the end of diastole. This ensures that the ventricles are filled to maximum capacity before systole.The wave of depolarization initiated by the SA node is picked up by the atrioventricular (AV) node, conducted via the bundle of His, the left and right bundle branches and the spreading network of Purkinje fibres into the ventricular muscle where it initiates ventricular contraction. This electrical activity is recorded as the electrocardiogram (ECG) whose components are as follows:
| P wave | SA node discharge and atrial depolarization |
| PQ interval | Delay while electrical impulse is conducted through conducting fibres |
| QRS waves | Ventricular contraction |
| T wave | Repolarization for next heart beat (diastole). |
ANGINA PECTORIS (P280)
WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR
 The pain may radiate to the shoulders, arms, neck or jaw and may not even be felt in the chest at all.
The pain may radiate to the shoulders, arms, neck or jaw and may not even be felt in the chest at all.MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
The aim is to balance oxygenated blood supply to the myocardium with demand in order that painful episodes may be avoided. The presence of angina indicates advanced arterial disease which could lead to a more serious and possibly fatal event such as a myocardial infarction (MI) or cerebrovascular accident (CVA). The patient will therefore be investigated and key indicators such as blood pressure and blood lipids monitored regularly. Direct interventions to relieve the symptoms include percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) which involves passing a catheter to within the atherosclerotic lesion and then inflating a balloon to stretch the artery, widening the lumen of the artery and increasing blood flow (p282).
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (P284)
WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR
 There is a potential for cardiac arrhythmias some of which may prove rapidly fatal (ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation).
There is a potential for cardiac arrhythmias some of which may prove rapidly fatal (ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation).MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
 Early diagnosis is crucial as most deaths occur within the first hour and prompt treatment to dissolve away the clot in the coronary artery greatly improves the prognosis amongst survivors. A 12-lead ECG should be performed at the earliest opportunity as an elevated ST section is diagnostic of acute MI. Bloods are taken for the presence of certain chemicals known to be in myocardial cells. Their presence in the blood indicates that they have leaked from damaged myocardium and this confirms the diagnosis of MI. Troponin T or I levels rise within a few hours of MI. Myoglobin is another marker for damaged myocardial cells and together with troponin can be measured with a bedside test. The cardiac enzyme creatine phosphokinase (CPK) peaks between 12 and 24 hours while lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) peaks between 3 and 6 days and is useful for a late presentation.
Early diagnosis is crucial as most deaths occur within the first hour and prompt treatment to dissolve away the clot in the coronary artery greatly improves the prognosis amongst survivors. A 12-lead ECG should be performed at the earliest opportunity as an elevated ST section is diagnostic of acute MI. Bloods are taken for the presence of certain chemicals known to be in myocardial cells. Their presence in the blood indicates that they have leaked from damaged myocardium and this confirms the diagnosis of MI. Troponin T or I levels rise within a few hours of MI. Myoglobin is another marker for damaged myocardial cells and together with troponin can be measured with a bedside test. The cardiac enzyme creatine phosphokinase (CPK) peaks between 12 and 24 hours while lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) peaks between 3 and 6 days and is useful for a late presentation.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree