T
Testosterone, total, free
Basics the nurse needs to know
In the male, almost all the testosterone is synthesized by the testes. In the female, small amounts are synthesized by the ovaries and adrenal glands. Testosterone is the dominant androgen and, in the male, is responsible for spermatogenesis. Androgens affect many other organs and tissues, resulting in increased total body mass and hirsutism, the distribution of body hair. When hirsutism is excessive, it is caused by excessive testosterone or its hormonal precursor, androstenedione. In the female, the testosterone level is one of the tests to investigate hirsutism.
Interfering factors
NURSING CARE
Nursing measures include care of the venipuncture or capillary puncture site as described in Chapter 2, with the following additional measures.
Posttest
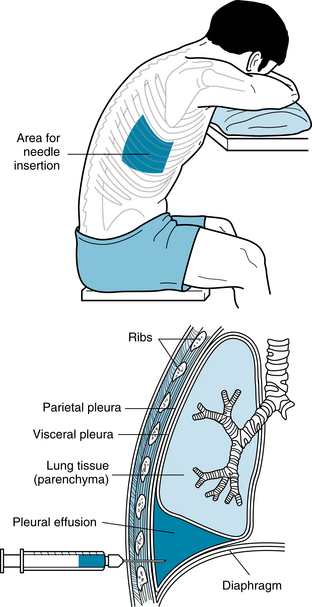
Thoracentesis, pleural fluid analysis, and pleural biopsy
Also called: Pleural tap, Pleural fluid aspiration
Interfering factors
NURSING CARE
Pretest
During the test
Posttest
Thyroglobulin autoantibodies
Also called: Antithyroid Antibodies
Purpose of the test
Thyroglobulin antibodies are evaluated to detect autoimmune-based thyroid disease.
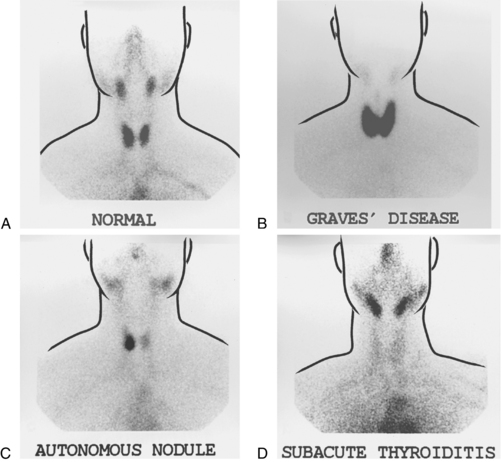
Thyroid scan
Also called: Radionuclide Thyroid Scanning
Basics the nurse needs to know
To produce its hormones, the thyroid gland must extract iodide from the extracellular fluid. Once it has taken up enough iodide to meet its needs, the iodide left in the extracellular fluid is excreted in urine. The thyroid gland cannot distinguish between dietary iodine and radioactive iodine. Thus it will take up the radioactive iodide, which can be scanned by a gamma camera. The functioning of the thyroid gland can be evaluated by the amount of radioactive iodide it takes up. In thyrotoxic states, more iodide is needed and the uptake is increased, whereas in hypothyroid states, less than normal amounts of iodide are needed, thus less is taken up by the thyroid gland.
Additional information on nuclear scans is presented on p. 455.
Interfering factors
NURSING CARE
Pretest
Describe the scanning equipment to the patient. The probe is placed over the anterior portion of the neck. Emphasize that no discomfort is involved but that the patient must lie absolutely still while the scan is performed. The nurse informs the patient that the oral radioactive iodine, if being used, has little or no taste. It comes in capsule or liquid form. Explain to the patient the need for two scans because the uptake of the radioactive iodine is usually maximized at 24 hours but some thyroid conditions may cause the peak uptake to occur earlier.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree