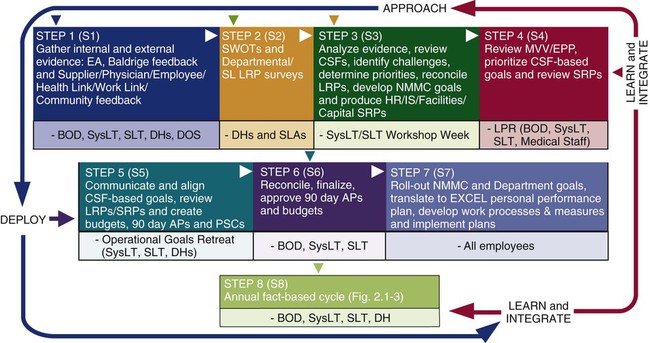
1. Define strategic management and strategic planning. 2. Discuss the importance of the strategic planning process. 3. Identify the components of the strategic plan. 4. Compare and contrast the various types of strategic planning processes. 5. Distinguish between short- and long-term plans and objectives. 6. Identify the role of the nurse manager in the strategic planning process. Simply put, strategic planning is the process by which an organization/nursing department or unit decides where it is going over the next year or longer and how it is going to get there. Typically, the process is organization-wide and the outcome of the process that, on an organizational level, cascades down to the patient care department and the individual units and employees. The strategic plan is the “map” of where the organization, department, or unit is going over the next year or longer. Managers of an organization need to focus on a series of key questions as they begin the strategic planning process (Finkler, Kovner, and Jones, 2007, p. 216): • Why does the organization exist? • What is the organization currently? • How can we make the transformation to what we want to be? The elements of a strategic plan include the following (Finkler et al., 2007, p. 217): • Statement of competitive challenges and strategy • Statement of short- and long-term goals • Statement of organizational policies • Statement of needed resources For example, the simple mission of North Mississippi Medical Center (NMMC) (2007) is: The corresponding vision statement of this organization is: And the values of this organization are: • NMMC’S purpose is to provide compassionate health care with optimal outcomes and NMMC’s Mission reflects the organization’s secure roots in the communities it serves. Its ambitious Vision reflects a deeply-held commitment to excellence in every activity. The CARES Values acronym (Compassion • Accountability • Respect • Excellence • Smile) expresses NMMC’s focus on exceptional customer service. • The Mission and Vision are translated into measurable actions through the CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS (CSFs): PEOPLE, SERVICE, QUALITY, FINANCIAL, GROWTH. The order of the CSFs is intentional. It starts with creating an environment that draws and nurtures the best PEOPLE to provide the best SERVICE. Great SERVICE results in happy customers and excellent QUALITY. High QUALITY and efficiency produce good FINANCIAL results and requests for more services, which results in GROWTH. All activities are organized and managed according to the CSFs, thereby creating organizational alignment and a comprehensive structure for operational excellence. Usually, budgets are included in the strategic and annual plan, and with individual departmental and unit plans. Budgets specify the funds needed for the resources that are necessary to implement the annual plan. Budgets also depict how the funds will be spent. (See Chapter 14 for information on budgets.) The strategic planning process of NMMC is diagrammed in Figure 13-1, and an example of their broad strategic plan is shown in Figure 13-2. Note that the goals are formulated according to the critical success factors identified by the organization. The performance indicators list the measures that will be used to measure progress toward achievement of the goals. The benchmarks relate the performance of the competitors or “best in class,” and the targets are the short- and long-term goals.
Strategic Management and Planning
WHAT IS STRATEGIC PLANNING?
ELEMENTS OF A STRATEGIC PLAN
MISSION AND VISION STATEMENTS
STATEMENT OF SHORT- AND LONG-TERM GOALS
Action Planning
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Strategic Management and Planning
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access