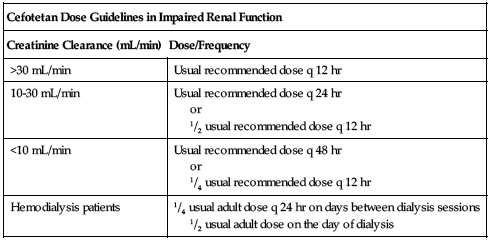
or
1/2 usual recommended dose q 12 hr
or
1/4 usual recommended dose q 12 hr
1/2 usual adult dose on the day of dialysis
Dilution
IV injection:
Reconstitute each 1 Gm of the lyophilized powder with 10 mL of SW for injection (2 Gm with 20 mL). Shake well and let stand until clear.
Intermittent IV: Vials:
A single dose may be further diluted or initially diluted with 50 to 100 mL of D5W or NS. Also available in dual-chamber DUPLEX containers and pharmacy bulk packaging. Refer to manufacturer’s prescribing information for specific preparation and storage requirements.
Filters:
No data available from manufacturer.
Storage:
Store vials below 22° C (72° F); protect from light. Administer within 24 hours of preparation or within 96 hours if refrigerated. Stable after dilution for 1 week if frozen; thaw at room temperature before use; discard remaining solution; do not refreeze. Slight yellowing does not affect potency.
Compatibility (underline indicates conflicting compatibility information)
Consider any drug NOT listed as compatible to be INCOMPATIBLE until consulting a pharmacist; specific conditions may apply.
May be used concomitantly with aminoglycosides (e.g., amikacin, gentamicin), but these drugs must never be mixed in the same infusion (mutual inactivation). If given concurrently, administer separately and flush the IV line before and after administration. Manufacturer recommends temporarily discontinuing other solutions infusing at the same site during intermittent infusion and states, “Do not add supplementary medications to premixed plastic IV containers” (e.g., Galaxy).
One source suggests the following compatibilities:
Y-site:
Allopurinol (Aloprim), amifostine (Ethyol), aztreonam (Azactam), bivalirudin (Angiomax), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), docetaxel (Taxotere), etoposide phosphate (Etopophos), famotidine (Pepcid IV), fenoldopam (Corlopam), filgrastim (Neupogen), fluconazole (Diflucan), fludarabine (Fludara), gemcitabine (Gemzar), granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hetastarch in electrolytes (Hextend), insulin (regular), linezolid (Zyvox), melphalan (Alkeran), meperidine (Demerol), morphine, paclitaxel (Taxol), palonosetron (Aloxi), propofol (Diprivan), remifentanil (Ultiva), sargramostim (Leukine), tacrolimus (Prograf), teniposide (Vumon), theophylline, thiotepa, vancomycin.
Rate of administration
See Compatibility. May be given through Y-tube or three-way stopcock of infusion set.
IV injection:
A single dose equally distributed over 3 to 5 minutes.
Intermittent IV:
A single dose equally distributed over 30 minutes.
Actions
A broad-spectrum, second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Bactericidal to selected gram-negative, gram-positive, and anaerobic organisms. Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Effective against many otherwise resistant organisms. Peak serum levels achieved at end of infusion. Widely distributed in most tissues, body fluids (CSF minimal), bone, gallbladder, myocardium, and skin and soft tissue. Half-life is from 3 to 4.6 hours. Primarily excreted in the urine. Crosses placental barrier. Secreted in breast milk.
Indications and uses
Treatment of serious lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, skin and skin structure, gynecologic, intra-abdominal, and bone and joint infections. Most effective against specific organisms (see literature). ■ Perioperative prophylaxis.
Contraindications
Previous hypersensitivity reaction to cephalosporins or related antibiotics (penicillins). Absolute only if reaction was serious and in patients who have experienced a cephalosporin-associated hemolytic anemia. ■ Premixed solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with known allergies to corn or corn products.
Precautions
Specific sensitivity studies are indicated to determine susceptibility of the causative organism to cefotetan. ■ To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain its effectiveness, cefotetan should be used to treat or prevent only those infections proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. ■ Continue for at least 2 or 3 days after all symptoms of infection subside. ■ Avoid prolonged use of drug; superinfection caused by overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms may result. ■ Use caution in patients with impaired renal function, a history of GI disease (especially colitis), bleeding disorders or allergies, and those receiving an extended course of cephalosporins. ■ Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported. May range from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Consider in patients who present with diarrhea during or after treatment with cefotetan. ■ Hemolytic anemia, including fatalities, has been reported. Discontinue cefotetan immediately if anemia develops during the course of therapy. May present during treatment or up to 2 to 3 weeks following therapy completion.
Monitor:
Watch for early symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. ■ Use extreme caution in the penicillin-sensitive patient; incidence of cross-sensitivity may be up to 10%. ■ May cause hypoprothrombinemia (deficiency of prothrombin [factor II]); 10 mg/week of prophylactic vitamin K may be indicated in elderly, debilitated, or other patients with vitamin K deficiency. Monitor PT. ■ May cause thrombophlebitis. Use small needles and large veins, and rotate infusion sites. ■ Observe for electrolyte imbalance and cardiac irregularities. Contains 3.5 mEq sodium per Gm. ■ Monitor for S/S of hemolytic anemia, including CBC if indicated. ■ See Drug/Lab Interactions; additional monitoring may be indicated (e.g., renal function, drug serum levels, PT).
Patient education:
Avoid alcohol or alcohol-containing preparations; may cause abdominal cramps, flushing, headache, nausea and vomiting, shortness of breath, sweating, and tachycardia. ■ Report promptly any bleeding or bruising or symptoms of allergy (e.g., difficulty breathing, hives, itching, rash). ■ Promptly report diarrhea or bloody stools that occur during treatment or up to several months after an antibiotic has been discontinued; may indicate CDAD and require treatment.
Maternal/child:
Category B: safety for use during pregnancy not established. Use only if clearly needed. ■ Use caution if breast-feeding. ■ Safety for use in pediatric patients not established. Immature renal function of infants and small children will increase blood levels of all cephalosporins.
Elderly:
See Dose Adjustments. ■ Safety and effectiveness similar to younger adults; however, greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. ■ Monitoring of renal function suggested.
Drug/lab interactions
May produce symptoms of acute intolerance with alcohol (a disulfiram-like reaction with abdominal cramps, headache, flushing, nausea and vomiting, shortness of breath, sweating, tachycardia). Patient must abstain from alcohol during treatment and until at least 72 hours after discontinuation. ■ Risk of nephrotoxicity may be increased with aminoglycosides and other nephrotoxic agents (e.g., loop diuretics [furosemide (Lasix)]). ■ Sources differ on inhibition of excretion by probenecid. ■ May be antagonized by bacteriostatic antibiotics (e.g., chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracyclines); may interfere with bactericidal action. ■ Bleeding tendency increased with any medicine that affects blood clotting (e.g., heparin and oral anticoagulants [warfarin (Coumadin)], thrombolytic agents [e.g., alteplase (tPA)], salicylates, NSAIDs [e.g., ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn)], sulfinpyrazone [Anturane]). ■ Large amounts of cephalosporins and/or salicylates may induce hypoprothrombinemia. ■ False increases in creatinine levels with Jaffe method. ■ False-positive for urine glucose except with enzyme-based tests (e.g., Clinistix). ■ Positive direct Coombs’ test. ■ See Compatibility and Side Effects.
Side effects
Full scope of hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Bleeding episodes; burning, discomfort, and pain at injection site; CDAD; diarrhea; elevated alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT, and LDH; eosinophilia; nausea; prolonged PT; seizures (large doses); thrombocytosis. Hypoprothrombinemia (rare) and hemolytic anemia may occur.
Antidote
Notify physician of any side effects. Discontinue the drug if indicated. Treat hypersensitivity reactions as indicated and resuscitate as necessary. Mild cases of CDAD may respond to discontinuation of cefotetan. Treat CDAD with fluids, electrolytes, protein supplements, and oral vancomycin (Vancocin) or metronidazole (Flagyl) as indicated. In severe cases, surgical evaluation may be indicated. Bleeding episodes may respond to vitamin K or require discontinuation of drug. Fresh-frozen plasma, packed red cells, or platelet concentrates may be indicated in abnormal bleeding tendencies confirmed by lab evaluations. If bleeding is due to platelet dysfunction, discontinue and use an alternate antibiotic. Blood transfusions (e.g., packed red cells) may be indicated if hemolytic anemia develops. Hemodialysis is only slightly useful in overdose.
Cefoxitin sodium
(seh-FOX-ih-tin SO-dee-um)
Mefoxin
Antibacterial (cephalosporin)
pH 4.2 to 7
Usual dose
Range is 1 to 2 Gm every 6 to 8 hours. Dose based on severity of disease, susceptibility of pathogens, and condition of patient.
| Cefoxitin Dosing Guidelines | ||
| Type of Infection | Dose and Frequency | Total Daily Dose |
| Uncomplicated forms* of infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract infection, cutaneous infection | 1 Gm every 6 to 8 hr | 3 to 4 Gm |
| Moderately severe or severe infections | 1 Gm every 4 hr or 2 Gm every 6 to 8 hr | 6 to 8 Gm |
| Infections commonly needing antibiotics in higher doses (e.g., gas gangrene) | 2 Gm every 4 hr or 3 Gm every 6 hr | 12 Gm |

*Including patients in whom bacteremia is absent or unlikely.
Perioperative prophylaxis:
2 Gm 30 minutes to 1 hour before incision. Follow with 2 Gm every 6 hours for 24 hours.
Prophylaxis during cesarean section:
Either a single 2-Gm dose after clamping the umbilical cord or a 3-dose regimen consisting of 2 Gm given as soon as the umbilical cord is clamped followed by 2 Gm in 4 hours and again in 8 hours.
Pediatric dose
Pediatric patients over 3 months of age:
Mild to moderate infections: 80 to 100 mg/kg/24 hr in equally divided doses every 6 to 8 hours (20 to 25 mg/kg every 6 hours or 26.66 to 33.33 mg/kg every 8 hours). Severe infections: 100 to 160 mg/kg/24 hr in equally divided doses every 4 to 6 hours (16.66 to 26.66 mg/kg every 4 hours or 25 to 40 mg/kg every 6 hours). Do not exceed adult dose and/or 12 Gm.
Perioperative prophylaxis in pediatric patients over 3 months of age:
30 to 40 mg/kg 30 minutes to 1 hour before incision and every 6 hours for 24 hours.
Neonatal dose (unlabeled)
Use sterile cefoxitin sodium USP only. Other formulations may contain benzyl alcohol.
90 to 100 mg/kg/24 hr in equally divided doses every 8 hours (30 to 33.3 mg/kg every 8 hours).
Dose adjustments
Reduced dose or extended intervals may be indicated in the elderly; consider age-related impaired organ function, nutritional status, and concomitant disease or drug therapy. ■ In impaired renal function, the initial dose should be as previously listed, but all remaining doses should be based on CrCl according to the following chart. See Drug/Lab Interactions.
| Cefoxitin Maintenance Dose in Adults with Impaired Renal Function | ||
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Dose (Gm) | Frequency |
| 30-50 mL/min | 1-2 Gm | q 8-12 hr |
| 10-29 mL/min | 1-2 Gm | q 12-24 hr |
| 5-9 mL/min | 0.5-1 Gm | q 12-24 hr |
| <5 mL/min | 0.5-1 Gm | q 24-48 hr |
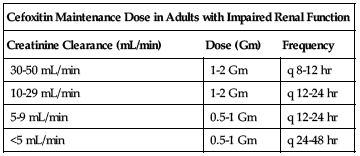
Hemodialysis patients should receive a loading dose of 1 to 2 Gm after each dialysis in addition to the maintenance dose listed in the previous chart.
In pediatric patients, the manufacturer recommends reducing the dose and frequency consistent with the recommendations for adults.
Dilution
1 Gm of the lyophilized solution must be reconstituted with at least 10 mL, and 2 Gm with 10 or 20 mL, of SWFI, BWFI, D5W, or NS. A single dose may be further diluted in 50 to 100 mL of most common infusion solutions (see chart on inside back cover and literature). The use of butterfly needles and dilution in up to 1,000 mL of D5W, D5NS, or NS are preferred when administering larger doses as a continuous infusion. Also available in dual-chamber DUPLEX containers and as a frozen, premixed solution. Refer to manufacturer’s prescribing information for specific preparation and storage requirements. May be given through a Y-tube, three-way stopcock, additive infusion set, or as a continuous infusion.
Storage:
Storage before use is dependent on product. Reconstituted solutions are stable at RT for 6 hours and 7 days if refrigerated. Solutions diluted in 50 to 1,000 mL diluent are stable for an additional 18 hours at RT and an additional 48 hours if refrigerated.
Compatibility (underline indicates conflicting compatibility information)
Consider any drug NOT listed as compatible to be INCOMPATIBLE until consulting a pharmacist; specific conditions may apply.
May be used concomitantly with aminoglycosides (e.g., amikacin, gentamicin), but these drugs must never be mixed in the same infusion (mutual inactivation). If given concurrently, administer separately and flush the IV line before and after administration. Manufacturer recommends temporarily discontinuing other solutions infusing at the same site during intermittent infusion.
One source suggests the following compatibilities:
Additive:
Aztreonam (Azactam), clindamycin (Cleocin), mannitol, metronidazole (Flagyl IV), multivitamins (M.V.I.), sodium bicarbonate (Neut), verapamil.
Y-site:
Acetaminophen (Ofirmev), acyclovir (Zovirax), amifostine (Ethyol), amphotericin B cholesteryl (Amphotec), anidulafungin (Eraxis), aztreonam (Azactam), bivalirudin (Angiomax), cisatracurium (Nimbex), cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), docetaxel (Taxotere), doxorubicin liposomal (Doxil), etoposide phosphate (Etopophos), famotidine (Pepcid IV), fluconazole (Diflucan), foscarnet (Foscavir), gemcitabine (Gemzar), granisetron (Kytril), hetastarch in electrolytes (Hextend), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), linezolid (Zyvox), magnesium sulfate, meperidine (Demerol), morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), propofol (Diprivan), ranitidine (Zantac), remifentanil (Ultiva), teniposide (Vumon), thiotepa, vancomycin.
Rate of administration
See Compatibility. Each 1 Gm or fraction thereof over 3 to 5 minutes or longer as indicated by amount of solution and condition of the patient. Rate of continuous infusion should be by physician order.
Actions
A semi-synthetic, second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is bactericidal to many gram-positive, gram-negative, and anaerobic organisms. Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Has activity in the presence of some beta-lactamases, both penicillinases and cephalosporinases, of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Peak serum levels achieved by end of infusion. Widely distributed into many body tissues and fluids (CSF minimal). Passes into pleural and joint fluids and is detectable in antibacterial concentrations in bile. Half-life is 41 to 59 minutes. Excreted rapidly in the urine. Crosses the placental barrier. Secreted in breast milk.
Indications and uses
Treatment of serious lower respiratory, urinary, intra-abdominal, gynecologic, bone and joint, skin and skin structure infections and septicemia. Effective only if the causative organism is susceptible. If C. trachomatis is a suspected pathogen, antichlamydial coverage is indicated. ■ Perioperative prophylaxis in patients undergoing uncontaminated gastrointestinal surgery, vaginal or abdominal hysterectomy, or cesarean section.
Unlabeled uses:
Treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease (CDC recommendation). ■ Treatment of oral bacterial Eikenella corrodens.
Contraindications
Previous hypersensitivity reaction to cephalosporins; see Precautions. ■ Premixed solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with known allergies to corn or corn products.
Precautions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including fatalities, have been reported and include reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity or sensitivity to multiple allergens experiencing severe reactions when treated with cephalosporins. Check history of previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. Actual incidence of cross-allergenicity not established but may be more common with first-generation cephalosporins. ■ Sensitivity studies indicated to determine susceptibility of the causative organism to cefoxitin. ■ To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain its effectiveness, cefoxitin should be used to treat or prevent only those infections proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. ■ Continue for at least 2 to 3 days after all symptoms of infection subside. ■ Avoid prolonged use of drug; superinfection caused by overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms may result. ■ Use caution in patients with impaired renal function, allergies, or a history of GI disease (especially colitis). ■ Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported. May range from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Consider in patients who present with diarrhea during or after treatment with cefoxitin. ■ Continue treatment for group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections for 10 days or more to decrease the risk of rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis.
Monitor:
Watch for early symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. ■ Use extreme caution in the penicillin-sensitive patient; cross-sensitivity has been reported. ■ Thrombophlebitis may result from prolonged or high dosage; use small needles and larger veins, and rotate infusion sites. ■ Periodic monitoring of CBC, SCr, and liver function tests is recommended during prolonged therapy. ■ See Drug/Lab Interactions; additional monitoring may be indicated (e.g., renal function, drug serum levels, PT).
Patient education:
Report promptly any bleeding or bruising or symptoms of allergy (e.g., difficulty breathing, hives, itching, rash). ■ Promptly report diarrhea or bloody stools that occur during treatment or up to several months after an antibiotic has been discontinued; may indicate CDAD and require treatment.
Maternal/child:
Category B: safety for use during pregnancy and breast-feeding not established. No problems documented. ■ Safety and effectiveness for use in pediatric patients from birth to 3 months of age not established. ■ Do not use formulations containing benzyl alcohol in infants and children under 3 months. ■ Immature renal function will increase blood levels. ■ Eosinophilia and elevated AST associated with higher doses in infants and children.
Elderly:
Response similar to that seen in younger adults. Dose selection should be cautious; see Dose Adjustments. Monitoring of renal function suggested.
Drug/lab interactions
Risk of nephrotoxicity may be increased with aminoglycosides and other nephrotoxic agents (e.g., loop diuretics such as furosemide [Lasix]). ■ Probenecid inhibits excretion. Reduced dose of cefoxitin may be required with concomitant use. ■ May be antagonized by bacteriostatic antibiotics (e.g., chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracyclines); may interfere with bactericidal action. ■ False-positive reaction for urine glucose except with enzyme-based tests (e.g., Clinistix). ■ Positive Coombs’ test. ■ False increases in creatinine levels with Jaffe method. ■ See Compatibility and Side Effects.
Side effects
Local site reactions are most common. Anorexia; CDAD; colitis; flushing; hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis; eosinophilia; leukopenia; nausea and vomiting; neutropenia; oral thrush; phlebitis; prolonged PT; proteinuria; seizures (large doses); thrombophlebitis; transient elevation of AST, ALT, BUN, and alkaline phosphatase; and urticaria have occurred. Hypoprothrombinemia (rare) and hemolytic anemia may occur. Aplastic anemia, erythema multiforme, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, hepatic dysfunction (including cholestasis), pancytopenia, renal dysfunction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and toxic nephropathy have been reported with cephalosporin-class antibiotics.
Antidote
Notify physician of any side effects. Discontinue the drug if indicated. Treat CDAD with fluids, electrolytes, protein supplements, and oral vancomycin (Vancocin) or metronidazole (Flagyl) as indicated. In severe cases, surgical evaluation may be indicated. Treat hypersensitivity reactions as indicated and resuscitate as necessary. Hemodialysis may be useful in overdose.
Ceftaroline fosamil
(cef-TAR-oh-leen FOS-a-mil)
Teflaro
Antibacterial (cephalosporin)
pH 4.8 to 6.5
Usual dose
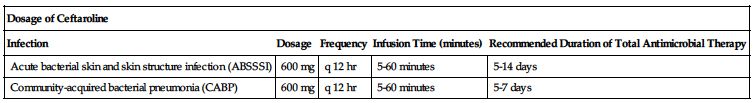
600 mg every 12 hours as an IV infusion. Duration of therapy should be guided by the severity and the site of infection and the patient’s clinical and bacteriologic progress as shown in the following chart.
| Dosage of Ceftaroline | ||||
| Infection | Dosage | Frequency | Infusion Time (minutes) | Recommended Duration of Total Antimicrobial Therapy |
| Acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection (ABSSSI) | 600 mg | q 12 hr | 5-60 minutes | 5-14 days |
| Community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP) | 600 mg | q 12 hr | 5-60 minutes | 5-7 days |
Dose adjustments
Dose adjustment required with renal impairment as outlined in the following chart.
| Dosage of Ceftaroline in Patients with Renal Impairment | |
| Estimated CrCl* (mL/min) | Recommended Dosage Regimen |
| >50 mL/min | 600 mg q 12 hr |
| >30 to ≤50 mL/min | 400 mg q 12 hr |
| ≥15 to ≤30 mL/min | 300 mg q 12 hr |
| End-stage renal disease, including hemodialysis† | 200 mg q 12 hr‡ |
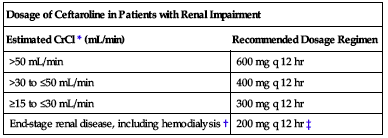
*CrCl as calculated by Cockcroft-Gault formula.
†End-stage renal disease is defined as CrCl <15 mL/min.
‡Ceftaroline is hemodialyzable; administer after hemodialysis on hemodialysis days.
■ Dose adjustment is not indicated based on gender, race, or hepatic function. ■ Reduced dose may be indicated in the elderly based on age-related renal impairment.
Dilution
Reconstitute with 20 mL of SWFI, NS, D5W, or LR as shown in the following chart. Mix gently. Time to dissolution is less than 2 minutes.
| Preparation of Ceftaroline for Intravenous Use | |||
| Dosage Strength (mg) | Volume of Diluent to Be Added (mL) | Approximate Ceftaroline Concentration (mg/mL) | Amount to Be Withdrawn |
| 400 | 20 mL | 20 mg/mL | Total volume |
| 600 | 20 mL | 30 mg/mL | Total volume |
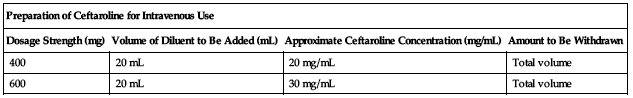
Further dilute the reconstituted solution in 50 to 250 mL of NS, D5W, D2.5/0.45NS, or LR. Use the same diluent for further dilution unless SWFI was used. If SWFI was used as the initial diluent, further dilute the reconstituted solution in NS, D5W, D2.5/0.45NS, or LR. When preparing a ceftaroline dose in a 50-mL infusion bag, withdraw 20 mL of the infusion solution before injecting the reconstituted drug into the bag. Infusion solution ranges from clear light yellow to dark yellow depending on the concentration and the storage conditions.
Filter:
Data not available.
Storage:
Store unopened vials at CRT. Diluted solution should be used within 6 hours when stored at RT or within 24 hours when refrigerated.
Compatibility (underline indicates conflicting compatibility information)
Consider any drug NOT listed as compatible to be INCOMPATIBLE until consulting a pharmacist; specific conditions may apply.
Manufacturer states, “Should not be mixed with or physically added to solutions containing other drugs.” Compatibility with other drugs has not been established.
One source suggests the following compatibilities for specific time frames; consult pharmacist:
Y-site:
Acyclovir (Zovirax), amikacin, aminophylline, amiodarone (Nexterone), azithromycin (Zithromax), bumetanide, calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, ciprofloxacin (Cipro IV), cisatracurium (Nimbex), clindamycin (Cleocin), cyclosporine (Sandimmune), dexamethasone (Decadron), digoxin (Lanoxin), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine, dopamine, doripenem (Doribax), enalaprilat (Vasotec IV), esomeprazole (Nexium IV), famotidine (Pepcid IV), fentanyl, fluconazole (Diflucan), furosemide (Lasix), gentamicin, granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hydrocortisone sodium succinate (Solu-Cortef), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin (regular), levofloxacin (Levaquin), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, mannitol (Osmitrol), meperidine (Demerol), methylprednisolone sodium succinate (Solu-Medrol), metoclopramide (Reglan), metoprolol (Lopressor), metronidazole (Flagyl IV), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, moxifloxacin (Avelox), multivitamin infusion (M.V.I.), norepinephrine (Levophed), ondansetron (Zofran), pantoprazole (Protonix IV), potassium chloride, promethazine (Phenergan), propofol (Diprivan), ranitidine (Zantac), remifentanil (Ultiva), sodium bicarbonate, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (SMZ-TMP), tobramycin, vasopressin, voriconazole (VFEND IV).
Rate of administration
A single dose equally distributed over 5 to 60 minutes.
Actions
A semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Ceftaroline fosamil, a prodrug, is converted into the bioactive ceftaroline in plasma by a phosphatase enzyme. Bactericidal to many gram-negative and gram-positive organisms. Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Protein binding is minimal (20%). Ceftaroline undergoes hydrolysis, forming an inactive metabolite. Half-life is approximately 2.2 to 3 hours. Both ceftaroline and its metabolites are primarily eliminated by the kidneys.
Indications and uses
Treatment of adults with infections caused by susceptible strains of microorganisms in conditions that include acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) and community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP).
Contraindications
Known serious hypersensitivity to ceftaroline or other members of the cephalosporin class.
Precautions
Hypersensitivity reactions, some fatal, and serious skin reactions have been reported in patients receiving beta-lactam antibiotics and include reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity or sensitivity to multiple allergens experiencing severe reactions when treated with cephalosporins. Check history of previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, or other allergens. Actual incidence of cross-allergenicity not established but may be more common with first-generation cephalosporins. ■ Specific sensitivity studies are indicated to determine susceptibility of the causative organism to ceftaroline. ■ To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain its effectiveness, ceftaroline should be used to treat only those infections proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. ■ Although cross-resistance may occur, some isolates resistant to other cephalosporins may be susceptible to ceftaroline. ■ Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported. May range from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Consider in patients who present with diarrhea during or after treatment with ceftaroline. ■ Seroconversion from a negative to a positive direct Coombs’ test occurred in approximately 10% of patients in Phase 3 trials. No adverse reactions representing hemolytic anemia were reported. If anemia develops during or after treatment with ceftaroline, drug-induced hemolytic anemia should be considered and diagnostic studies, including a direct Coombs’ test, should be performed.
Monitor:
Watch for early symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. ■ Obtain baseline CBC with differential and platelet count and SCr.
Patient education:
Promptly report S/S of a hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., rash, hives, wheezing, shortness of breath). ■ Promptly report diarrhea or bloody stools that occur during treatment or up to several months after an antibiotic has been discontinued; may indicate CDAD and require treatment.
Maternal/child:
Category B: safety for use during pregnancy and breast-feeding not established; use only if clearly needed. ■ Safety and effectiveness for use in pediatric patients not established.
Elderly:
No specific problems documented. Efficacy and safety appear similar to that seen in younger patients. Consider age-related renal impairment; see Dose Adjustments.
Drug/lab interactions
No clinical drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted. There is minimal potential for drug-drug interactions between ceftaroline and CYP450 substrates, inhibitors, or inducers; drugs known to undergo active renal secretion; and drugs that may alter renal blood flow. ■ In vitro studies have not demonstrated any antagonism between ceftaroline and other commonly used antibiotics (e.g., amikacin, azithromycin, aztreonam, daptomycin, levofloxacin, linezolid, meropenem, tigecycline, vancomycin).
Side effects
The most common side effects were diarrhea, nausea, and rash. Hypersensitivity reactions were the most frequently reported serious side effects leading to discontinuation of therapy. Other less frequently reported side effects included CDAD, constipation, hypokalemia, increased transaminases (ALT, AST), phlebitis, seroconversion from a negative to a positive direct Coombs’ test, and vomiting. Several other side effects were reported in less than 2% of the population studied.
Post-marketing:
Agranulocytosis.
Antidote
Notify physician of any side effects. Discontinue the drug if indicated. Treat hypersensitivity reactions as indicated (e.g., diphenhydramine [Benadryl], epinephrine [Adrenalin], albuterol) and resuscitate as necessary. Discontinue ceftaroline for suspected drug-induced hemolytic anemia and initiate supportive therapy as indicated (e.g., transfusion). Mild cases of CDAD may respond to discontinuation of ceftaroline. Treat CDAD with fluids, electrolytes, protein supplements, and oral vancomycin (Vancocin) or metronidazole (Flagyl) as indicated. In severe cases, surgical evaluation may be indicated. Ceftaroline is removed by hemodialysis.
Ceftazidime
(sef-TAY-zih-deem)
Fortaz, Tazicef
Antibacterial (cephalosporin)
pH 5 to 8
Usual dose
Range is from 250 mg to 2 Gm every 8 to 12 hours. Dosage based on severity of infection, condition and renal function of the patient, and susceptibility of the causative organism.
Uncomplicated GU infections:
250 mg every 12 hours.
Complicated GU infections:
500 mg every 8 to 12 hours.
Uncomplicated pneumonia; skin and skin structure infections:
500 mg to 1 Gm every 8 hours.
Bone and joint infections:
2 Gm every 12 hours.
Severe or life-threatening infections (especially in immunocompromised patients), meningitis, serious gynecologic and intra-abdominal infections:
2 Gm every 8 hours.
Pseudomonal lung infections in cystic fibrosis patients (must have normal renal function):
30 to 50 mg/kg of body weight every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 Gm/24 hr.
Melioidosis (unlabeled):
50 mg/kg (maximum dose: 2 Gm) every 8 hours.
Pediatric dose
Pediatric patients 1 month to 12 years of age:
30 to 50 mg/kg of body weight every 8 hours. Reserve higher doses for immunocompromised pediatric patients or for those with cystic fibrosis or meningitis. Do not exceed 6 Gm/24 hr.
Neonatal dose
Neonates up to 4 weeks of age:
30 mg/kg every 12 hours.
The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests the following doses:
Neonates 7 days of age or younger regardless of weight:
50 mg/kg every 12 hours.
Neonates from 8 to 28 days of age weighing 2 kg or less:
50 mg/kg every 8 to 12 hours.
Neonates from 8 to 28 days of age weighing more than 2 kg:
50 mg/kg every 8 hours.
Dose adjustments
Reduced dose or extended intervals may be indicated in the elderly; consider age-related impaired organ function, nutritional status, and concomitant disease or drug therapy. ■ In impaired renal function, an initial loading dose of 1 Gm may be given, but all remaining doses should be based on CrCl according to the following chart. If the normal dose would be lower than the doses in the chart, use the lower dose. Adjustment for pediatric patients is similar to adults; consider body surface area or lean body mass and reduce dosing frequency.
| Ceftazidime Maintenance Dose in Impaired Renal Function | ||
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Dose | Frequency |
| 31-50 mL/min | 1 Gm | q 12 hr |
| 16-30 mL/min | 1 Gm | q 24 hr |
| 6-15 mL/min | 500 mg | q 24 hr |
| <5 mL/min | 500 mg | q 48 hr |
| Hemodialysis patients | 1 Gm | After each dialysis session |
| Peritoneal dialysis patients | 500 mg | q 24 hr |
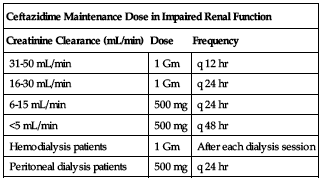
In patients with impaired renal function who have severe infection (normally requiring a 6 Gm/24 hr dose), the dose in the previous chart may be increased by 50% or the dosing frequency may be increased. In patients undergoing hemodialysis, give a loading dose of 1 Gm followed by 1 Gm after each dialysis. ■ In peritoneal dialysis patients (CAPD), give a loading dose of 1 Gm followed by 500 mg every 24 hours. In addition to IV use, ceftazidime can be incorporated in the dialysis fluid at a concentration of 250 mg for 2 L of dialysis fluid. ■ Dose reduction not required in impaired hepatic function.
Dilution
IV injection:
Directions for the initial preparation of ceftazidime solutions are outlined in the following chart.
| Preparation of Ceftazidime Solutions | |||
| Size | Amount of Diluent to Be Added (mL) | Approximate Available Volume (mL) | Approximate Ceftazidime Concentration (mg/mL) |
| 500-mg vial | 5.3 | 5.7* | 100 |
| 1-Gm vial | 10 | 10.8† | 100 |
| 2-Gm vial | 10 | 11.5‡ | 170 |

*To obtain a dose of 500 mg, withdraw 5 mL from vial after reconstitution.
†To obtain a dose of 1 Gm, withdraw 10 mL from vial after reconstitution.
‡To obtain a dose of 2 Gm, withdraw 11.5 mL from vial after reconstitution.
Reconstitute with SWFI as outlined in the chart. Shake well. Dilution generates CO2. Invert vial and completely depress plunger of syringe. Insert needle through stopper and keep it within the solution. Expel bubbles from solution in syringe before injection.
Intermittent IV infusion:
A single dose may be further diluted in 50 to 100 mL of D5W, NS, or other compatible infusion solutions for injection (see literature or chart on inside back cover). Also available in dual-chamber DUPLEX containers, in ADD-Vantage vials, in Twist vials, premixed in frozen Galaxy bags, and in pharmacy bulk packaging. Refer to manufacturer’s prescribing information for specific preparation and storage requirements.
Storage:
Store unopened vials in carton at CRT. Protect from light. Administer within 12 hours of preparation if stored at CRT, or refrigerate for up to 3 days. May be frozen for up to 3 months after initial dilution; thaw at room temperature (see instructions); do not refreeze. Will be light yellow to amber in color depending on concentration and diluent.
Compatibility (underline indicates conflicting compatibility information)
Consider any drug NOT listed as compatible to be INCOMPATIBLE until consulting a pharmacist; specific conditions may apply.
May be used concomitantly with aminoglycosides (e.g., amikacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin), but these drugs must never be mixed in the same infusion (mutual inactivation). If given concurrently, administer separately and flush IV line before and after administration. Manufacturer recommends temporarily discontinuing other solutions infusing at the same site during intermittent infusion and states, “Do not add supplementary medications to premixed plastic IV containers.”
One source suggests the following compatibilities:
Additive:
Clindamycin (Cleocin), fluconazole (Diflucan), heparin, linezolid (Zyvox), metronidazole (Flagyl IV), potassium chloride, sodium bicarbonate.
Y-site:
Acyclovir (Zovirax), allopurinol (Aloprim), amifostine (Ethyol), aminophylline, anidulafungin (Eraxis), aztreonam (Azactam), bivalirudin (Angiomax), ciprofloxacin (Cipro IV), cisatracurium (Nimbex), daptomycin (Cubicin), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), dobutamine, docetaxel (Taxotere), dopamine, doxapram (Dopram), enalaprilat (Vasotec IV), epinephrine (Adrenalin), esmolol (Brevibloc), etoposide phosphate (Etopophos), famotidine (Pepcid IV), fenoldopam (Corlopam), filgrastim (Neupogen), fluconazole (Diflucan), fludarabine (Fludara), foscarnet (Foscavir), furosemide (Lasix), gallium nitrate (Ganite), gemcitabine (Gemzar), granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hetastarch in electrolytes (Hextend), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin (regular), ketamine (Ketalar), labetalol, linezolid (Zyvox), melphalan (Alkeran), meperidine (Demerol), methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nicardipine (Cardene IV), ondansetron (Zofran), paclitaxel (Taxol), propofol (Diprivan), ranitidine (Zantac), remifentanil (Ultiva), sargramostim (Leukine), sufentanil (Sufenta), tacrolimus (Prograf), telavancin (Vibativ), teniposide (Vumon), theophylline, thiotepa, tigecycline (Tygacil), valproate (Depacon), vancomycin, vinorelbine (Navelbine), zidovudine (AZT, Retrovir).
Rate of administration
See Compatibility. May be given through Y-tube or three-way stopcock of infusion set.
IV injection:
A single dose equally distributed over 3 to 5 minutes.
Intermittent IV:
A single dose over 15 to 30 minutes.
Actions
A broad-spectrum, third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Bactericidal to selected gram-negative, gram-positive, and anaerobic organisms. Effective against many otherwise resistant organisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Peak serum levels achieved by end of infusion. Therapeutic levels distributed into many body fluids and tissues, including CSF and aqueous humor. Half-life is 1.9 hours. Excreted unchanged in the urine. Crosses placental barrier. Secreted in breast milk.
Indications and uses
Treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms (see prescribing information): lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, skin and skin structure, bone and joint, gynecologic, intra-abdominal, and CNS infections (including meningitis), and bacterial septicemia.
Unlabeled uses:
Treatment of melioidosis; empiric treatment of febrile neutropenia.
Contraindications
History of immediate hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis, serious skin reactions) to ceftazidime or the cephalosporin class of antibiotics, penicillins, or other beta-lactam antibiotics; see Precautions. ■ Premixed solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with known allergies to corn or corn products.
Precautions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including fatalities, have been reported and include reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity or sensitivity to multiple allergens experiencing severe reactions when treated with cephalosporins. Check history of previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. Actual incidence of cross-allergenicity not established but may be more common with first-generation cephalosporins. ■ Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with administration of corn-derived, dextrose-containing products in patients with or without a history of hypersensitivity to corn products. Ceftazidime in the DUPLEX container contains dextrose. ■ Specific sensitivity studies indicated to determine susceptibility of causative organism to ceftazidime. Inducible type I beta-lactamase resistance has been noted with some organisms and can develop during therapy, leading to clinical failure. Periodic susceptibility testing may be indicated. ■ To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain its effectiveness, ceftazidime should be used to treat or prevent only those infections proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. ■ An immune-mediated hemolytic anemia has been observed in patients receiving cephalosporin antibiotics, including ceftazidime. Fatalities have been reported. ■ Use with caution in patients with renal impairment. Elevated levels of ceftazidime in these patients can lead to asterixis, coma, encephalopathy, myoclonus, neuromuscular excitability, and seizures; see Dose Adjustments. ■ May be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Patients at risk include those with renal or hepatic impairment, those with poor nutritional status, those receiving a protracted course of antimicrobial therapy, and/or those previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy; see Monitor. ■ Avoid prolonged use of drug; superinfection caused by overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms may result. ■ Use caution in patients with allergies or a history of GI disease (especially colitis). ■ Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported. May range from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Consider in patients who present with diarrhea during or after treatment with ceftazidime. ■ Continue for at least 2 days after all symptoms of infection subside.
Monitor:
Obtain baseline CBC and SCr. ■ Watch for early symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. ■ Monitor CBC. If a patient develops anemia while taking ceftazidime, consider the diagnosis of a cephalosporin-associated anemia. Ceftazidime should be held until the etiology is determined. ■ May cause thrombophlebitis. Use small needles and large veins, and rotate infusion sites. ■ Monitor PT and administer vitamin K as indicated; see Precautions. ■ See Drug/Lab Interactions; additional monitoring may be indicated (e.g., renal function, drug serum levels, PT).
Patient education:
Report promptly any bleeding or bruising, symptoms of allergy (e.g., difficulty breathing, hives, itching, rash), or neurologic symptoms (e.g., confusion, myoclonus, seizures). ■ Promptly report diarrhea or bloody stools that occur during treatment or up to several months after an antibiotic has been discontinued; may indicate CDAD and require treatment.
Maternal/child:
Category B: safety for use during pregnancy and breast-feeding not established. No problems documented. Use caution. ■ Immature renal function of infants and small children will increase blood levels of all cephalosporins. ■ Only specific solutions can be used in pediatric patients.
Elderly:
No specific problems documented. ■ See Usual Dose and Dose Adjustments.
Drug/lab interactions
Risk of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity may be increased with aminoglycosides and other nephrotoxic and/or ototoxic agents (e.g., loop diuretics such as furosemide [Lasix]). ■ May be antagonized by bacteriostatic antibiotics (e.g., chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracyclines); may interfere with bactericidal action. ■ May reduce the effectiveness of oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptives. ■ False-positive Coombs’ test. ■ May have a false-positive reaction for urine glucose except with enzyme-based tests (e.g., Clinistix). ■ See Compatibility and Side Effects.
Side effects
The most common adverse reactions occurring in fewer than 2% of patients include hypersensitivity reactions, GI symptoms, and CNS reactions. Full scope of hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis and cardiopulmonary arrest); abdominal pain; angioedema; burning, discomfort, and pain at injection site; candidiasis; CDAD; colitis; diarrhea; dizziness; elevated alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT, GGT, and BUN/SCr; erythema multiforme; fever; headache; jaundice; nausea and vomiting; paresthesia; prolonged PT; pruritus; rash; renal impairment; seizures (large doses or in patients with renal impairment); Stevens-Johnson syndrome; toxic epidermal necrolysis; toxic nephropathy; urticaria; vaginitis. Hypoprothrombinemia (rare) and hemolytic anemia may occur. Aplastic anemia, erythema multiforme, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, hepatic dysfunction (including cholestasis), pancytopenia, renal dysfunction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and toxic nephropathy have been reported with cephalosporin-class antibiotics.
Overdose:
Asterixis, coma, encephalopathy, neuromuscular excitability, and seizures may occur in patients with renal impairment; see Precautions.
Post-marketing:
Hemorrhage, hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice, toxic nephropathy.
Antidote
Notify physician of any side effects. Discontinue the drug if indicated. Treat hypersensitivity reaction as indicated and resuscitate as necessary. Mild cases of CDAD may respond to discontinuation of ceftazidime. Treat CDAD with fluids, electrolytes, protein supplements, and oral vancomycin (Vancocin) or metronidazole (Flagyl) as indicated. In severe cases, surgical evaluation may be indicated. Hemodialysis may be useful in overdose.
Ceftazidime/avibactam
(sef-TAY-zih-deem a-vih-BAK-tam)
Avycaz
Antibacterial
(cephalosporin/beta-lactamase inhibitor)
Usual dose
2.5 Gm (2 Gm ceftazidime/0.5 Gm avibactam) every 8 hours as an infusion over 2 hours.
| Ceftazidime-Avibactam Dosing in Patients with Normal Renal Function | ||||
| Infection | Dose | Frequency | Infusion Time (hours) | Recommended Duration of Total Antimicrobial Treatment |
| Complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI)* | 2.5 Gm (2 Gm/0.5 Gm) | Every 8 hours | 2 hours | 5 to 14 days |
| Complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), including pyelonephritis | 2.5 Gm (2 Gm/0.5 Gm) | Every 8 hours | 2 hours | 7 to 14 days |
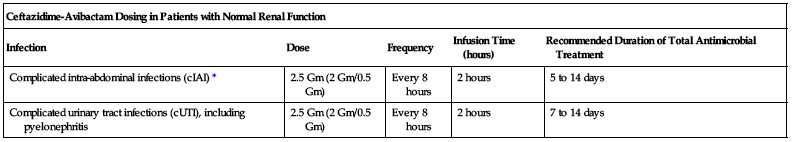
*Use in conjunction with metronidazole (Flagyl) 500 mg intravenously every 8 hours.
Dose adjustments
No dose adjustment is recommended based on age, gender, or hepatic impairment. ■ Dose adjustment required for patients with moderate and severe renal impairment and end-stage renal disease according to the following chart.
| Ceftazidime-Avibactam Dosing in Patients with Renal Impairment and cIAI or cUTI | |
| Estimated CrCl (mL/min) | Recommended Dose Regimen |
| >50 mL/min | 2.5 Gm (2 Gm/0.5 Gm) IV (over 2 hours) every 8 hours. |
| 31 to 50 mL/min | 1.25 Gm (1 Gm/0.25 Gm) IV (over 2 hours) every 8 hours. |
| 16 to 30 mL/min | 0.94 Gm (0.75 Gm/0.19 Gm) IV (over 2 hours) every 12 hours. |
| 6 to 15 mL/min* | 0.94 Gm (0.75 Gm/0.19 Gm) IV (over 2 hours) every 24 hours. |
| ≤5 mL/min* | 0.94 Gm (0.75 Gm/0.19 Gm) IV (over 2 hours) every 48 hours. |
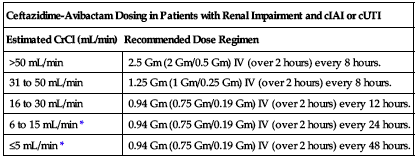
*Both ceftazidime and avibactam are hemodialyzable; administer after hemodialysis on hemodialysis days.
Dilution
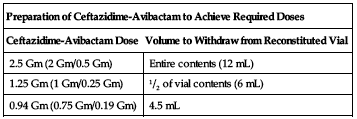
Available as single-use vials containing 2 Gm ceftazidime and 0.5 Gm avibactam. Reconstitute each vial with 10 mL of SWFI, NS, D5W, all combinations of dextrose and sodium chloride injection containing up to 2.5% dextrose and 0.45% NS, or LR injection. Mix gently. Reconstituted solution will have an approximate final volume of 12 mL, an approximate ceftazidime concentration of 0.167 Gm/mL, and an approximate avibactam concentration of 0.042 Gm/mL. Must be further diluted before infusion. Withdraw the required dose from the vial according to the following chart and transfer into an infusion bag containing the same diluent used for reconstitution of the powder (except SWFI) to achieve a total volume between 50 and 250 mL. If SWFI was used for reconstitution, use any of the other appropriate diluents listed previously for dilution.
| Preparation of Ceftazidime-Avibactam to Achieve Required Doses | |
| Ceftazidime-Avibactam Dose | Volume to Withdraw from Reconstituted Vial |
| 2.5 Gm (2 Gm/0.5 Gm) | Entire contents (12 mL) |
| 1.25 Gm (1 Gm/0.25 Gm) | 1/2 of vial contents (6 mL) |
| 0.94 Gm (0.75 Gm/0.19 Gm) | 4.5 mL |
Ensure contents are completely dissolved. Infusion solution ranges from clear to light yellow.
Filters:
Specific information not available.
Storage:
Before use, store at CRT in original carton to protect from light. The reconstituted solution may be held for no longer than 30 minutes before dilution in a suitable infusion solution. Fully diluted solutions may be stored for 12 hours at room temperature or for 24 hours refrigerated at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F). Use refrigerated solution within 12 hours of subsequent storage at RT.
Compatibility
Compatibility with other drugs not established. Manufacturer states compatible with the more commonly used IV infusion fluids in infusion bags (including Baxter Mini-Bag Plus); see Dilution.
Rate of administration
A single dose as an infusion equally distributed over 2 hours.
Actions
Ceftazidime-avibactam is an antibacterial combination product consisting of the cephalosporin ceftazidime pentahydrate and the beta-lactamase inhibitor avibactam sodium. Ceftazidme is a cephalosporin antibacterial drug with in vitro activity against certain gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Active against several gram-negative bacteria in clinical infections. Its bactericidal action results from inhibition of cell wall biosynthesis and is mediated through binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Avibactam is a non–beta-lactam beta-lactamase inhibitor that inactivates some beta-lactamases and protects ceftazidime from degradation by certain beta-lactamases. Less than 10% of ceftazidime is protein bound. Both ceftazidime and avibactam are excreted mainly by the kidneys, primarily as unchanged drug. Terminal half-life is approximately 2.8 hours. Ceftazidime is excreted in human milk in low concentrations.
Indications and uses
Used in combination with metronidazole (Flagyl) for the treatment of patients 18 years or older with complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) caused by designated susceptible microorganisms. ■ Treatment of patients 18 years or older with complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), including pyelonephritis caused by designated susceptible microorganisms. ■ Reserve ceftazidime-avibactam for use in patients who have limited or no alternative treatment options. Limited clinical safety and efficacy data currently available.
Contraindications
Known serious hypersensitivity to ceftazidime-avibactam, ceftazidime, avibactam-containing products, or other members of the cephalosporin class.
Precautions
For IV infusion only; do not administer as an IV bolus. ■ In a cIAI trial, clinical cure rates were lower in a subgroup of patients with a baseline CrCl of 30 mL/min to less than or equal to 50 mL/min compared with patients with a CrCl of greater than 50 mL/min. Reduction in clinical cure rates was more marked in patients treated with ceftazidime-avibactam plus metronidazole compared with meropenem-treated patients. Within this subgroup, patients treated with ceftazidime/avibactam received a 33% lower daily dose than is currently recommended for patients with a CrCl of 30 mL/min to less than or equal to 50 mL/min; see Monitor. ■ Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions and serious skin reactions have been reported in patients receiving beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. Check history of previous hypersensitivity reactions to other cephalosporins, penicillins, or carbapenems. Cross-sensitivity among beta-lactam antibacterial drugs has been established. ■ Specific sensitivity studies are indicated to determine susceptibility of the causative organism to ceftazidime-avibactam. ■ To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain its effectiveness, ceftazidime-avibactam should be used to treat only those infections proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. ■ No cross-resistance with other classes of antimicrobials has been identified. Some isolates resistant to other cephalosporins (including ceftazidime) and to carbapenems may be susceptible to ceftazidime-avibactam. ■ Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported for nearly all systemic antibacterial agents and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Consider in patients who present with diarrhea during or after treatment with ceftazidime-avibactam. ■ Central nervous system reactions (e.g., asterixis, coma, encephalopathy, myoclonia, neuromuscular excitability, nonconvulsive status epilepticus, and seizures) have been reported in patients treated with ceftazidime, particularly in patients with renal impairment. Adjust dose based on CrCl. ■ Seroconversion from a negative to a positive direct Coombs’ test result has occurred. No adverse reactions representing hemolytic anemia were reported.
Monitor:
Monitor CrCl at least daily in patients with changing renal function. Adjust dose of ceftazidime-avibactam accordingly; see Dose Adjustments. ■ Monitor for S/S of a hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., hypotension, rash, urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing).
Patient education:
Promptly report S/S of a hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., hives, rash, shortness of breath, wheezing). ■ Promptly report diarrhea or bloody stools that occur during treatment or up to several months after an antibiotic has been discontinued; may indicate CDAD and require treatment. ■ Promptly report neurologic S/S (e.g., encephalopathy [disturbance of consciousness including confusion, hallucinations, stupor, and coma], myoclonus, and seizures). ■ Full course of therapy must be completed.
Maternal/child:
Category B: use during pregnancy only if clearly needed. ■ Use caution during breast-feeding. ■ Safety and effectiveness for use in patients less than 18 years of age not established.
Elderly:
Because of limited data, differences in outcomes or specific risks with ceftazidime-avibactam cannot be ruled out for patients 65 years of age and older. ■ Consider age-related renal impairment, monitoring of renal function, and dose with caution; see Dose Adjustments.
Drug/lab interactions
Formal drug interaction studies have not been conducted. ■ In vitro, avibactam is a substrate of OAT1 and OAT3. Coadministration with the OAT1/OAT3 inhibitor probenecid prolongs the half-life of avibactam and is not recommended. ■ In vitro studies have not demonstrated antagonism between ceftazidime-avibactam and colistin, levofloxacin (Levaquin), linezolid (Zyvox), metronidazole (Flagyl), tigecycline (Tygacil), tobramycin, or vancomycin. ■ May have a false-positive reaction for urine glucose except with enzyme-based tests (e.g., Clinistix).
Side effects
Most common side effects reported are anxiety, constipation, nausea, and vomiting. Hypersensitivity reactions, skin reactions, central nervous system reactions, and CDAD may be severe. Other reported side effects include abdominal pain, dizziness, increased ALT, increased alkaline phosphatase, and upper abdominal pain. Other side effects have been reported in fewer than 5% of patients.
Antidote
Notify physician of any side effects. Discontinue the drug if indicated. Treat hypersensitivity reactions as indicated (e.g., diphenhydramine [Benadryl], epinephrine [Adrenalin], albuterol) and resuscitate as necessary. Mild cases of CDAD may respond to discontinuation of ceftazidime-avibactam. Treat CDAD with fluids, electrolytes, protein supplements, and oral vancomycin (Vancocin) or metronidazole (Flagyl) as indicated. In severe cases, surgical evaluation may be indicated. Both ceftazidime and avibactam can be removed from the circulation by hemodialysis.
Ceftolozane/tazobactam
(sef-TOL-oh-zane/TAZ-oh-BAK-tam)
Zerbaxa
Antibacterial (cephalosporin/beta-lactamase inhibitor)
Usual dose
1.5 Gm (ceftolozane 1 Gm and tazobactam 0.5 Gm) every 8 hours as an infusion over 1 hour. Guide duration of treatment by the severity and site of the infection and the patient’s clinical and bacteriologic progress.
| Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Dosing in Patients with a CrCl Greater Than 50 mL/min | ||||
| Infection | Dose | Frequency | Infusion Time (hours) | Duration of Treatment |
| Complicated intra-abdominal infections* | 1.5 Gm | Every 8 hours | 1 hour | 4 to 14 days |
| Complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis | 1.5 Gm | Every 8 hours | 1 hour | 7 days |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


