CHAPTER 2 NOC OUTCOMES: Activity tolerance; discomfort level; endurance; fatigue level; psychomotor energy; self-care status; self-care: activities of daily living; vital signs; energy conservation • Environmental: Smoking; smoke inhalation; second-hand smoke • Obstructed airway: Airway spasm; retained secretions; excessive mucus; presence of artificial airway; foreign body in airway; secretions in the bronchi; exudates in the alveoli • Physiological: Neuromuscular dysfunction; hyperplasia of the bronchial walls; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; infection; asthma; allergic/reactive airways NOC OUTCOMES: Aspiration prevention; mechanical ventilation response: respiratory status: airway patency; respiratory status: ventilation • Threat to or change in role status • Unconscious conflict about essential values/goals of life • Familial association/hereditary • Interpersonal transmission/contagion • Situational/maturational crises • Threat to or change in health status • Threat to or change in interaction patterns • Threat to or change in role function • Threat to or change in environment • Threat to or change in economic status Definition: At risk for entry of gastrointestinal secretions, oropharyngeal secretions, solids, or fluids into tracheobronchial passages • Reduced level of consciousness • Depressed cough and gag reflexes • Presence of tracheostomy or endotracheal tube • Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter • Situations hindering elevation of upper body • Increased intragastric pressure • Decreased gastrointestinal motility • Facial, oral, neck surgery or trauma NOC OUTCOMES: Aspiration prevention; body positioning: self initiated; gastrointestinal function; nausea and vomiting control; respiratory status; risk control; swallowing status Definition: Inspiration and/or expiration that does not provide adequate ventilation NOC OUTCOMES: Respiratory status: airway patency; respiratory status: ventilation; respiratory status: gas exchange; vital signs Definition: Inadequate blood pumped by the heart to meet metabolic demands of the body NOC OUTCOMES: Cardiac pump effectiveness; cardiopulmonary status; circulation status; fluid overload severity; tissue perfusion: abdominal organs, cardiac, cellular, cerebral, and peripheral; vital signs NIC INTERVENTIONS: Cardiac care: acute; invasive hemodynamic monitoring; hemodynamic regulation; cardiac precautions; dysrhythmia management; oxygen therapy; hypovolemia management; hypervolemia management; electrolyte management: hypomagnesemia; electrolyte management: hyperkalemia; cardiac care: rehabilitative For a full, detailed care plan on this topic, go to http://evolve.elsevier.com/Haugen/careplanning/. DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will regain usual reality orientation and level of consciousness as evidenced by: NOC OUTCOMES: Cognitive orientation; neurological status: consciousness; fatigue level; anxiety level; agitation level; sleep; electrolyte and acid-base balance; respiratory status: gas exchange; blood glucose level • Functional: Recent environmental changes; habitual denying/ignoring of urge to defecate; insufficient physical activity; irregular defecation habits; inadequate toileting (e.g., timeliness, positioning for defecation, privacy); abdominal muscle weakness. • Psychological: Depression; emotional stress; mental confusion • Pharmacological: Anticonvulsants; antilipemic agents; laxative overdose; calcium carbonate; aluminum-containing antacids; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents; opiates; anticholinergics; diuretics; iron salts; phenothiazines; sedatives; sympathomimetics; bismuth salts; antidepressants; calcium channel blockers • Mechanical: Rectal abscess or ulcer; pregnancy; rectal anal fissures; tumors; megacolon (Hirschsprung’s disease); electrolyte imbalance; rectal prolapse; prostate enlargement; neurological impairment; rectal anal stricture; rectocele; postsurgical obstruction; hemorrhoids; obesity • Physiological: Poor eating habits; decreased motility of gastrointestinal tract; inadequate dentition or oral hygiene; insufficient fiber intake; insufficient fluid intake; change in usual foods and eating pattern; dehydration NOC OUTCOMES: Bowel elimination; gastrointestinal function; hydration; nausea and vomiting severity; symptom control • External: Chemical contamination of food and/or water; bioterrorism; disasters; insufficient or absent use of decontamination protocol; inappropriate or no use of protective clothing; living in poverty; poor sanitation; climate conditions • Internal: Gestational age during exposure; developmental stage; gender; nutritional factors; the presence of preexisting disease NOC OUTCOMES: Respiratory status: gas exchange; physical injury severity; anxiety level; fear level; community disaster readiness For a full, detailed care plan on this topic, go to http://evolve.elsevier.com/Haugen/careplanning/. For a full, detailed care plan on this topic, go to http://evolve.elsevier.com/Haugen/careplanning/. Definition: Passage of loose, unformed stools NOC OUTCOMES: Bowel continence; bowel elimination; fluid balance; symptom severity; gastrointestinal function
Selected Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions, Rationales, and Documentation
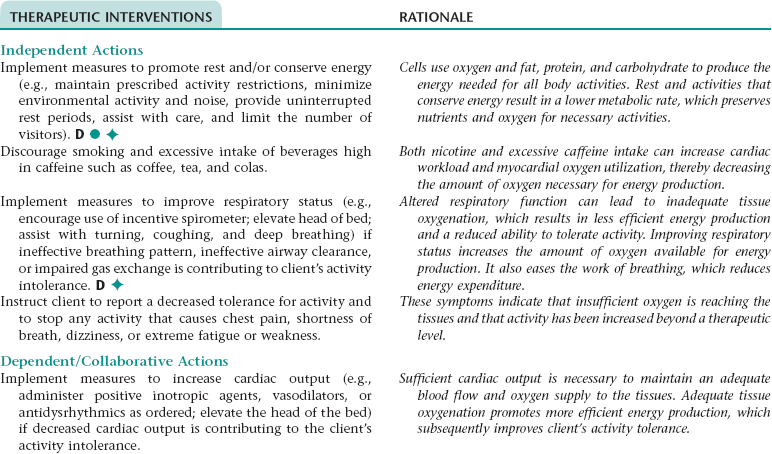
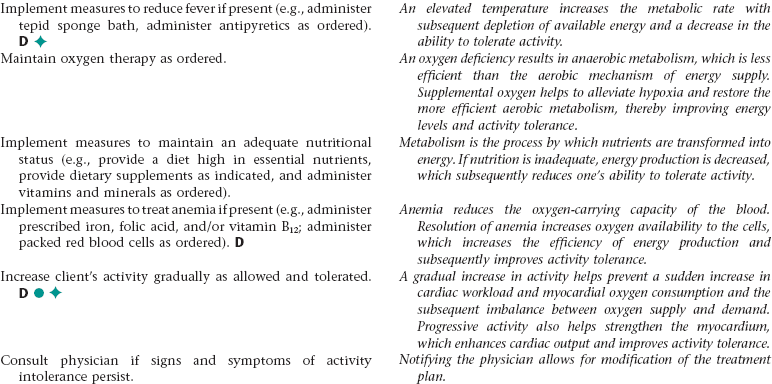
Nursing Diagnosis ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE NDx
Nursing Diagnosis AIRWAY CLEARANCE, INEFFECTIVE NDx
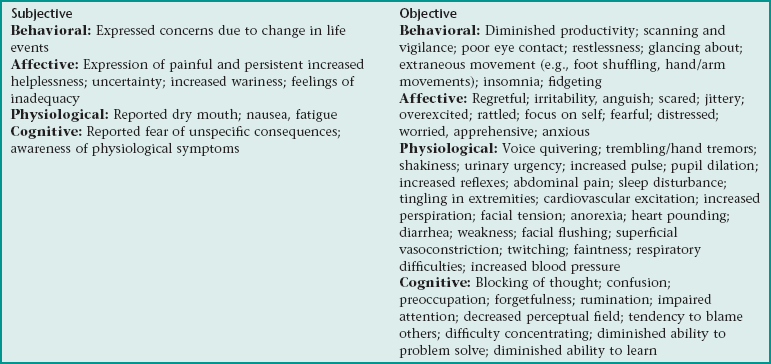
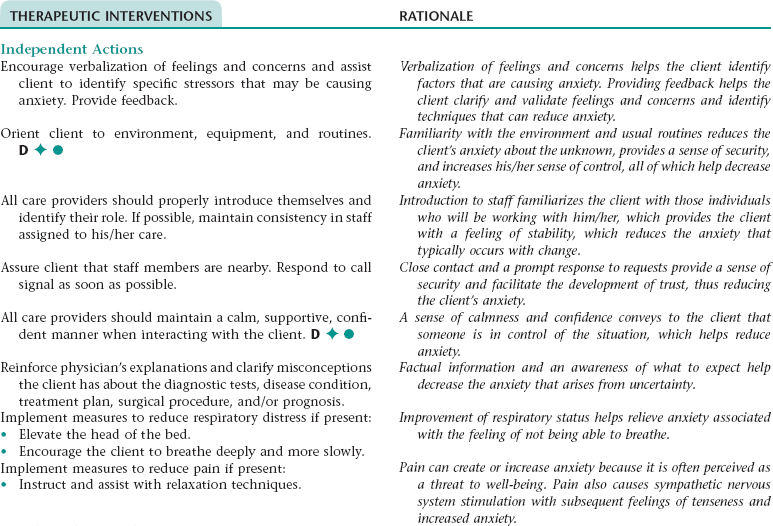
Nursing Diagnosis ANXIETY NDx
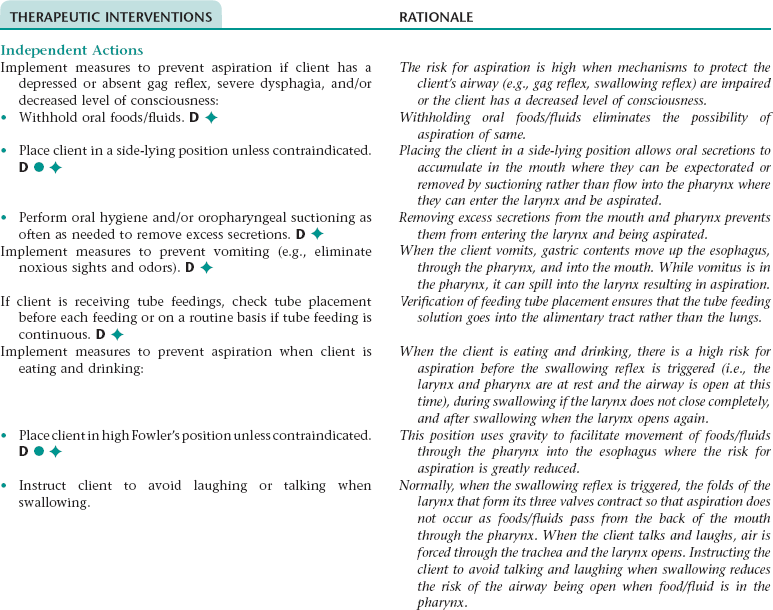
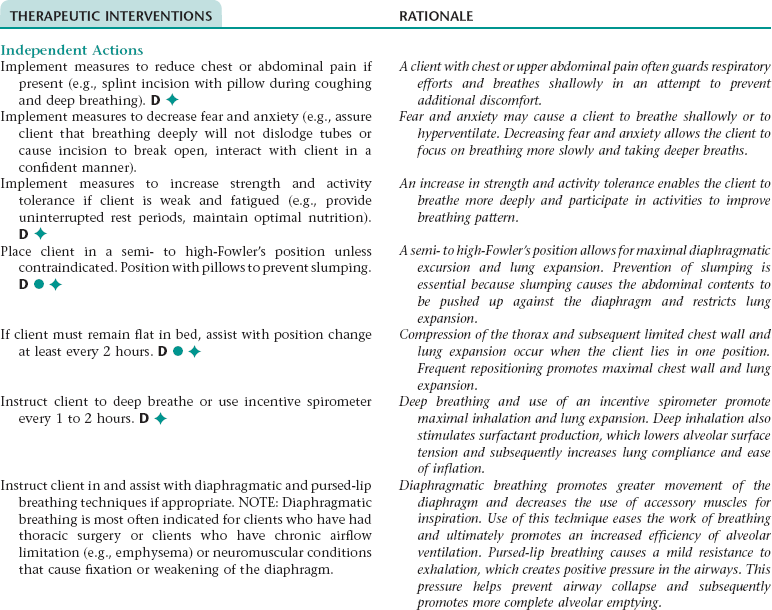
Nursing Diagnosis ASPIRATION, RISK FOR NDx
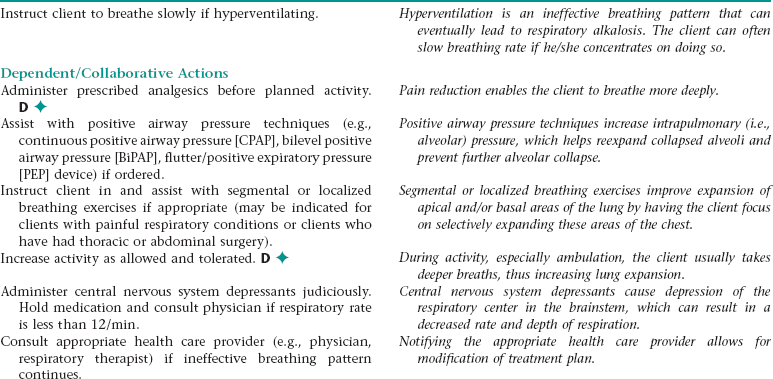
Nursing Diagnosis BREATHING PATTERN, INEFFECTIVE NDx
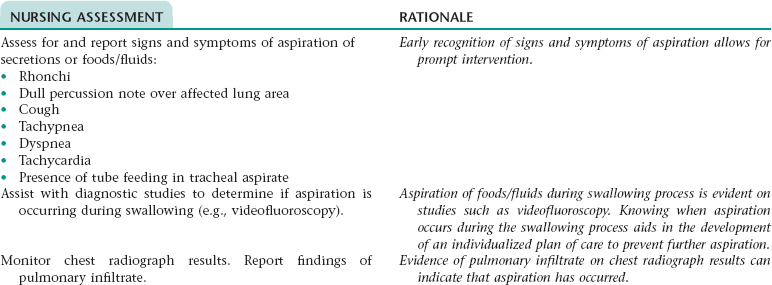
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for signs and symptoms of an ineffective breathing pattern (e.g., shallow respirations, tachypnea, limited chest excursion, dyspnea, use of accessory muscles when breathing).
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of an ineffective breathing pattern allows for prompt intervention.
Monitor for and report a significant decrease in oximetry results.
Oximetry is a noninvasive method of measuring arterial oxygen saturation. The results assist in evaluating respiratory status.
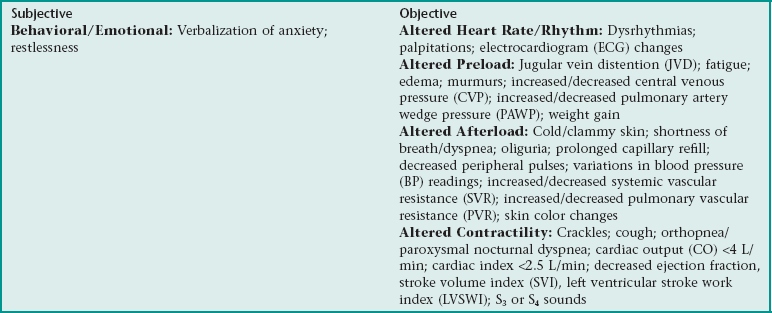
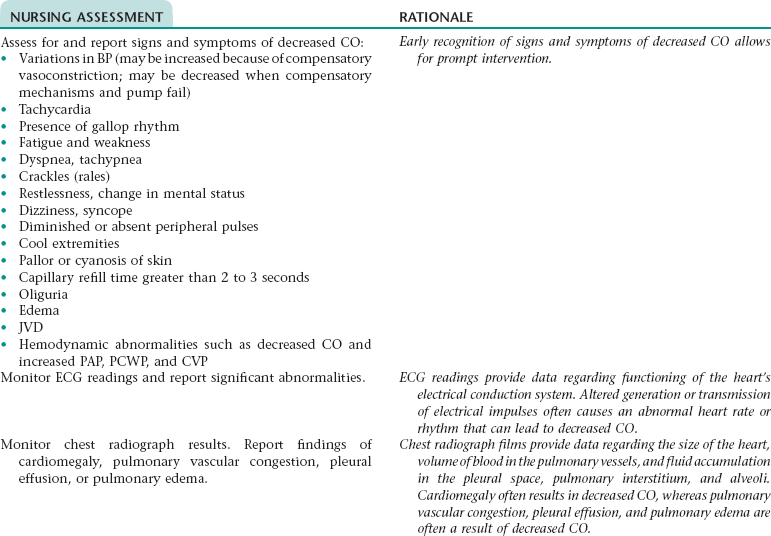
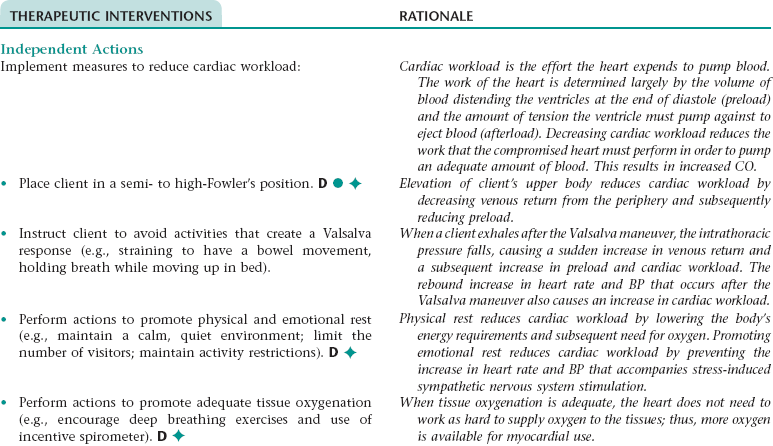
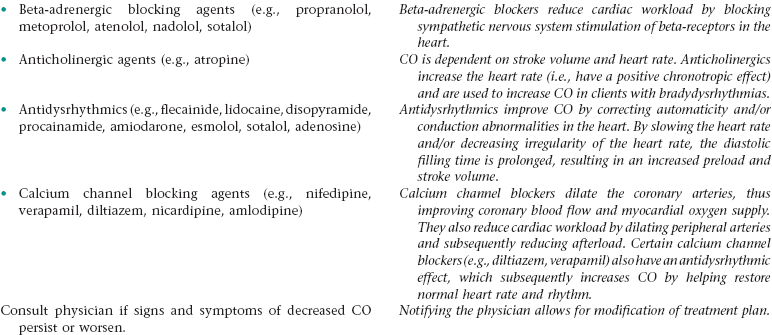
Nursing Diagnosis CARDIAC OUTPUT, DECREASED NDx
 Nursing Diagnosis COMFORT, READINESS FOR ENHANCED NDx
Nursing Diagnosis COMFORT, READINESS FOR ENHANCED NDx
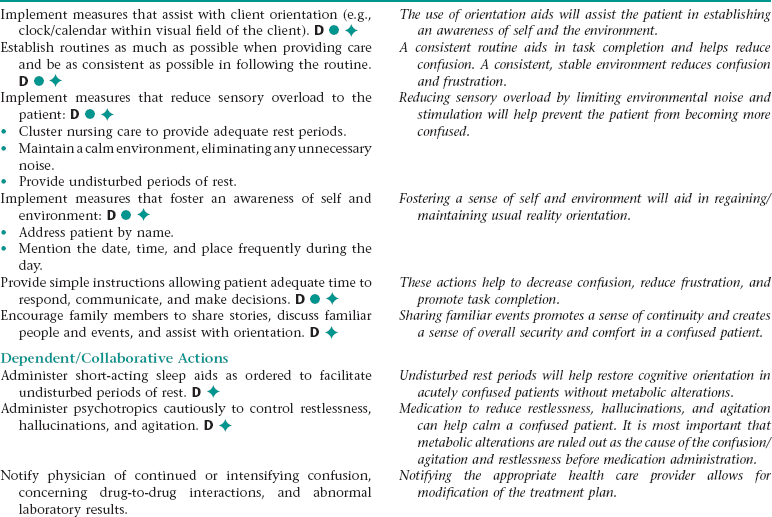
Nursing Diagnosis CONFUSION, RISK FOR ACUTE NDx
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for signs and symptoms of acute confusion (e.g., changes in level of consciousness, changes in baseline behavior, increased agitation, hallucinations, and impaired perceptive ability).
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of acute confusion allows for prompt intervention.
Assess vital signs for evidence of poor perfusion (e.g., hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea).
Poor perfusion to vital organs such as the brain, which can be exacerbated by hypotension or extreme tachycardia, can alter normal cognitive states, leading to confusion.
Monitor serum glucose levels, drug levels for abnormalities. Monitor pulse oximetry for hypoxemia.
Altered metabolic parameters (e.g., hypoglycemia and hypoxia) can contribute to confusion and as a priority must be ruled out as potential causes of confusion. Failure to rule out possible metabolic causes of confusion can lead to serious adverse patient outcomes.
Assess for contributing factors (e.g., substance abuse/withdrawal, episodes of high fever, exposure to toxic substances, drug-to-drug interactions, chronic illness exacerbations, sleep alterations, diet/nutritional alterations).
Because of the reversible nature of acute confusion, contributing factors should be identified and corrected to return the patient to his/her normal state of cognition.
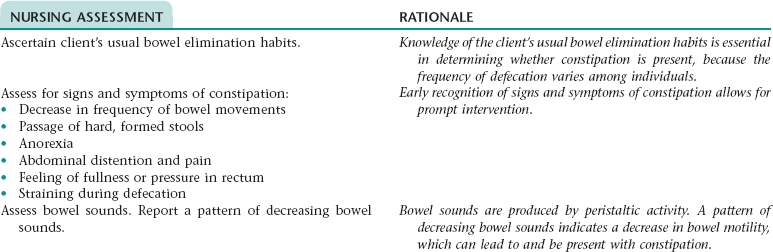
Nursing Diagnosis CONSTIPATION NDx
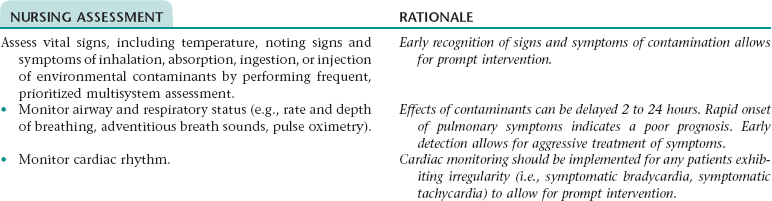
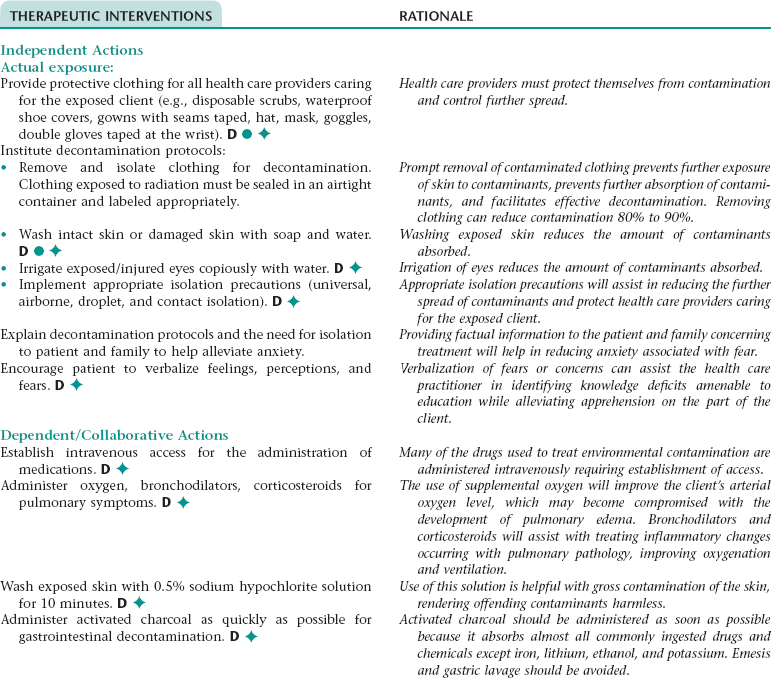
Nursing Diagnosis CONTAMINATION NDx/CONTAMINATION, RISK FOR NDx
 Nursing Diagnosis COPING, INEFFECTIVE NDx
Nursing Diagnosis COPING, INEFFECTIVE NDx
 Nursing Diagnosis DECISION-MAKING, READINESS FOR ENHANCED NDx
Nursing Diagnosis DECISION-MAKING, READINESS FOR ENHANCED NDx
Nursing Diagnosis DIARRHEA NDx
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Selected Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions, Rationales, and Documentation
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access