Sample Test 1
Questions
1. What’s the best unit of measure for identifying early shock in a trauma client?
[ ] A. Hemoglobin (Hb) and hematocrit (HCT)
[ ] B. Central venous pressure (CVP)
[ ] C. Blood pressure
[ ] D. Heart rate
View Answer
1. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: CVP is the best unit of measure for identifying shock in a trauma client. CVP measures right-sided heart pressure, which reflects blood and fluid status. A normal CVP measurement is 4 to 10 cm H2O pressure. A value less than 4 cm H2O may indicate hypovolemia or vasodilation. Hb and HCT aren’t the best indicators of early shock in a trauma client because they may be normal in the early phase of shock unless there has been massive blood loss. It normally takes 4 to 6 hours for the actual blood loss to be reflected in the Hb level and HCT.
Nursing process step: Assessment
2. Immediately after delivery of a neonate’s head, the nurse should:
[ ] A. suction the airway.
[ ] B. feel for the umbilical cord around the neonate’s neck.
[ ] C. stimulate the baby to cry.
[ ] D. deliver the upper shoulder.
View Answer
2. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: The nurse should look and feel around the neonate’s neck to determine whether the umbilical cord is wrapped around it. If the umbilical cord is present, the nurse should attempt to slip it over the neonate’s head. If the cord is too tight, the nurse should clamp it in two places and cut between the clamps, after which the airway may be suctioned. The neonate may need to be stimulated to cry after delivery. The shoulders aren’t delivered until the nurse has checked for the umbilical cord.
Nursing process step: Intervention
3. Which statement regarding the outcome of reimplantation is true?
[ ] A. Reimplantation is less successful in guillotine injuries than in crush injuries.
[ ] B. The more distal the amputation, the more successful the chance of reimplantation.
[ ] C. Amputation reimplantation is more successful in adults than in children.
[ ] D. The outcome of reimplantation is the same whether the injury occurred on an oil-coated machine or a shard of glass.
View Answer
3. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Parts that are distally positioned, such as fingers and toes, have less muscle tissue involvement and, therefore, have a good reimplantation rate. Because of extensive damage to blood vessels and the increased risk of debris-contaminated tissue, crush injuries have a less successful reimplantation rate than guillotine injuries (those that are severed with an extremely sharp cutting edge rather than a twisted or torn type of injury). A clean injury (caused by sharp glass or a sharp knife, for example) has less need for debridement than contaminated injuries such as those sustained in a crush from a surface that’s coated with soil, rust, or oil. Other
factors that affect reimplantation success include the client’s age (children have more successful implantations due to generally healthier vascular systems) and care of the amputated part before reattachment (amputated parts should be kept cool and reattached within 6 hours of the injury).
Nursing process step: Analysis
4. What’s the treatment for a client who has inhaled cyanide?
[ ] A. Administration of naloxone
[ ] B. Administration apomorphine (Apokyn) to perform gastric emptying
[ ] C. Administration of hydroxocobalamin
[ ] D. Administration of activated charcoal
View Answer
4. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Ingestion or inhalation of cyanide produces an intracellular anoxic poisoning by preventing oxidative phosphorylation; the result is anaerobic metabolism, lactic acidosis, and decreased adenosine triphosphate production. Cyanide ingestion quickly results in apnea, seizures, and coma. Hydroxocobalamin injection is used to treat cyanide inhalation. Naloxone is used in the treatment of opioid analgesic overdose. Apomorphine is an antiparkinsonian drug and isn’t used to treat cyanide poisoning. Activated charcoal is used in a variety of toxic poisonings, although it isn’t commonly used in clients who have ingested ethanol, hydrocarbon, or cyanide.
Nursing process step: Intervention
5. What does the Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1989 (COBRA) mandate for a client who comes to a hospital that doesn’t offer the services required?
[ ] A. The client must be medically screened and stabilized before transport to another health care agency.
[ ] B. The client can be transferred to another facility, regardless of condition, before admission to the emergency department.
[ ] C. The COBRA mandate has no requirements regarding this situation.
[ ] D. The emergency department has the right to refuse clients whenever necessary.
View Answer
5. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: This rule prohibits unstable, critical clients from being diverted to hospitals farther away rather than being transported to the closest emergency department. Even though the hospital may not offer the needed services, the client must be medically stable before transport to another facility, as specifically mandated in COBRA. The emergency department can’t refuse critical or unstable clients for any reason.
6. Hypertensive crisis secondary to monoamine oxidase inhibitor use also results in:
[ ] A. hypothermia.
[ ] B. bradycardia.
[ ] C. hyperthermia.
[ ] D. heart block.
View Answer
6. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Hypertensive crisis secondary to psychotropic drug therapy is characterized by hyperthermia, chest pain, tachycardia, and palpitations.
Nursing process step: Assessment
7. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is characterized by:
[ ] A. hypothermia related to dopaminergic hypoactivity in the hypothalamus.
[ ] B. muscular rigidity, akinesia, agitation.
[ ] C. hyperpyrexia, bradycardia, hypotension.
[ ] D. hyperpyrexia, diaphoresis, hypotension.
View Answer
7. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is thought to occur as a result of dopaminergic blockade at receptor sites secondary to administration of neuroleptic agents. Classic signs include hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension, akinesia, and agitation.
Nursing process step: Assessment
8. Continuous nitroglycerin infusion is indicated for the management of which condition?
[ ] A. Increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
[ ] B. Cerebral hemorrhage
[ ] C. Head trauma
[ ] D. Pulmonary edema
View Answer
8. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Nitroglycerin reduces preload and is, therefore, beneficial in the management of acute pulmonary edema. Nitroglycerin’s vasodilator properties prevent its use in the management of cerebral hemorrhage, head trauma, and increased ICP.
Nursing process step: Intervention
9. Which communication technique is most effective when interacting with an anxious client?
[ ] A. Silence
[ ] B. Active listening
[ ] C. Questioning
[ ] D. Verbalizing support
View Answer
9. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Interacting with an anxious client requires that the nurse be an active listener and provide an environment in which the client can maintain self-control. Questioning an anxious client tends to increase his anxiety, and verbalizing support takes away his self-control. Silence may imply doubt on the part of the listener.
Nursing process step: Analysis
10. What should be given to the client who has taken an overdose of a beta-adrenergic blocker?
[ ] A. Lidocaine
[ ] B. Glucagon
[ ] C. Dextrose 50% in water (D50W)
[ ] D. Bretylium
View Answer
10. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: After a beta-adrenergic blocker or calcium channel blocker overdose, glucagon is administered in a dose of 50 to 150 mcg/kg to reverse the effects of betablockade. Glucagon enhances myocardial contractility and increases heart rate and atrioventricular conduction in a separate cellular pathway distinct from the adrenergic receptor pathway. Therefore, it can stimulate the myocardium in the presence of beta-adrenergic blockade. Lidocaine and bretylium are used in the treatment of ventricular tachyarrhythmias. D50W is used in the treatment of hypoglycemia.
Nursing process step: Intervention
11. Triage is effective when an infant with a glassy stare is classified as:
[ ] A. acutely ill and categorized emergent.
[ ] B. not acutely ill and categorized nonurgent.
[ ] C. acutely ill and categorized urgent.
[ ] D. acutely ill and categorized nonurgent.
View Answer
11. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: The ability to respond and focus in children is comparable to adult orientation to person, place, and time. A glassy stare (indicating an inability to focus) in an infant may result from serious central nervous system derangement, necessitating emergent treatment.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
12. Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) can occur in the presence of a head injury, brain lesion, stroke, or other neurological disorder. What can be done to help reduce ICP?
[ ] A. Place the client in Trendelenburg’s position.
[ ] B. Encourage the client to use a pillow to splint coughing.
[ ] C. Place a pillow under the client’s legs.
[ ] D. Elevate the head of the bed by 40 degrees.
View Answer
12 Correct answer-D.
Rationales: Normal ICP is between 0 to 10 mm Hg. By elevating the head of the bed by 40 degrees, the body uses gravity to help promote intracranial drainage, thus decreasing pressure. If elevated ICP persists, ischemia and necrosis of brain tissue may occur. Placing a client in Trendelenburg’s position has the opposite effect and can raise ICP. The client’s legs shouldn’t be elevated greater than 90 degrees. Coughing is discouraged because it can raise ICP.
Nursing process step: Intervention
13. What are the expected compensatory cardiovascular mechanisms in response to shock?
[ ] A. Increased pulse rate and increased contractility of the heart
[ ] B. Decreased pulse rate and increased contractility of the heart
[ ] C. Increased pulse rate and decreased contractility of the heart
[ ] D. Decreased pulse rate and decreased contractility of the heart
View Answer
13. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Initial response to low perfusion states results in increased secretion of catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Vasoconstriction of the peripheral vessels shunts blood to the vital organs (heart and brain). The heart rate and contractility increase in an effort to increase preload. When compensatory mechanisms fail, peripheral vessels dilate and peripheral and splanchnic pooling occur.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
14. What’s the most commonly reported physical abnormality resulting from critical incident stress?
[ ] A. Appetite loss
[ ] B. Sleep disturbance
[ ] C. Intimacy loss
[ ] D. Fatigue
View Answer
14. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Sleep disturbances (nightmares, insomnia) are the earliest and most frequently reported physical symptom after critical incident stress. Loss of appetite, loss of intimacy, and fatigue may also be seen but are less common.
Nursing process step: Assessment
15. Successful fluid replacement in a 2-year-old child is evidenced by which urine output level?
[ ] A. 0.5 to 1 mL/kg/hour
[ ] B. 0.75 to 1.5 mL/kg/hour
[ ] C. 1 to 2 mL/kg/hour
[ ] D. 3 to 5 mL/kg/hour
View Answer
15. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: A 2-year-old child receiving adequate fluid replacement has a normal urine output of 1 to 2 mL/kg/hour.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
16. Turner’s sign, found on physical assessment, is indicative of:
[ ] A. retroperitoneal hemorrhage.
[ ] B. mediastinal bleeding.
[ ] C. increased intracranial pressure (ICP).
[ ] D. splenic injury.
View Answer
16. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Turner’s sign is a discoloration of the flank area as a result of a retroperitoneal bleed. Blood in the mediastinum is indicative of an aortic disruption and is best seen on an upright chest X-ray. Increased ICP is exhibited by alterations in mental status, blood pressure, heart rate, and respirations. Splenic injury produces referred pain to the left shoulder and neck and is known as Kehr’s sign.
Nursing process step: Assessment
17. A client who has suffered brain death with neurogenic diabetes insipidus will develop:
[ ] A. hypernatremia, hyperkalemia, hyperosmolar serum, hyposmolar urine.
[ ] B. hypernatremia, hypokalemia, hyperosmolar serum and urine.
[ ] C. hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, hyposmolar serum and urine.
[ ] D. hypernatremia, hypokalemia, hyperosmolar serum, hyposmolar urine.
View Answer
17. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Neurogenic diabetes insipidus occurs after insult to the hypothalamus or the posterior pituitary gland, resulting in an alteration in antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion. After traumatic injury to the brain, ADH levels can decrease, resulting in high urine output. Classic signs include high serum sodium, hypokalemia, and low urine osmolality due to excessive urine output.
Nursing process step: Assessment
18. A 4-year-old child with severe respiratory distress requires intubation and mechanical ventilation. Which endotracheal (ET) tube is the appropriate size for a child this age?
[ ] A. 3 mm
[ ] B. 4 mm
[ ] C. 5 mm
[ ] D. 6 mm
View Answer
18. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: The nurse should anticipate the use of a 5 mm ET tube. ET tube size is estimated using the following formula:
(16 + age in years) divided by 4 = ET tube size in millimeters
In this situation, the equation would be: (16 + 4) divided by 4 = 5 mm.
Nursing process step: Analysis
19. An electrocardiogram is performed and shows ST elevation in leads II, III, and aVf. The myocardial infarction (MI) is occurring in which part of the heart?
[ ] A. Anterior wall
[ ] B. Inferior wall
[ ] C. Posterior wall
[ ] D. Lateral wall
View Answer
19. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: The presence of ST elevation in leads II, III, and aVf indicate that the client is having an inferior wall MI. An anterior wall MI will show ST elevation in leads V1 through V6. A lateral wall MI will show ST elevation in leads I, aVl, V5, and V6. Posterior wall infarctions are indicated by ST depression in leads V1 to V4 as well as by reciprocal changes of the anterior wall, the portion of the heart opposite of the posterior wall.
Nursing process step: Analysis
20. After heart transplantation, what’s the usual presenting sign or symptom of acute myocardial infarction?
[ ] A. Substernal chest pain
[ ] B. Heart failure
[ ] C. Tachycardia
[ ] D. Jaw pain
View Answer
20. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Heart failure is the most common presenting symptom after heart transplantation. Because of the lack of vagal innervation of the transplanted heart, tachycardia, chest pain, and jaw pain related to ischemia aren’t possible.
Nursing process step: Assessment
21. After an industrial accident, a client with a laceration to the hand and wrist comes to the triage area. Assessment priority should be directed toward:
[ ] A. tetanus immunization status.
[ ] B. time of last oral intake.
[ ] C. presence of industrial contaminants.
[ ] D. neurovascular status of injured extremity.
View Answer
21. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Of primary importance in a client with an orthopedic injury is the determination of neurovascular status. Impaired neurovascular status may be limbthreatening or life-threatening. Tetanus immunization, last oral intake, and the presence of contaminants are secondary concerns.
Nursing process step: Assessment
22. The physician orders a continuous infusion of epinephrine 1 mg in 250 mL of dextrose 5% in water (D5W) by way of infusion pump at 125 mcg/minute. What’s the infusion rate in milliliters per hour (assuming the use of microdrip 60 gtt/mL tubing)?
[ ] A. 15 mL/hour
[ ] B. 19 mL/hour
[ ] C. 23 mL/hour
[ ] D. 31 mL/hour
View Answer
22. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: The concentration of epinephrine is 1 mg divided by 250 mL = 0.004 mg/mL or 4 mcg/mL. To infuse 125 mcg/minute, the nurse should infuse 31 mL/hour. Use the following formula: Dosage in micrograms per minute multiplied by 60 minutes divided by the concentration of drug = pump setting: 125 mcg/minute × 60 minutes = (7,500) divided by 4 mcg/mL = 1,875 divided by 60 = 31.25 mL/hour. Round to 31 mL/hour.
Nursing process step: Analysis
23. A client comes to the emergency department complaining of rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and syncope. Cardiac monitoring shows supraventricular tachycardia. Vital signs reveal pulse, 164 beats/minute; blood pressure, 80/50 mm Hg; and respirations, 28 breaths/minute. I.V. access is established and oxygen is administered. The emergency department nurse should anticipate an order for:
[ ] A. digoxin (Lanoxin).
[ ] B. diltiazem (Cardizem).
[ ] C. bretylium.
[ ] D. adenosine (Adenocard).
View Answer
23. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Adenosine is the drug of choice for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia; 6 mg is given rapid I.V. push over 1 to 3 seconds. If there’s no response in 1 to 2 minutes, 12 mg may be given. Bretylium is used to treat refractory ventricular fibrillation. Digoxin and diltiazem are considered third-line drugs in the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia.
Nursing process step: Intervention
24. Classic signs of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) include all of the following except:
[ ] A. widening pulse pressure.
[ ] B. tachycardia.
[ ] C. altered level of consciousness (LOC).
[ ] D. bradycardia.
View Answer
24. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Tachycardia isn’t an indicator of increased ICP. The earliest and most sensitive indicator of increased ICP is a change in LOC. A compensatory mechanism that attempts to provide adequate cerebral perfusion pressure as ICP increases is Cushing’s triad. Signs of the triad include widening pulse pressure, bradycardia, and increased systolic blood pressure.
Nursing process step: Assessment
25. A client comes to the emergency department complaining of left calf pain that occurs during his morning walk each day. He states that the pain disappears with rest. Which condition should the emergency department nurse suspect?
[ ] A. Claudication
[ ] B. Compartment syndrome
[ ] C. Muscle cramps
[ ] D. Deep vein thrombosis
View Answer
25. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Extremity pain that’s regularly produced by the same of degree of exercise and is relieved by rest is probably claudication. The other conditions aren’t immediately relieved by rest and aren’t consistent in presentation.
Nursing process step: Assessment
26. Which nursing intervention is appropriate for a sudden cardiac death survivor?
[ ] A. Notifying the client’s support system, including family, friends, and clergy
[ ] B. Making decisions for the client and encouraging the client to rest
[ ] C. Providing the client with privacy so that he can reflect on the situation
[ ] D. Discussing advance directive information immediately after the event
View Answer
26. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Survivors of sudden death need the support of loved ones. Therefore, the emergency department nurse should ensure that the family has been notified. The survivor needs to participate in decision making regarding the treatment plan. Providing opportunities for decision making decreases the client’s feelings of powerlessness. When possible, have someone stay with the client to promote feelings of security. Advance directive information should be discussed prior to the event so that the client’s wishes can be carried out.
Nursing process step: Intervention
27. Rhabdomyolysis is caused by muscle damage and the subsequent release of myoglobin into the circulatory system. Which of the following results would you expect to see in rhabdomyolysis?
[ ] A. Dark brown urine, decreased serum creatine kinase, and hyperkalemia
[ ] B. Elevated serum creatine kinase, dark brown urine, and positive Kernig’s sign
[ ] C. Hyperkalemia, dark brown urine, and elevated serum creatine kinase
[ ] D. Hyperkalemia, decreased serum creatine kinase, and dark brown urine
View Answer
27. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Hyperkalemia and an increase in serum creatine kinase are predominant findings in rhabdomyolysis. Dark brown urine results from the myoglobinuria that accompanies rhabdomyolysis. A positive Kernig’s sign may indicate subarachnoid hemorrhage or meningitis, but not rhabdomyolysis.
Nursing process step: Analysis
28. Which device best ensures continued correct placement of an endotracheal tube for a client being transported to the emergency department by helicopter?
[ ] A. Cardiac monitor
[ ] B. Electronic end-tidal carbon dioxide detector
[ ] C. Pulse oximeter
[ ] D. Laryngoscope
View Answer
28. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: During helicopter transfer, assessment of breath sounds is difficult. An electronic end-tidal carbon dioxide detector best ensures that the client is ventilating. Cardiac monitors show rate changes, but a rate change is a nonspecific finding. Pulse oximetry isn’t accurate in the presence of vibrations such as those experienced during transfer. A laryngoscope allows visual assessment of tube placement, but isn’t useful for constant monitoring.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
29. Bradycardia and atrioventricular (AV) node conduction disturbances are most commonly associated with:
[ ] A. cardiogenic shock.
[ ] B. anterior wall infarction.
[ ] C. inferior wall infarction.
[ ] D. heart failure.
View Answer
29. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: A client with inferior wall infarction may experience bradycardia and AV conduction disturbances. Anterior wall infarction may lead to tachycardia and heart block. Tachycardia is also a sign of heart failure and cardiogenic shock, both complications of myocardial infarction.
Nursing process step: Assessment
30. Which tissue pressure measurement is indicative of compartment syndrome?
[ ] A. 5 to 10 mm Hg
[ ] B. 10 to 20 mm Hg
[ ] C. 20 to 30 mm Hg
[ ] D. 30 to 40 mm Hg
View Answer
30. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Normal tissue pressure is less than 20 mm Hg. Tissue pressures in excess of 30 mm Hg with suspicious clinical findings are usually indicative of compartment syndrome and require further intervention.
Nursing process step: Analysis
31. Parkinson’s disease occurs because of degeneration of which part of the brain?
[ ] A. Temporal lobe
[ ] B. Pituitary gland
[ ] C. Basal ganglia
[ ] D. Medulla
View Answer
31. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative condition of the basal ganglia. It can also be induced as a result of drug therapy. Such drugs include neuroleptics, antihypertensives, and antiemetics.
Nursing process step: Assessment
32. The following clients come to the emergency department for treatment after a building explosion and collapse. Which client should receive priority care?
[ ] A. A 17-year-old with an open head injury, a Glasgow Coma Scale of 3, fixed and dilated pupils, a pulse rate of 140 beats/minute, and a blood pressure of 60 mm Hg on palpation
[ ] B. A 32-year-old with several facial lacerations who’s otherwise stable with a Glasgow Coma Scale of 15
[ ] C. A 43-year-old with a severed left leg, controlled bleeding at the severance site, a pulse rate of 138 beats/minute, a respiratory rate of 32 breaths/minute, and a blood pressure of 88/64 mm Hg
[ ] D. An unresponsive 68-year-old who arrives with third-degree burns over 95% of her body and a blood pressure of 60 mm Hg on palpation
View Answer
32. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: The client with a severed leg has a serious injury that requires immediate attention and is amenable to medical intervention. Therefore, that client should receive priority in this situation. The client with an open head injury and the client with severe burns are hemodynamically compromised and have grave prognoses. In addition, the resources to treat them during a disaster are inadequate. The client with facial lacerations is stable and the injuries are relatively minor; therefore, that client’s care can be delayed.
Nursing process step: Assessment
33. A nitroprusside (Nitropress) drip is prepared by mixing 50 mg of the drug in 250 mL of dextrose 5% in water (D5W). The nurse is instructed to administer 3 mcg/kg/minute. The client weighs 89 kg. Which drip rate is correct (the drip factor of the pump tubing is 60 gtt/mL)?
[ ] A. 10 mL/hour
[ ] B. 32 mL/hour
[ ] C. 75 mL/hour
[ ] D. 80 mL/hour
View Answer
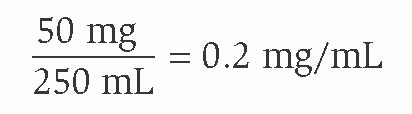
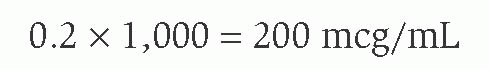

33. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: First determine the concentration:
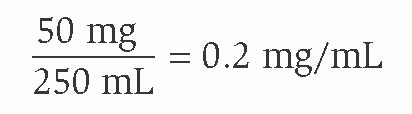
then, because the dose is ordered mcg/kg/min, convert to mcg/mL:
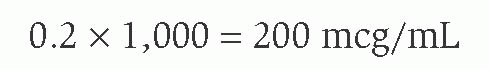
Then set up the following equation:

Round off to 80 mL/hour.
Nursing process step: Analysis
34. Which statement about the principles of disaster documentation is true?
[ ] A. Always use small disaster tags so that they can remain with the client throughout his stay in the emergency department.
[ ] B. Have as many carbon copies as possible on the tag so that they can be used to update the command post instead of verbally communicating.
[ ] C. Maintain record-keeping and charting as close to day-to-day operations as possible.
[ ] D. Documentation on forms specific for disaster situations should be used.
View Answer
34. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: During times of increased stress, confusion, and overwhelming client volumes, the use of familiar forms and medical records increases compliance with documentation of client care. Disaster tags can minimize and standardize documentation. They’re most useful if they have multiple copies, and these copies are distributed to the command post, public relations, or admissions.
Nursing process step: Analysis
35. Which statement by a client indicates an understanding of genital herpes treatment?
[ ] A. “As long as I am taking the acyclovir (Zovirax) I can continue sexual activity.”
[ ] B. “I’ll share my prescription for acyclovir with my partner.”
[ ] C. “I know that lesions may be getting ready to erupt if I have itching and a tingling sensation in the vaginal area.”
[ ] D. “I need to douche twice a day for the next week with Betadine and water.”
View Answer
35. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Prodromal symptoms, which include itching, tingling, and paresthesia, may occur a few hours to 2 days before actual eruption of herpes lesions. Acyclovir reduces the duration of viral shedding, which begins just before lesion appearance and continues for about 12 days, but sexual activity should cease until lesions are healed or a posttreatment examination is done. All partners should have their own examination and treatment regimen. Douching isn’t recommended because it disturbs the normal flora that assists with preventing infection.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
36. Kawasaki disease is manifested by which sign?
[ ] A. Erythema of the palms and soles
[ ] B. Butterfly rash
[ ] C. Exophthalmos
[ ] D. Koplik’s spots
View Answer
36. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Kawasaki disease is a form of vasculitis that attacks multiple body systems. Signs and symptoms include elevated temperature, conjunctivitis, “strawberry” tongue and lips, cervical lymphadenopathy, erythema of the palms and soles, and periungual desquamation. A butterfly rash (malar erythema) is associated with lupus erythematosus. Exophthalmos is associated with Graves’ disease, a thyroid disorder. Koplik’s spots, which are associated with rubeola, are reddened areas with gray-blue centers on the buccal mucosa.
Nursing process step: Assessment
37. A 13-year-old male enters the emergency department after waking up with sudden onset of abdominal pain. His mother reports that the pain is so bad that it has caused the client to vomit. On physical examination, he is noted to have redness and edema in his scrotum. What diagnosis should be ruled out as soon as possible?
[ ] A. Epididymitis
[ ] B. Testicular torsion
[ ] C. Priapism
[ ] D. Chlamydia
View Answer
37. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Testicular torsion is the sudden twisting of the spermatic cord, causing vascular compromise to the affected testicle. Emergent surgical intervention or manual detorsion under local anesthesia is needed within 2 to 6 hours, depending on the severity of the torsion. Epididymitis is an inflammatory, nonemergent infection that can be associated with a sexually transmitted infection. Although an emergency, priapism (painful persistent erection) doesn’t affect the testes.
Nursing process step: Assessment
38. Expected outcomes for a family after a sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) diagnosis include all of the following except:
[ ] A. verbalizing positive memories of the infant.
[ ] B. accepting a referral for a SIDS support group.
[ ] C. verbalizing concerns about the cause of death.
[ ] D. verbalizing that the baby may have smothered or choked to death.
View Answer
38. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Verbalizing that the baby may have smothered or choked demonstrates that they aren’t well-informed or don’t comprehend what they have been told about SIDS. It’s normal for family members to be concerned about the cause of death and to verbalize positive memories about the child. Accepting a referral for a SIDS support group demonstrates that they are ready to move on.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
39. Which isn’t indicative of a positive peritoneal lavage?
[ ] A. Aspiration of 10 mL of gross blood
[ ] B. Presence of intestinal contents
[ ] C. Return of fluid that doesn’t contain blood or white blood cells
[ ] D. Return of cloudy fluid
View Answer
39. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: The return of cloudy fluid or the aspiration of gross blood or intestinal contents represents a positive peritoneal tap. The return of clear fluid indicates a negative tap.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
40. A client comes to the emergency department (ED) complaining of substernal chest pain. Cardiac monitoring reveals sinus bradycardia with uniform premature ventricular contractions. After a saline lock has been started, the client becomes unresponsive. The monitor reveals ventricular fibrillation. The ED nurse defibrillates the client at 200 joules, 300 joules, and 360 joules. The client remains in ventricular fibrillation. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is initiated. The client is intubated by the physician. What’s the next action?
[ ] A. Defibrillate at 360 joules.
[ ] B. Administer epinephrine 1 mg I.V.
[ ] C. Administer lidocaine 15 mg/kg I.V.
[ ] D. Administer sodium bicarbonate 1 mEq/kg I.V.
View Answer
40. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Following the advanced cardiac life support guidelines for ventricular fibrillation, the appropriate action is to administer epinephrine 1 mg I.V. The client may be defibrillated at 360 joules within 30 to 60 seconds. Lidocaine may then be administered in persistent ventricular fibrillation. Sodium bicarbonate isn’t indicated at this point, and its use should be guided by arterial blood gas levels.
Nursing process step: Intervention
41. The decision to transfer a client should be based on all of the following except:
[ ] A. written policies of the emergency department.
[ ] B. medical insurance approval.
[ ] C. need for a specialized unit.
[ ] D. need for a specialized procedure.
View Answer
41. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Decisions regarding client transfer must be based on need for additional or specialized care. Lack of insurance isn’t a reason to prevent transfer of a client to a specialized facility.
Nursing process step: Assessment
42. A client who’s experiencing a situational crisis comes to the emergency department (ED). The ED nurse should:
[ ] A. obtain an order to administer anti-anxiety medication such as diazepam (Valium).
[ ] B. encourage verbalization of feelings, give emotional support, and initiate health-related teaching.
[ ] C. orient the client to reality (person, place, and time) and apply safety restraints.
[ ] D. insist that the client identify the precipitating factors and his emotional response to the event.
View Answer
42. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Immediate psychosocial interventions should focus on getting the client to identify the cause of the distress and to identify coping behaviors successfully used in the past. The ED nurse must support the client and initiate health-related teaching. Giving anti-anxiety medications won’t address the underlying problem. These clients aren’t disoriented and don’t require restraints. Denial may be used as a coping mechanism before the client is ready to face the situation. The client shouldn’t be pressured to talk about the crisis.
Nursing process step: Intervention
43. Tetany results when pathogenic organisms are introduced into human tissue. Which bacteria are responsible for this disease?
[ ] A. Pasteurella multocida
[ ] B. Clostridium
[ ] C. Enterobacter
[ ] D. Streptococcus
View Answer
43. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Clostridium tetani is a gram-positive anaerobic spore that produces bacteria that inhabit the intestinal tracts of humans and animals. The bacterium enters the bloodstream and travels to the central nervous system. Clostridium can survive in soil for years. Pasteurella multocida, Enterobacter, and Streptococcus are commonly associated with dog bites.
Nursing process step: Analysis
44. When evaluating the care of a client with bipolar disease in the emergency department (ED), what’s the priority determination?
[ ] A. The client’s thought process was organized before discharge.
[ ] B. The client was safe in the ED environment and was able to verbalize the appropriate use of lithium (Lithonate) on discharge.
[ ] C. The client’s nutritional status was evaluated.
[ ] D. The client’s auditory hallucinations had subsided before discharge.
View Answer
44. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: The client’s safety is the first priority in the ED. A psychiatric client should be told how to take his medication, and he should be able to verbalize an understanding of the instructions. It’s unrealistic to expect the client’s thought process to be organized or the client’s auditory hallucinations to subside completely before discharge. The ED isn’t the place for a complete nutritional evaluation.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
45. After falling 20′ (6 m) from a platform, a client is admitted to the emergency department. He’s complaining of chest pain that radiates to the back. Chest X-rays show widening of the mediastinum. What do these symptoms probably represent?
[ ] A. Ruptured hemidiaphragm
[ ] B. Pneumothorax
[ ] C. Ruptured trachea
[ ] D. Ruptured aorta
View Answer
45. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: The widened mediastinum along with clinical correlation represents a ruptured aorta. Blood leaking into the mediastinum increases intrathoracic pressure, resulting in pain and increased respiratory rate. A ruptured hemidiaphragm or pneumothorax is evident on chest X-ray and doesn’t involve a widening of the mediastinum. A ruptured trachea could produce a pneumomediastinum on chest X-ray.
Nursing process step: Assessment
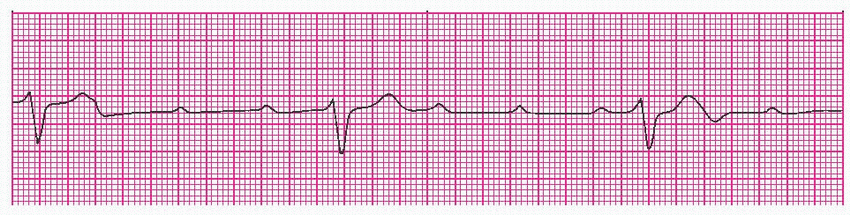
46. A client arrives in the emergency department and is placed on the electrocardiograph. Identify the rhythm.
|
[ ] A. Idioventricular
[ ] B. Third-degree heart block
[ ] C. Sinus bradycardia
[ ] D. Wenckebach
View Answer
46. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: In third-degree heart block, there’s no relation between P waves and QRS complexes. The atria and ventricles beat independently of one another. Idioventricular rhythms are wide complex and are usually slower and without P waves. Sinus bradycardia has a P wave for each QRS complex. Wenckebach has progressively longer PR intervals until a QRS complex is dropped. It has a regularly irregular rhythm.
Nursing process step: Assessment
47. Which of the following may cause a child to become fatigued during increased work of breathing?
[ ] A. Increased residual capacity
[ ] B. Increased tidal volumes
[ ] C. Lower glucose stores than an adult
[ ] D. Decreased metabolic demands
View Answer
47. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Glucose is needed to sustain the work of the diaphragm in breathing. Because a child has small stores of glucose, he’s likely to suffer respiratory distress more quickly than an adult. Decreased metabolic demands don’t cause fatigue. Increased vital capacity and tidal volumes improve oxygenation and decrease the work of breathing.
Nursing process step: Analysis
48. What’s the most common cause of retinal detachment?
[ ] A. Degenerative changes in elderly clients
[ ] B. Direct trauma associated with sports activities
[ ] C. Blunt trauma from assault to the eye
[ ] D. Hereditary factors
View Answer
48. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Degenerative changes in the elderly, direct trauma, blunt trauma, and hereditary factors can all lead to retinal detachment. The most common cause, however, is degenerative changes in elderly clients. Minimal to moderate trauma to the eye may cause retinal detachment, but in such cases, predisposing factors play an important role. Severe trauma may cause retinal tears and detachment, even if there are no predisposing factors.
Nursing process step: Assessment
49. Which equipment will be prepared for use before the transport of a conscious burn client?
[ ] A. An ice container for irrigation saline
[ ] B. A cooling blanket
[ ] C. An end-tidal carbon dioxide detector
[ ] D. An I.V. infusion pump
View Answer
49. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Monitoring I.V. infusion rates is commonly difficult in transport; therefore, an I.V. infusion regulating pump is helpful. Iced saline is important for initial burn cooling, but it could precipitate hypothermia during transport. Cooling blankets are similarly not warranted. Pain should be controlled with analgesics. An end-tidal carbon dioxide monitor is of no value unless the client is intubated.
Nursing process step: Analysis
50. Which symptom distinguishes myocardial contusion from angina?
[ ] A. Chest pain that isn’t affected by coronary vasodilators
[ ] B. Arrhythmias
[ ] C. Hypotension, distended jugular veins, and muffled heart sounds
[ ] D. Electrocardiogram (ECG) changes
View Answer
50. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: The pain associated with myocardial contusion isn’t affected by coronary vasodilators. Both myocardial contusion and angina may result in arrhythmias and ECG changes. Hypotension, distended jugular veins, and muffled heart sounds represent findings of cardiac tamponade.
Nursing process step: Assessment
51. A dystonic reaction can be caused by which medication?
[ ] A. Diazepam (Valium)
[ ] B. Haloperidol
[ ] C. Amitriptyline
[ ] D. Clonazepam (Klonopin)
View Answer
51. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Haloperidol is a phenothiazine and is capable of causing dystonic reactions. Diazepam and clonazepam are both benzodiazepines, and amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant. Benzodiazepines and tricyclic antidepressants don’t cause dystonic reactions. Benzodiazepines can cause drowsiness, lethargy, and hypotension. Tricyclic antidepressants can cause a decreased level of consciousness, tachycardia, dry mouth, and dilated pupils.
Nursing process step: Intervention
52. A 3-year-old child weighing 15 kg is brought to the emergency department after being found floating in a pond. Initially, the child’s electrocardiogram shows ventricular fibrillation. What’s the appropriate initial energy level for defibrillation of this client?
[ ] A. 15 joules
[ ] B. 30 joules
[ ] C. 100 joules
[ ] D. 200 joules
View Answer
52. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: The initial defibrillation attempt would be 2 joules/kg (2 × 15 = 30). If unsuccessful, double the energy level for the second and third attempts.
Nursing process step: Analysis
53. Before administering a chelating drug to a client with heavy metal poisoning, the nurse should include which priority nursing assessment?
[ ] A. Level of consciousness (LOC)
[ ] B. Respiratory status
[ ] C. Urine output
[ ] D. Blood pressure
View Answer
53. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Chelating agents bind with a heavy metal, and the compound formed is primarily excreted in the urine. The client should have adequate urine output before administration of chelating agents. The nurse should monitor renal function and urine output during and after therapy. LOC, respiratory status, and blood pressure should be monitored, but they aren’t specific to chelation therapy.
Nursing process step: Assessment
54. During an unusually busy day in the emergency department, the following clients come to the triage nurse within a 6-minute period. One bed is available for examinations. Which client should take priority?
[ ] A. A 13-year-old male with groin pain that was more severe 1½ hours ago
[ ] B. A 58-year-old male with urgency and hesitancy to urinate; onset was 6 hours ago
[ ] C. A 27-year-old female with severe bilateral lower abdominal pain
[ ] D. A 42-year-old female with flank pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting
View Answer
54. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Testicular torsion occurs as a sudden onset of testicular pain and, possibly, nausea, vomiting, and swelling of testes. Pain that significantly decreases may be a detrimental sign pointing to testicular ischemia, which may occur from 2 to 4 hours past initial onset. The other clients are in pain and moderate distress, but they can wait if necessary.
Nursing process step: Assessment
55. A client comes to the emergency department (ED) complaining of a sudden onset of chest pain that increases with deep breathing and when lying flat. The pain decreases somewhat when sitting up and leaning forward. Vital signs are blood pressure, 100/60 mm Hg; pulse, 100 beats/minute; respirations, 22 breaths/minute; and temperature, 103.4° F (39° C). Which condition should the ED nurse suspect?
[ ] A. Myocardial infarction (MI)
[ ] B. Pleurisy
[ ] C. Pericarditis
[ ] D. Endocarditis
View Answer
55. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium. The symptoms described are indicative of pericarditis. The pain of MI generally doesn’t change with deep breathing or a change in position. Pleurisy and endocarditis are usually gradual in onset.
Nursing process step: Assessment
56. Why should Allen’s test be performed before the insertion of an arterial line?
[ ] A. To ensure that the monitor has been zeroed correctly
[ ] B. To ensure that collateral circulation to the hand is adequate
[ ] C. To ensure that no phlebitis is present in the radial artery
[ ] D. To ensure that the transducer is at the level of the right atrium
View Answer
56. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Allen’s test is performed to ensure that collateral circulation to the hand is adequate. The radial and ulnar arteries are compressed simultaneously. The client is then instructed to open and close his fist several times. The hand will become blanched. The radial artery is released, and the hand is observed for hyperemia. The procedure is repeated with the ulnar artery.
Nursing process step: Analysis
57. An 80-kg hypertensive client is ordered nitroprusside (Nitropress) to infuse at 5 mcg/kg/minute by way of an infusion pump. The concentration is 100 mg in 250 mL of dextrose 5% in water. What’s the infusion rate in milliliters per hour (assuming the use of microdrip 60 gtt/mL tubing)?
[ ] A. 53 mL/hour
[ ] B. 56 mL/hour
[ ] C. 60 mL/hour
[ ] D. 70 mL/hour
View Answer
57. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: The concentration of nitroprusside is 0.4 mg/mL, or 400 mcg/mL (100 mg divided by 250 mL). To infuse 5 mcg/kg/minute, the nurse needs to infuse 60 mL/hour and should use this formula: Dosage in micrograms per kilogram per minute multiplied by the client’s weight in kilograms multiplied by 60 minutes divided by the concentration of the drug in micrograms per milliliter: 5 mcg/kg/minute × 80 kg = (400) × 60 minutes = (24,000) divided by 400 mcg/mL = 60 mL/hour.
Nursing process step: Analysis
58. Prolonged seizure activity can result in:
[ ] A. hyperglycemia.
[ ] B. alkalosis.
[ ] C. hypothermia.
[ ] D. acidosis.
View Answer
58. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Status epilepticus is seizure activity that exceeds 30 minutes’ duration or is a series of seizures that doesn’t allow for full recovery between events. Prolonged seizure activity can result in loss of base reserve that will lead to metabolic acidosis. Other complications associated with status epilepticus include hyperthermia, hypoglycemia, cardiac arrhythmias, hypoxia, increased intracranial pressure, and airway obstruction.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
59. A client with an insect in his left ear comes to the emergency department. What’s the most effective way to remove the insect?
[ ] A. Irrigate the ear with copious amounts of water.
[ ] B. Using an ear speculum to visualize the insect, gently grasp and remove it using forceps.
[ ] C. Instill mineral oil or alcohol into the ear canal.
[ ] D. Instill hydrogen peroxide into the ear.
View Answer
59. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Insects are the most common foreign materials in the ears of adults. To remove an insect from a client’s ear, the nurse should instill mineral oil or alcohol to fill the ear canal and then direct a light at the canal opening. The insect will crawl toward the light and out of the canal. Instilling water or hydrogen peroxide will cause the insect to swell and make removing it more difficult. Using forceps may cause the insect to break into pieces and necessitate further intervention.
Nursing process step: Intervention
60. At which point is the client owed a duty of care?
[ ] A. At the time of arrival at the emergency department (ED)
[ ] B. After admission to the ED
[ ] C. After the physician has examined the client and found an emergency condition
[ ] D. At the time a treatment plan has been established
View Answer
60. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: On arrival at the ED, the client is owed a duty of care by the physician and hospital staff.
61. Which are the most common early systemic signs of septic shock?
[ ] A. Hyperthermia, tachycardia, wide pulse pressure, tachypnea, respiratory alkalosis, and mental obtundation
[ ] B. Hypothermia, bradycardia, narrow pulse pressure, tachypnea, respiratory acidosis, and coma
[ ] C. Hypothermia, tachycardia, narrow pulse pressure, tachypnea, respiratory alkalosis, and confusion
[ ] D. Hyperthermia, bradycardia, wide pulse pressure, tachypnea, respiratory acidosis, and mental obtundation
View Answer
61. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: The early clinical indicators for septic shock include hyperthermia, tachycardia, wide pulse pressure, tachypnea (resulting in respiratory alkalosis), and mental obtundation ranging from mild disorientation to confusion, lethargy, agitation, and coma. While alive in the body, bacteria and other microorganisms release endotoxins. Endotoxins activate the mediators—tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and interferon g—which elicit a febrile response, resulting in hyperthermia. (Note that clients who are elderly, very young, or immunocompromised may be unable to elicit a febrile response to the chemical mediators and may develop hypothermia). Tachycardia is initiated by the sympathetic response to the increase in body temperature and the decrease in cardiovascular insufficiency from the dilation of the ventricles and vasodilation of the vasculature. Tachypnea results from the direct effects of endotoxins or secondary to kallikreins, bradykinin, prostaglandins, or complement activation. The wide pulse pressure comes from decreases in systemic vascular resistance and vasodilation of the vasculature. The altered mental state is thought to be from an altered state of amino acid metabolism or a disruption of the blood-brain barrier.
Nursing process step: Assessment
62. Hyperflexion of the upper extremities and hyperextension of the lower extremities are described as:
[ ] A. decortication.
[ ] B. hypotonia.
[ ] C. spasticity.
[ ] D. decerebration.
View Answer
62. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Decorticate and decerebrate posturing are indicative of cerebral damage. In decortication, the upper extremities are abducted with obvious flexion of the arms, wrists, and fingers; the lower extremities are hyperextended with plantar flexion. Hypotonia (flaccidity) presents with decreased muscle tone and weakness. Spasticity is an increase in muscle resistance to passive movement and is followed by a sudden decrease in resistance. Decerebration presents as hyperextension of the upper and lower extremities.
Nursing process step: Analysis
63. Which injury is most consistent with shaken baby syndrome?
[ ] A. Bilateral arm fractures
[ ] B. Basilar skull fractures
[ ] C. Retinal hemorrhages
[ ] D. Petechiae on the trunk
View Answer
63. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Retinal hemorrhages result from a temporary obstruction of venous return and are consistent with being shaken. Bilateral arm fractures, basilar skull fractures, and petechiae on the trunk may result from other forms of child abuse.
Nursing process step: Assessment
64. Achieving which prothrombin time (PT) is the goal of warfarin (Coumadin) therapy?
[ ] A. Equal to that of the control
[ ] B. Less than that of the control
[ ] C. 1½ times that of the control
[ ] D. Three times that of the control
View Answer
64. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: The recommended therapeutic range is 1½ to 2½ times the control time. PT equal to or less than the control is of no therapeutic value. PT greater than three times the control has no added benefit and may be associated with a higher risk of bleeding.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
65. What’s an appropriate treatment for a client with a diagnosis of herpes?
[ ] A. Decrease fluid intake.
[ ] B. Insert an indwelling urinary catheter.
[ ] C. Keep lesions moist.
[ ] D. Apply tight-fitting Dacron undergarments.
View Answer
65. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Many women present with distended bladders because of the intense, scalding pain from urine touching the lesions. These women can benefit from the use of an indwelling urinary catheter for bladder relief and continuous urine drainage. Fluid intake should be increased rather than decreased to dilute the acidic urine and to correct or prevent dehydration. Lesions should be kept dry, and loose-fitting cotton underwear is recommended. Other treatment regimens include the use of sitz baths and anesthetic ointments as well as acyclovir ointment for pain control.
Nursing process step: Intervention
66. Irritation of the vagal centers in the medulla produces:
[ ] A. vomiting.
[ ] B. headache.
[ ] C. papilledema.
[ ] D. restlessness and irritability.
View Answer
66. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Vomiting occurs secondary to increased intracranial pressure (ICP) as the vagal centers of the medulla become irritated. Headache is usually in response to increased ICP, localized swelling, and distortion of blood vessels. Papilledema occurs as the result of edema of the optic nerve. Restlessness and irritability (altered level of consciousness) are signs of increased ICP, not stimulation of the vagal center.
Nursing process step: Assessment
67. When an error in documentation is made in the medical record, how should the error be corrected?
[ ] A. Tear out the sheet with the error and recopy all the information on a new sheet, make the correct entry, and initial the sheet to indicate that it’s a copy.
[ ] B. Apply correction fluid over the error and record the correct information over it.
[ ] C. Draw a single line through the incorrect entry, date the error and initial it, and give the reason for the error.
[ ] D. Scribble through the incorrect information as well as possible and then make the correct entry.
View Answer
67. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Anything other than a single line, date, initials, and reason is suspect to legal counsel, insurance examiners, and other responsible authorities.
68. During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), it is suggested that the end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) be maintained at what level to ensure adequate placement of the endotracheal tube?
[ ] A. Less than 10 mm Hg
[ ] B. Between 10 mm Hg and 20 mm Hg
[ ] C. Between 20 mm HG and 30 mm Hg
[ ] D. Greater than 40 mm Hg
View Answer
68. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Continuous waveform capnography is the most reliable method of confirming and monitoring correct placement of an endotracheal tube. Because blood must circulate through the lungs for carbon dioxide to be exhaled and measured, capnography can also serve as a physiologic monitor of the effectiveness of chest compressions. A reading of greater than 40 mm Hg is consistent with a substantial improvement of blood flow.
Nursing process step: Analysis
69. What’s the antidote for heparin overdose?
[ ] A. Fresh frozen plasma
[ ] B. Dimercaprol (BAL In Oil)
[ ] C. Naloxone
[ ] D. Protamine sulfate
View Answer
69. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Protamine sulfate, when given alone, acts as an anticoagulant. When given in the presence of heparin, a stable salt is formed and the anticoagulant ability of both medications is lost. Fresh frozen plasma is the antidote for warfarin ingestion. Dimercaprol is used to promote the excretion of arsenic, gold, and mercury. Naloxone is effective in reversing the effects of opioids.
Nursing process step: Intervention
70. What’s the primary treatment for a client who complains of back pain?
[ ] A. Rest
[ ] B. Cold applications
[ ] C. Weight loss
[ ] D. Stretching exercises
View Answer
70. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: The primary treatment for a client with back pain is rest. Anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic medications will help the client rest. Applying heat, not cold, is recommended. Weight loss and stretching exercises are interventions that should be initiated after acute pain subsides.
Nursing process step: Intervention
71. Which diagnostic finding indicates the need for mechanical ventilation?
[ ] A. A partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) of 80 mm Hg on room air
[ ] B. A vital capacity less than 10 mL/kg
[ ] C. A normal work of breathing
[ ] D. A partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2) of 42 mm Hg
View Answer
71. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: The key rationale for initiation of mechanical ventilation is apnea, PaCO2 greater than 50 mm Hg, pH less than 7.25, a gradient greater than 350 mm Hg, increased work of breathing, and a vital capacity of less than 10 mL/kg.
Nursing process step: Assessment
72. What’s an essential part of the emergency department record for the client discharged home?
[ ] A. Remarks of other personnel caring for the client
[ ] B. Discharge instructions and follow-up instructions
[ ] C. The client’s comments regarding the care received
[ ] D. The apparent intellectual level of the client
View Answer
72. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Discharge and follow-up instructions can serve as a defense in litigation if it can be demonstrated that the client was nonadherent to instructions and, therefore, furthered his or her own injury. The client’s remarks, the remarks of other personnel, and the client’s intellectual level should be included in the record only if the discharging nurse believes that the comments illustrate the client’s ability or willingness to adhere to instructions.
73. An 18-year-old male arrives at the emergency department via EMS after being struck by a car while riding his motorcycle without a helmet. He was reported to have lost consciousness at the scene, but he is now awake and asking repetitive questions. Suddenly he loses consciousness and requires endotracheal intubation. A computed tomography (CT) scan shows diffuse blood located between the skull and dura mater with apparent shift. What is the likely differential diagnosis for this client?
[ ] A. Subdural hematoma
[ ] B. Concussion
[ ] C. Diffuse axonal injury
[ ] D. Epidural hematoma
View Answer
73. Correct answer—D.
Rationales: Epidural hematoma, a result of bleeding between the skull and the dura mater, can follow a direct blow to the head. Signs and symptoms typically include a brief loss of consciousness, followed by a lucid period, then another loss of consciousness. Subdural hematoma, which is more common, results from bleeding into the subdural space between the dura mater and the arachnoid space. Diffuse axonal injuries are caused by blunt trauma resulting in shearing or disruption of the neuronal structures. Early CT scans may be unremarkable in a concussion.
Nursing process step: Analysis
74. What’s a true statement about the responsibilities of the disaster committee?
[ ] A. The committee should review the disaster plan only after a disaster occurs.
[ ] B. The committee may disband after the disaster plan is developed or revised.
[ ] C. The committee needs to continually reevaluate and revise the disaster plan.
[ ] D. The committee should plan disaster exercises at times of low census to ensure maximum staff attendance.
View Answer
74. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Disaster preparedness planning is an ongoing process and shouldn’t end with the revision or development of a plan. Plan revision may occur after a disaster, but this isn’t the only time to make changes. Census fluctuations are too unpredictable to adequately plan a disaster exercise.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
75. After a motor vehicle accident, a client comes to the emergency department with an injury to the right leg. On physical assessment, the nurse notices that the client is unable to raise his leg when it is straightened and lacks sensation to the anterior thigh. Assessment of the left leg is normal. What’s the possible cause of this finding?
[ ] A. Damage to the median nerve
[ ] B. Damage to the femoral nerve
[ ] C. Damage to the tibial nerve
[ ] D. Damage to the peroneal nerve
View Answer
75. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Damage to the femoral nerve results in the client’s inability to raise the affected leg when it’s straight, extend the knee, or sense stimulus to the anterior thigh. Median nerve injuries are evidenced by inability to dorsiflex the affected wrist or extend the metacarpophalangeal joints. Sensory deviation with median nerve injury results in altered sensation to the dorsal web space between the thumb and index finger. Tibial nerve injuries result in altered plantar flexion of the foot and sensory changes to the sole. Peroneal nerve damage results in altered dorsiflexion of the foot and sensory changes to the web space between the great and second toes.
Nursing process step: Assessment
76. What’s the earliest and most common respiratory alteration in a client with an intracranial injury?
[ ] A. Apneustic breathing
[ ] B. Biot’s respirations
[ ] C. Cheyne-Stokes respirations
[ ] D. Cluster breathing
View Answer
76. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Cheyne-Stokes respirations are characterized by respirations of increasing depth and frequency followed by a period of apnea lasting for 10 to 60 seconds. The changes in rate and depth are in response to levels of carbon dioxide. Periods of apnea occur when the stimulation to respiratory centers diminishes. Apneustic breathing is characterized by a pause of 2 to 3 seconds after a full or prolonged inspiration. Biot’s respirations are irregular and unpredictable with deep and shallow random breaths and pauses. Cluster breathing appears as a group of irregular breaths with periods of apnea at irregular intervals.
Nursing process step: Assessment
77. Preoperative antibiotic therapy in a client with an open fracture to the distal tibia will:
[ ] A. allow systemic prophylaxis in the event the wound is deeper than initially believed.
[ ] B. not do any good because the open wound is easily cleaned and debrided during surgery.
[ ] C. reach an effective blood concentration before or at the time of wound closure and, thus, limit the threat of infection.
[ ] D. work equally effectively if administered orally or I.V.
View Answer
77. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Antibiotic therapy should be administered as soon as possible after traumatic injury. Research indicates that antibiotics given preoperatively are most effective because the bacterial count is low and the bacteria are most amenable to antibiotics. The goal of early antibiotic therapy is to reach an effective blood concentration before or at the time of wound closure and, thus, limit the threat of infection. I.V. administration of antibiotics results in higher concentrations than oral dosing.
Nursing process step: Evaluation
78. During a physical examination, which is the most characteristic finding in diagnosing asthma?
[ ] A. Dark circles under the eyes
[ ] B. Bluish, boggy nasal turbinates
[ ] C. Expiratory wheezing
[ ] D. Moist crackles
View Answer
78. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: The most characteristic finding of asthma is expiratory wheezing; however, absence of wheezing could indicate increased severity of the attack. The nurse should remember that not all wheezing signals asthma. Dark circles under the eyes, also known as allergic shiners, and bluish, boggy nasal turbinates are seen in clients with allergies as well as asthma. Therefore, these aren’t significant findings for diagnosing asthma. Moist crackles indicate the presence of fluid in the lungs’ small airways and are heard in clients with pneumonia and early stages of pulmonary edema.
Nursing process step: Assessment
79. Initial treatment for the adult client with a severe anaphylactic reaction includes:
[ ] A. administration of diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 25 mg I.M.
[ ] B. administration of epinephrine .01 to .05 mg of a 1:1,000 solution.
[ ] C. administration of epinephrine .01 to .025 mg of a 1:10,000 solution.
[ ] D. administration of cimetadine (Tagamet) 300 mg I.V.
View Answer
79. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: The initial pharmacologic treatment for an anaphylactic allergic reaction is epinephrine. Epinephrine slows the release of cellular chemical mediators and causes vasoconstriction. This vasoconstriction improves hypotensive states and decreases edematous tissue. In severe anaphylaxis, a 1:10,000 epinephrine solution should be administered I.V. slowly in a .01 to .025 mg dose. The administration of .01 to .05 mg of 1:1,000 subcutaneous epinephrine is an appropriate intervention as treatment for allergic reactions that aren’t true anaphylaxis. Diphenhydramine, a histamine receptor antagonist, can be administered in doses of 25 to 50 mg by way of oral, I.V., or I.M. routes. Cimetadine, also a histamine receptor antagonist, isn’t a first-line drug in the treatment of anaphylactic reactions.
Nursing process step: Intervention
80. The nurse should seek clarification of which order for a 5-year-old child who has ingested a large amount of paint thinner?
[ ] A. Ipecac
[ ] B. Activated charcoal
[ ] C. Gastric lavage
[ ] D. Oxygen delivered at 2 L/minute
View Answer
80. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Ipecac is contraindicated in the ingestion of most petroleum distillates, such as paint thinner, because of the potential for aspiration. The risk of aspiration must be weighed against the toxicity of the petroleum product ingested. Activated charcoal may be ordered to absorb toxins in the petroleum product. Gastric lavage may be ordered to remove toxins if the airway is protected by endotracheal intubation. Oxygen may be ordered if aspiration has occurred.
Nursing process step: Intervention
81. It’s important to assess which of the following in the client receiving magnesium sulfate?
[ ] A. Urine output, respirations, reflexes
[ ] B. Urine output, reflexes, vaginal bleeding
[ ] C. Urine output, reflexes
[ ] D. Vaginal bleeding and reflexes
View Answer
81. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: Magnesium sulfate is used to control seizures in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Urine output of less than 30 mL/hour should be reported. The drug should be withheld if respirations are fewer than 16 breaths/minute, because it may cause respiratory depression. Hypermagnesemia may result in depressed patellar reflexes. Vaginal bleeding isn’t associated with magnesium sulfate administration.
Nursing process step: Assessment
82. Honeybees and bumblebees cause a painful wound with swelling and intense itching. What’s true about the treatment of these stings?
[ ] A. Heat should be applied to the sting area.
[ ] B. Removal of the stinger is done by scraping the area with a dull object.
[ ] C. Removal of the stinger is accomplished by grasping the stinger and pulling it away from the skin.
[ ] D. Ice should be applied and the extremity lowered below the heart.
View Answer
82. Correct answer—B.
Rationales: Removal of the stinger is best done by using a dull object to scrape the stinger from the surface of the skin. Cold packs, not heat, should be applied to the site. Grasping and pulling the stinger aren’t recommended because those actions may release more venom from the sac. The area should be cleaned and cold packs applied to the site. Elevating the extremity reduces accompanying edema.
Nursing process step: Intervention
83. During client assessment, the nurse finds the client’s pupils to be pinpoint. What might this indicate?
[ ] A. Opioid overdose
[ ] B. Midbrain damage
[ ] C. Severe anoxia
[ ] D. Previous cataract surgery
View Answer
83. Correct answer—A.
Rationales: An opioid overdose or pontine hemorrhage produces pupils that can be described as “barely visible” or pinpoint. The client with midbrain damage has pupils that are nonreactive and midposition. Severe anoxia results in bilateral fixed and dilated pupils. Previous cataract surgery should be suspected in the client with keyhole-shaped pupils.
Nursing process step: Assessment
84. Symptoms suggesting a scabies infestation include:
[ ] A. raised, scaly, round patches with relatively flat centers on the hands, feet, trunk, and groin.
[ ] B. pink macular rash over palms, soles, hands, feet, wrists, and ankles.
[ ] C. pruritus that intensifies at night.
[ ] D. generalized urticaria.
View Answer
84. Correct answer—C.
Rationales: Symptoms associated with scabies infestation include red-brown linear markings on the wrists, between the fingers, at the belt and nipple line, and in the genital area. Pruritus is present and is accentuated at night when the activity of the mites increases. Raised, scaly, round patches with relatively flat centers on the hands, feet, trunk, and groin are associated with ringworm. A pink macular rash over the palms, soles, hands, feet, wrists, and ankles is associated with Rocky Mountain spotted fever. The rash later becomes petechial and mimics meningococcemia. Urticaria is rapidly appearing wheals or papules that are the result of a vascular allergic reaction that’s commonly accompanied by severe itching.
Nursing process step: Assessment
85. Which statement indicates a lack of understanding of long leg cast and extremity care?
[ ] A. “I’ll keep the cast dry.”
[ ] B. “If a foreign object drops into the cast, I’ll
attempt to retrieve it before calling my follow-up care provider.”
[ ] C. “I’ll wiggle my toes at least once each hour.”
[ ] D. “I’ll keep my leg elevated above the level of my heart for the next 24 hours.”
View Answer




85. Correct answer—B.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access