Dantrolene: Acts directly on skeletal muscle, relieving spasticity.
S
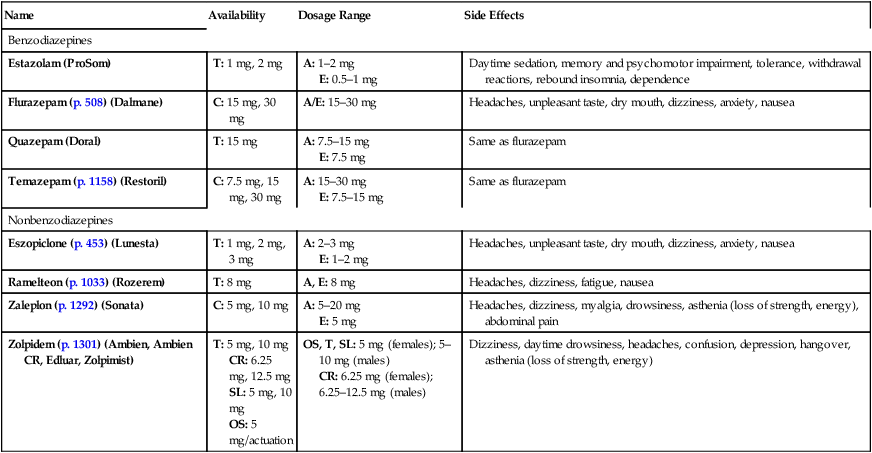
Name
Availability
Dosage Range
Side Effects
Benzodiazepines
Estazolam (ProSom)
T: 1 mg, 2 mg
A: 1–2 mg
E: 0.5–1 mg
Daytime sedation, memory and psychomotor impairment, tolerance, withdrawal reactions, rebound insomnia, dependence
Flurazepam (p. 508) (Dalmane)
C: 15 mg, 30 mg
A/E: 15–30 mg
Headaches, unpleasant taste, dry mouth, dizziness, anxiety, nausea
Quazepam (Doral)
T: 15 mg
A: 7.5–15 mg
E: 7.5 mg
Same as flurazepam
Temazepam (p. 1158) (Restoril)
C: 7.5 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg
A: 15–30 mg
E: 7.5–15 mg
Same as flurazepam
Nonbenzodiazepines
Eszopiclone (p. 453) (Lunesta)
T: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg
A: 2–3 mg
E: 1–2 mg
Headaches, unpleasant taste, dry mouth, dizziness, anxiety, nausea
Ramelteon (p. 1033) (Rozerem)
T: 8 mg
A, E: 8 mg
Headaches, dizziness, fatigue, nausea
Zaleplon (p. 1292) (Sonata)
C: 5 mg, 10 mg
A: 5–20 mg
E: 5 mg
Headaches, dizziness, myalgia, drowsiness, asthenia (loss of strength, energy), abdominal pain
Zolpidem (p. 1301) (Ambien, Ambien CR, Edluar, Zolpimist)
T: 5 mg, 10 mg
CR: 6.25 mg, 12.5 mg
SL: 5 mg, 10 mg
OS: 5 mg/actuation
OS, T, SL: 5 mg (females); 5–10 mg (males)
CR: 6.25 mg (females); 6.25–12.5 mg (males)
Dizziness, daytime drowsiness, headaches, confusion, depression, hangover, asthenia (loss of strength, energy)
Name
Indication
Dosage Range
Side Effects/Comments
Baclofen (p. 116) (Lioresal)
Spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury
Initially 5 mg 3 times/day
Increase by 5 mg 3 times/day q3days
Maximum: 20 mg 4 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Caution with renal impairment, seizure disorders
Withdrawal syndrome (e.g., hallucinations, psychosis, seizures)
Carisoprodol (p. 197) (Rela)
Discomfort due to acute, painful, musculoskeletal conditions
250–350 mg 4 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Hypomania at higher than recommended doses
Withdrawal syndrome
Hypersensitivity reaction (skin reaction, bronchospasm, weakness, burning eyes, fever) or idiosyncratic reaction (weakness, visual or motor disturbances, confusion) usually occurring within first 4 doses
Chlorzoxazone (Lorzone)
Discomfort due to acute, painful, musculoskeletal conditions
Initially 250–500 mg 3–4 times/day
Maximum: 750 mg 3–4 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects, rare hepatotoxicity
Hypersensitivity reaction (urticaria, itching)
Urine discoloration to orange, red, or purple
Cyclobenzaprine (p. 295) (Flexeril)
Muscle spasm, pain, tenderness, restricted movement due to acute, painful, musculoskeletal conditions
Initially 5–10 mg 3 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, urinary retention)
Quinidine-like effects on heart (QT prolongation)
Long half-life
Dantrolene (p. 312) (Dantrium)
Spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, spinal cord injury
Initially 25 mg/day for 1 week, then 25 mg 3 times/day for 1 week, then 50 mg 3 times/day for 1 week, then 100 mg 3 times/day
Maximum: 100 mg 4 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Contraindicated with hepatic disease
Dose-dependent hepatotoxicity
Diarrhea that is dose dependent and may be severe, requiring discontinuation
Diazepam (p. 352) (Valium)
Spasticity associated with cerebral palsy, spinal cord injury; reflex spasm due to muscle, joint trauma or inflammation
2–10 mg 3–4 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Abuse potential
Metaxalone (p. 757) (Skelaxin)
Discomfort due to acute, painful, musculoskeletal conditions
800 mg 3–4 times/day
Drowsiness (low risk), dizziness, GI effects
Paradoxical muscle cramps
Mild withdrawal syndrome
Contraindicated in serious hepatic or renal disease
Methocarbamol (p. 762) (Robaxin)
Discomfort due to acute, painful, musculoskeletal conditions
Initially 1,500 mg 4 times/day
Maintenance: 1,000 mg 4 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Urine discoloration to brown, brown-black, or green
Orphenadrine (Norflex)
Discomfort due to acute, painful, musculoskeletal conditions
100 mg 2 times/day
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Long half-life
Anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, urinary retention)
Rare aplastic anemia
Some products may contain sulfites
Tizanidine (p. 1199) (Zanaflex)
Spasticity
Initially 4 mg q6–8h (Maximum 3 times/day), may increase by 2–4 mg as needed/tolerated
Maximum: 36 mg (limited information on doses greater than 24 mg)
Drowsiness, dizziness, GI effects
Hypotension (20% decrease in B/P)
Hepatotoxicity (usually reversible)
Withdrawal syndrome (hypertension, tachycardia, hypertonia)
Effect is short lived (3–6 hrs)
Dose cautiously with creatinine clearance less than 25 ml/minRelated
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



S
S
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
