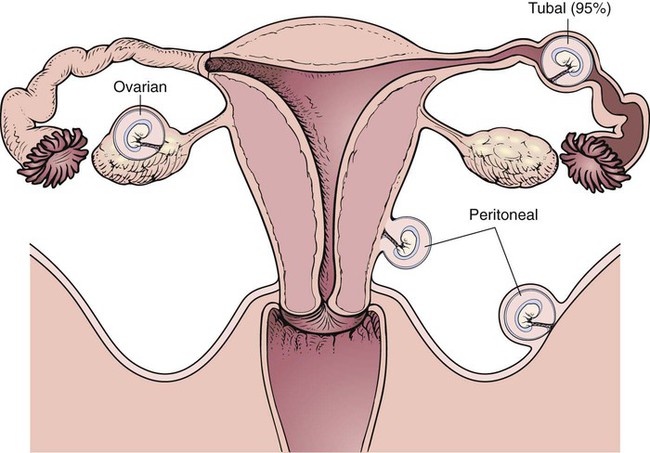
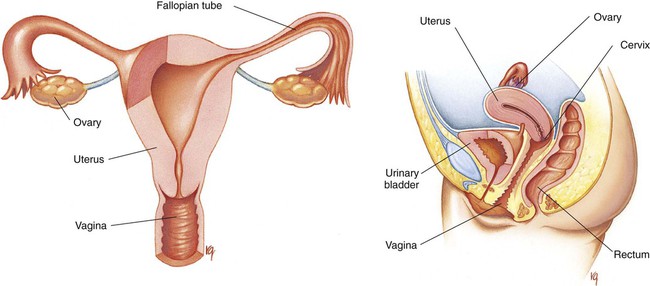
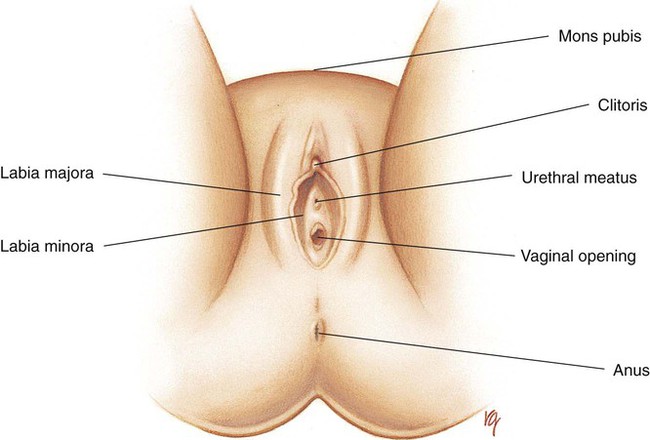
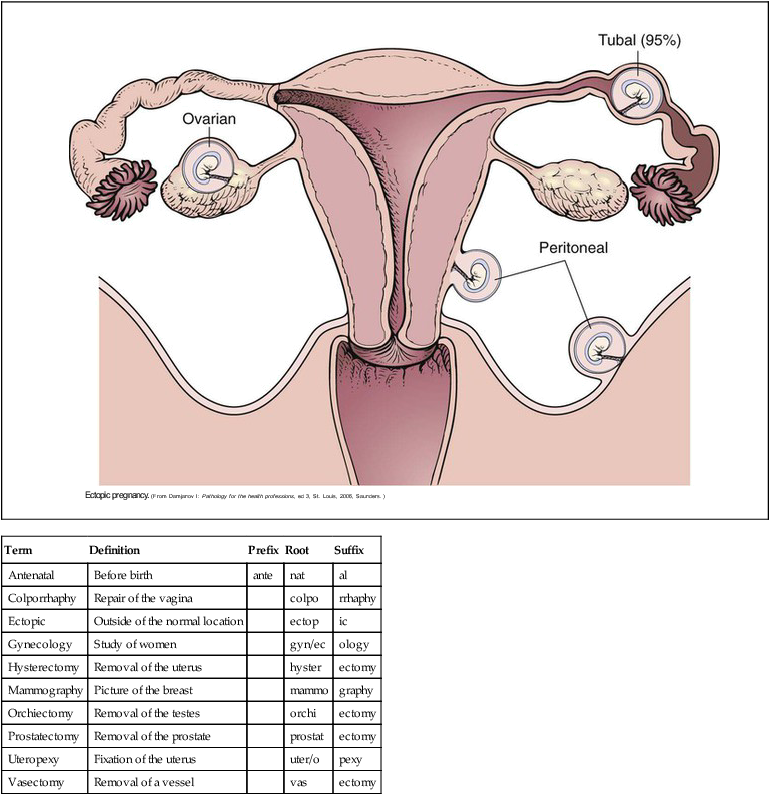
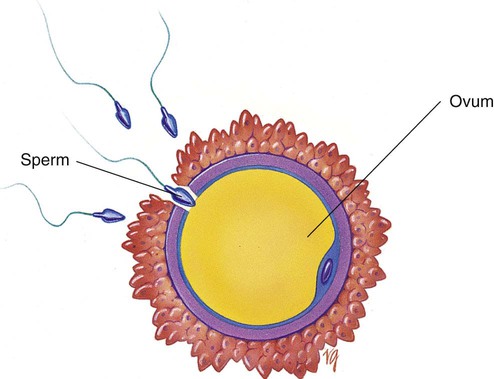
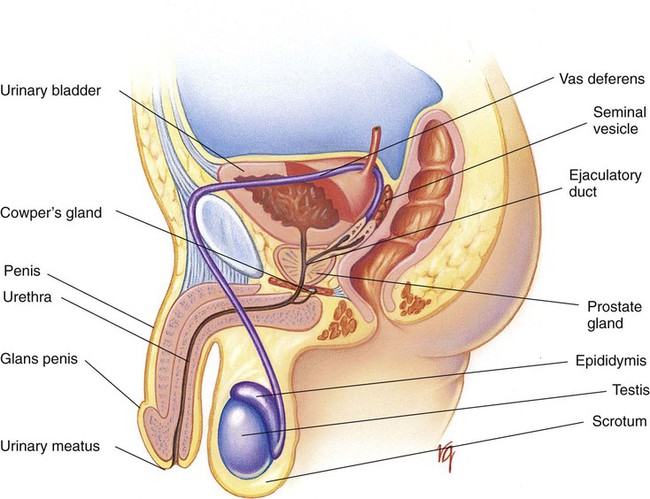
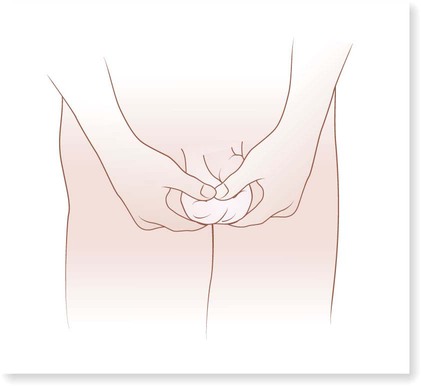
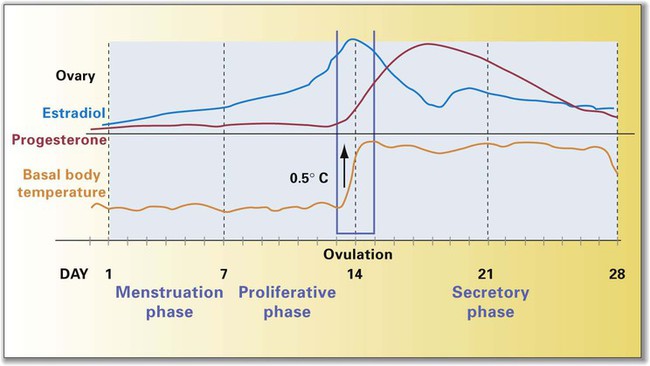
Chapter 21 (MEN-stroo-al) The recurring cycle of change of the reproductive organs induced by hormones in women Reproductive System Terminology* *A transition syllable or vowel may be added to or deleted from the word parts to make the combining form. The reproductive organs of both the male and female produce sex cells called gametes. The combination of genes of the female gamete (ova) and male gamete (sperm) is called fertilization (Fig. 21-1). From the time of conception to 2 weeks, the fertilized ovum is called a zygote. From 2 to 8 weeks’ gestation, the growing cells are called an embryo. From 8 weeks to birth, the unborn baby is called a fetus. During the first 30 days of life, the infant is considered to be a neonate. The organs of reproduction of the male are shown in Fig. 21-2. The testes, about 4 to 5 cm long, produce the sperm. The testes also secrete an androgenic hormone (testosterone), causing the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics such as facial and body hair, deepened voice, increased muscle mass, and thickening of the bones. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) recommends a monthly self-examination of the testes to detect testicular cancer (Fig. 21-3). For 2009, the NCI estimated that 8400 new cases and 380 deaths occurred as a result of testicular cancer in the United States. Testicular cancer represents about 1% of all cancers in men. However, it is the most common form of cancer in men between 15 and 40 years of age. The organs of reproduction in the female are shown in Fig. 21-4. The ovaries are glands that produce eggs (ova) and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. The external structures of the female reproductive system are collectively called the vulva (Fig. 21-5). The labia majora are folds of adipose tissue that protect the vaginal opening. The mons pubis is a pad of fat that joins the labia majora. The labia minora are pinkish folds of skin between the labia majora. The shedding of blood tissues of the uterus (menstruation) in the female signals the onset of puberty at about 10 to 16 years of age. The menstrual cycle, which lasts about 28 days, is a complex process of hormone secretion and tissue changes in the uterus (Table 21-1). A mature ovum is released from an ovary on about the 14th day of each cycle (Fig. 21-6). Some women experience pain a few hours after ovulation called mittelschmerz. This “middle pain” is believed to be caused by irritation of the peritoneum. If the released ovum is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus (endometrium) is released from the body along with the ovum. The sloughing of this bloody tissue, or menses, lasts from 3 to 7 days. The menstrual cycle continues until 45 to 50 years of age. The cessation of the cycle is called menopause (climacteric). Reduction in hormone production that occurs with menopause may cause a variety of symptoms, including “hot flashes,” or transient periods of feeling warm. Reduced levels of both estrogen and pituitary gonadotropins occur with menopause. Without these hormones, the woman’s ability to conceive or reproduce ceases. TABLE 21-1 FSH, Follicle-stimulating hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone. *If the ovum is fertilized after leaving the ovary, it is implanted in the rich uterine wall. The corpus luteum continues to secrete progesterone throughout the pregnancy to maintain the uterine wall and inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.
Reproductive System
 Define at least 10 terms relating to the reproductive system.
Define at least 10 terms relating to the reproductive system.
 Describe the function of the reproductive system.
Describe the function of the reproductive system.
 Identify at least 10 reproductive system structures and the function of each.
Identify at least 10 reproductive system structures and the function of each.
 Identify at least three methods of assessment of the reproductive system.
Identify at least three methods of assessment of the reproductive system.
 Describe common patterns of growth and development of the neonate.
Describe common patterns of growth and development of the neonate.
 Describe at least five disorders of the reproductive system.
Describe at least five disorders of the reproductive system.
Term
Definition
Prefix
Root
Suffix
Antenatal
Before birth
ante
nat
al
Colporrhaphy
Repair of the vagina
colpo
rrhaphy
Ectopic
Outside of the normal location
ectop
ic
Gynecology
Study of women
gyn/ec
ology
Hysterectomy
Removal of the uterus
hyster
ectomy
Mammography
Picture of the breast
mammo
graphy
Orchiectomy
Removal of the testes
orchi
ectomy
Prostatectomy
Removal of the prostate
prostat
ectomy
Uteropexy
Fixation of the uterus
uter/o
pexy
Vasectomy
Removal of a vessel
vas
ectomy
Structure and Function of the Reproductive System
Male Organs of Reproduction
Female Organs of Reproduction
Menstrual Cycle
Day(s)
Hormone Activity
Change in System
1
Pituitary secretes FSH
Pituitary secretes LH
Follicle cells mature and produce estrogen
Promotes estrogen production
2
Estrogen increases
Uterine lining begins to thicken; secondary sexual characteristics are maintained
3-13
No hormone activity
No change in system
14
Pituitary secretes FSH and LH
Mature follicle ruptures causing release of ovum (ovulation)*; follicle of ovary becomes corpus luteum
15
Corpus luteum secretes
Lining of uterus becomes more vascular; secretions of pituitary inhibited progesterone and estrogen
16-23
No hormone activity
No changes in system
24
No hormone activity
Corpus luteum degenerates if ovum is not fertilized
25
Progesterone and estrogen
Blood vessels to uterine lining constrict; tissues disintegrate and slough secretion decreases
26-27
No hormone activity
No changes in system
28
No hormone activity
Menses begin and last approximately 5 days
Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access