Renal Regulation
QUICK LOOK AT THE CHAPTER AHEAD
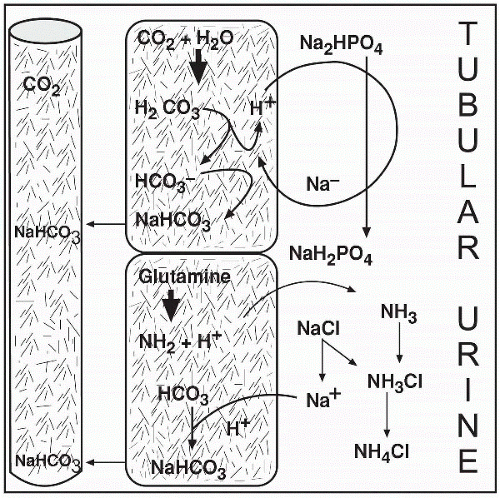
The kidneys are effective in acid-base balance because they permanently remove the hydrogen ion from the body. Though efficient, with the ability to last longer than other buffers, the renal system takes days to become completely effective when regulating pH. In this chapter we look at the different chemical combinations the renal system uses to regulate an acid-base imbalance.
The kidneys are effective in acid-base balance because they permanently remove H+ from the body. They also reabsorb acids or bases and produce bicarbonate ions. If the pH decreases, indicating a state of acidosis, the kidneys conserve or make new bicarbonate and excrete an acidic urine. Conversely, if the pH rises, indicating a state of alkalosis, the kidneys reabsorb the H+ and excrete a more alkaline urine. Unlike the respiratory system, which can affect the pH in minutes, the renal processes are slow, taking hours to days to effectively regulate the pH; however, the effects of this system can last longer than other systems.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree