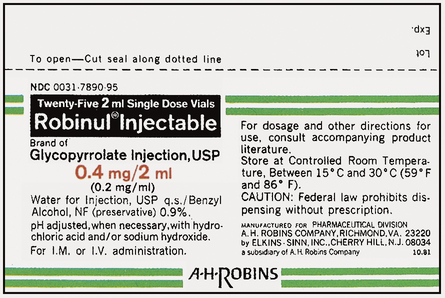
Upon completion of this chapter, the learner will be able to: 1. Define the key terms that relate to the chapter. 2. Identify the proper way to set up ratios with 100% accuracy. 3. List proportions found in the health care field. 4. Demonstrate how to set up a proportion with 100% accuracy. 5. Solve for “X” with 100% accuracy. 6. Use medication formulas with 100% accuracy to solve word problems. When you think about it, a ratio is simply a comparison between two objects or amounts. Look at the medication labels in Figures 5-1, 5-2, and 5-3. What are the examples in these three figures comparing? If you said medication per milliliter, you are correct. Each of the labels compares the medication dose to a specified amount of liquid, expressed in milliliters (ml). Now look at the labels of medications that are dispensed as tablets (Figures 5-4, 5-5, and 5-6). The labels express the dosage per tablet. The key to solving a proportion problem is how you set up your problem. Refer to the box Strategy 5-1 for steps in setting up a proportion.
Ratios and Proportions
Objectives 2, 3, 4
Ratio
Example:
The shelter houses 15 dogs to every 7 cats.
15:7, 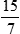 , or 15 to 7
, or 15 to 7
Example:
There are 7 boys and 12 girls in the class.
7:12, 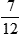 , or 7 to 12
, or 7 to 12

Objective 4
Proportion
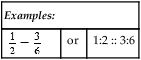
Examples:
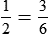
or
1:2 :: 3:6
Ratios and Proportions
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 MATH IN THE REAL WORLD 5-1
MATH IN THE REAL WORLD 5-1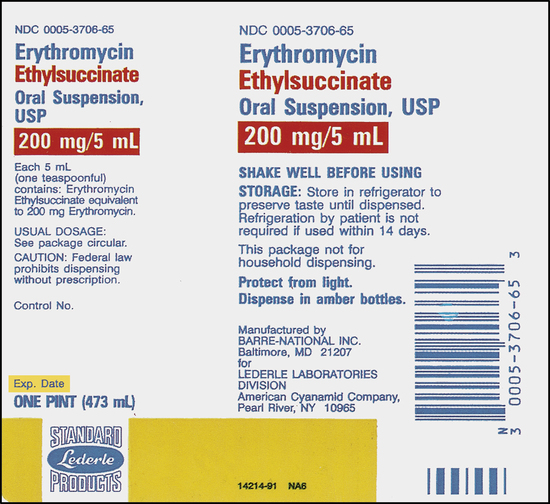




 MATH ETIQUETTE 5-1
MATH ETIQUETTE 5-1 PRACTICE THE SKILL 5-1
PRACTICE THE SKILL 5-1 STRATEGY 5-1
STRATEGY 5-1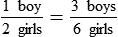
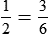

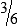
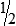
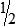
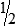
 STRATEGY 5-2
STRATEGY 5-2 STRATEGY 5-3
STRATEGY 5-3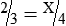
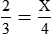
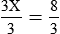
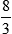
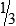
 HUMAN ERROR 5-1
HUMAN ERROR 5-1 STRATEGY 5-4
STRATEGY 5-4

