Do not confuse Altace with alteplase, Amaryl, or Artane, or ramipril with enalapril or Monopril. (Apo-Ranitidine
R
ramipril
![]()
ranitidine
![]()
![]() , Zantac, Zantac-75, Zantac-150, Zantac EFFERdose)
, Zantac, Zantac-75, Zantac-150, Zantac EFFERdose)
R
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification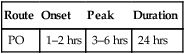
 classification
classification

