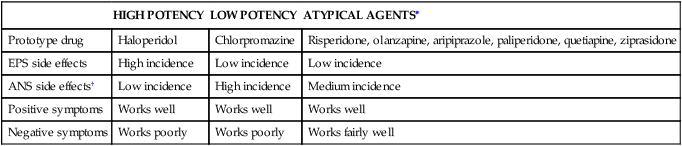
ANS, Autonomic nervous system; EPS, extrapyramidal system. ∗Atypical, newer antipsychotics are generally first-line treatment and maintenance therapy as a result of reduced extrapyramidal side effects and efficacy with negative symptoms. Choose them over older agents. †ANS side effects include anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, urinary retention, blurry vision, mydriasis), alpha1 blockade (orthostatic hypotension), and antihistamine effects (sedation).
Psychiatry
12 Differentiate among the classes of antipsychotic drugs
HIGH POTENCY
LOW POTENCY
ATYPICAL AGENTS∗
Prototype drug
Haloperidol
Chlorpromazine
Risperidone, olanzapine, aripiprazole, paliperidone, quetiapine, ziprasidone
EPS side effects
High incidence
Low incidence
Low incidence
ANS side effects†
Low incidence
High incidence
Medium incidence
Positive symptoms
Works well
Works well
Works well
Negative symptoms
Works poorly
Works poorly
Works fairly well
21 What are the side effects of the atypical antipsychotics?
 Olanzapine: Weight gain, sedation, hypotension, dry mouth
Olanzapine: Weight gain, sedation, hypotension, dry mouth
 Quetiapine: Sedation, orthostatic hypotension, akathisia, weight gain, dry mouth
Quetiapine: Sedation, orthostatic hypotension, akathisia, weight gain, dry mouth
 Ziprasidone: Nausea, weakness, mild QT prolongation
Ziprasidone: Nausea, weakness, mild QT prolongation
 Aripiprazole: Headache, nausea, akathisia, tremor, constipation
Aripiprazole: Headache, nausea, akathisia, tremor, constipation
 Paliperidone: Parkinsonism, dystonia, dyskinesia, akathisia, QT prolongation
Paliperidone: Parkinsonism, dystonia, dyskinesia, akathisia, QT prolongation
 Clozapine: Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, metabolic syndrome, sedation, constipation
Clozapine: Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, metabolic syndrome, sedation, constipation
Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access


















































