CHAPTER 34 A prostatectomy is the removal of the prostate gland. The prostate may be removed in three ways: abdominally by a suprapubic or a retropubic approach; by a perineal approach; or transurethrally. A brief description of the procedure follows: 1. After the abdomen is opened, a Balfour retractor with blades may be placed for visualization. 2. A Harrington retractor may be needed to retract the abdominal structures superiorly. 3. Long Allis forceps may be used to stabilize the bladder. 4. A Bard-Parker long scalpel handle #3 with a #10 blade may be used to incise into the bladder. 5. Long, curved Metzenbaum dissecting scissors may be used to extend the incision. 6. A small Richardson retractor may be used to hold the bladder walls open. 7. The prostate gland is enucleated manually. 8. Horizon clip appliers and clips may be used for hemostasis. 9. A long, fine needle holder and long Autraugrip may be used to close the bladder. 10. After closing the abdominal layers, the skin may be closed with staples with the aid of Adson tissue forceps.
Prostatectomy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


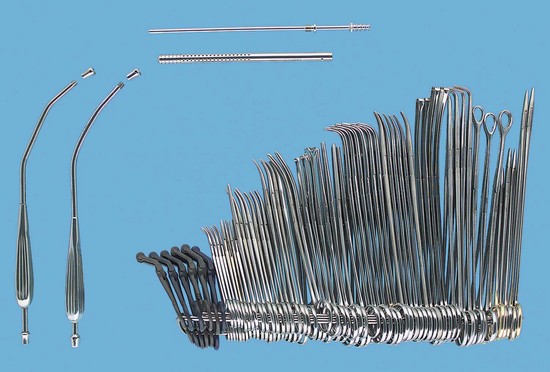
 inch; 4 tonsil hemostatic forceps; 2 mayo-Péan hemostatic forceps, curved; 2 Allis tissue forceps, medium; 1 Babcock tissue forceps, medium; 4 Ochsner hemostatic forceps, straight, long jaw; 6 Mixter hemostatic forceps, 9 inch; 6 tonsil hemostatic forceps, long; 4 Allis tissue forceps, extra long, curved; 4 Mixter hemostatic forceps, extra long; 3 Foerster sponge forceps; 2 Crile-Wood needle holders, 7 inch; 2 Crile-Wood needle holders, 8 inch; 2 mayo-Hegar needle holders, 12 inch.
inch; 4 tonsil hemostatic forceps; 2 mayo-Péan hemostatic forceps, curved; 2 Allis tissue forceps, medium; 1 Babcock tissue forceps, medium; 4 Ochsner hemostatic forceps, straight, long jaw; 6 Mixter hemostatic forceps, 9 inch; 6 tonsil hemostatic forceps, long; 4 Allis tissue forceps, extra long, curved; 4 Mixter hemostatic forceps, extra long; 3 Foerster sponge forceps; 2 Crile-Wood needle holders, 7 inch; 2 Crile-Wood needle holders, 8 inch; 2 mayo-Hegar needle holders, 12 inch.