Potassium
QUICK LOOK AT THE CHAPTER AHEAD
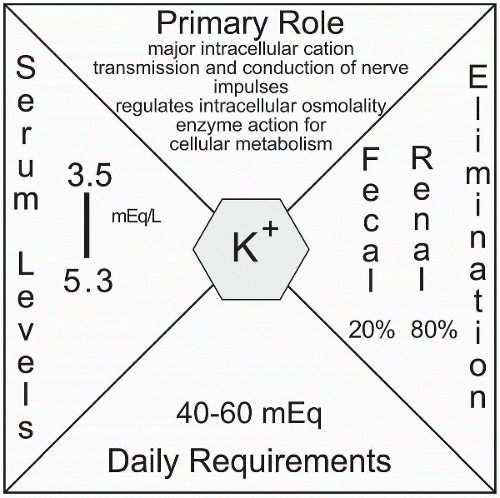
Potassium is the primary intracellular cation regulating intracellular osmolality. Intracellular levels of potassium range from 140 to 150 mEq/L compared with the extracellular level of 3.5 to 5.3 mEq/L. In this chapter we explain the functions of potassium and how it is regulated and maintained.
Potassium is the primary intracellular cation, assuming the role of sodium inside the cells and regulating intracellular osmolality. Intracellular levels of potassium range from 140 to 150 mEq/L compared with the extracellular level of 3.5 to 5.3 mEq/L. The sodium-potassium active transport pump is responsible for maintaining this gradient. Primarily regulated by the renal system, 90% of potassium is routinely reabsorbed by the proximal tubule and loop of Henle, with the remainder selectively retained to maintain homeostasis. A normal dietary intake of 40 to 60 mEq allows the average healthy person to balance these losses. Foods such as meats, vegetables, fresh and dried
fruits, nuts, and chocolate are good dietary sources. If dietary intake is low, however, or the patient is taking diuretics, potassium may also be supplemented through intravenous fluids or pill or powder supplements. Potassium-sparing diuretics may also help to decrease the total amount of potassium being eliminated from the body. Care should be taken if the patient is receiving multiple transfusions, because potassium is released in stored transfused blood.
fruits, nuts, and chocolate are good dietary sources. If dietary intake is low, however, or the patient is taking diuretics, potassium may also be supplemented through intravenous fluids or pill or powder supplements. Potassium-sparing diuretics may also help to decrease the total amount of potassium being eliminated from the body. Care should be taken if the patient is receiving multiple transfusions, because potassium is released in stored transfused blood.
 Intracellular levels of potassium range from 140 to 150 mEq/L compared with the extracellular level of 3.5 to 5.3 mEq/L.
Intracellular levels of potassium range from 140 to 150 mEq/L compared with the extracellular level of 3.5 to 5.3 mEq/L. A dietary intake of 40 to 60 mEq of potassium is normal for the average healthy person.
A dietary intake of 40 to 60 mEq of potassium is normal for the average healthy person.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access