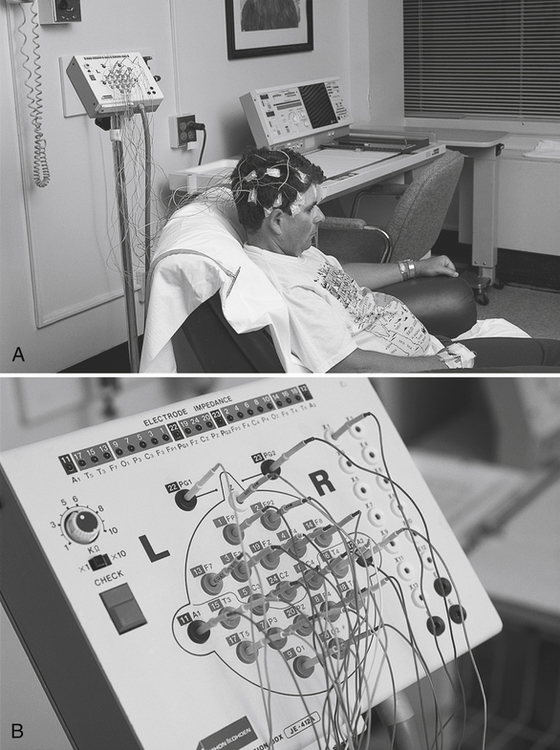
On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define the terms in the vocabulary list. 2. Write the meaning of the abbreviations in the abbreviations list. 3. Describe the purpose of electrodiagnostics, and describe the indications that would initiate a doctor’s order for a patient to undergo an electrodiagnostic procedure. 4. State the difference between a noninvasive procedure and an invasive procedure. 5. Describe the purposes of an electroencephalogram (EEG) and a quantitative electroencephalogram (QEEG). 6. State the category of medication (provide an example) that should be noted on the requisition when ordering an EEG. 7. Identify and describe the purpose of three evoked potentials. 8. Describe the purpose(s) of performing a caloric study, an electromyogram (EMG), and a nerve conduction study (NCS). 9. Explain the general purpose of cardiovascular electrodiagnostic procedures. 10. State the category of medication (provide an example) that should be noted on the requisition when an ECG is ordered. 11. List and describe three noninvasive cardiovascular electrodiagnostic procedures. 12. List and describe one cardiovascular nuclear medicine procedure and two cardiovascular ultrasound procedures. 13. Discuss the purpose of cardiac catheterization and the purpose of inserting a Swan-Ganz catheter and an arterial line (art-line or a-line). 14. Identify and discuss the purposes of at least three vascular plethysmography procedures. 15. Identify at least three vascular ultrasound studies, and discuss the purpose of each. 16. List at least six endoscopic procedures and the body parts visualized, and discuss the importance of patient preparation before a visual examination of the gastrointestinal system. 17. Identify three gastrointestinal studies that may be performed in the endoscopy department. 18. Discuss the general function of the cardiopulmonary (respiratory care) department, list at least four cardiopulmonary procedures, and identify the category of medication (provide an example) that would need to be noted when ordering arterial blood gas (ABG) monitoring. 19. Discuss the function of the sleep study department, and list a patient’s symptoms that would initiate a doctor’s order for a sleep study. A noninvasive test that determines the flexibility and health of the arterial wall. A noninvasive study that provides information about the patient’s cardiac function. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) A graphic recording of the electrical impulses that the heart generates during the cardiac cycle. A graphic recording of the electrical activity of the brain. Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) A method of studying evoked potentials within the heart. The visualization of the interior of organs and cavities of the body with an endoscope. Biopsies may be obtained during an endoscopy. Endoscopic surgeries are discussed in Chapter 17. Impedance Plethysmography (IPG) A noninvasive study that is performed to estimate blood flow and quantify blood volumes. A chronic ailment that consists of recurrent attacks of drowsiness and sleep during the daytime. Nerve Conduction Studies (NCSs) The cessation of breathing during sleep. A blockage in a canal, vessel, or passage of the body. Quantitative Electroencephalogram (QEEG) A study conducted to measure the body’s lung capacity and function. The transmission of data electronically to a distant location. A cardiovascular study done with the use of a “tilt table” to test for syncope. Transesophageal Echocardiography Two-dimensional (2D) M-Mode Echocardiogram A technique used to “see” actual heart structures and their motions. Electrodiagnostics includes procedures used to evaluate the cardiovascular, nervous, and muscular systems to diagnose conditions and diseases. Indications to perform these procedures include numbness, tingling, weakness, muscle cramping, or pain. Most electrodiagnostic studies are performed with the use of electrical activity and electronic devices to evaluate disease or injury to a specified area of the body. Some type of electrode is applied to the patient to record electrical activity in most tests. Electrical impulses can be generated spontaneously or can be stimulated. The heart generates electrical impulses spontaneously during the cardiac cycle; these may be recorded by performing an electrocardiogram (ECG). Electrical impulses may be stimulated by an electrical shock applied to the body when an electromyogram (EMG) is performed. The most common electrodiagnostic procedures are discussed in this chapter and include tests done in various hospital departments. An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a recording of the electrical activity of the brain. The procedure is performed to identify and assess patients with seizures and to study brain function. Results of the study may be used to diagnose brain tumors, epilepsy, other brain diseases, or injuries and to confirm brain death or cerebral silence (Fig. 16-1). The role of the health unit coordinator (HUC) is to communicate the order to the electroencephalography department via computer or by completion of a downtime requisition. Anticonvulsant medications such as phenobarbital (Luminal) and phenytoin (Dilantin) should be noted when a procedure involving the neurologic system is ordered (Fig. 16-2).
Other Diagnostic Studies
Abbreviation
Meaning
Example of Usage on a Doctor’s Order Sheet
ABG
arterial blood gases
ABG on RA
ABI
ankle brachial index
ABI today
ASI
arterial stiffness index
ASI
BAER
brainstem auditory evoked response; also called auditory brainstem evoked potential (ABEP)
BAER to evaluate hearing loss
CBG
capillary blood gases
CBG @ 10 am
DVT
deep vein thrombosis
Admit Dx: poss DVT lt leg
ECG, EKG
electrocardiography
ECG before surgery; EKG today
EEG
electroencephalography
Schedule EEG
EGD
esophagogastroduodenoscopy
NPO for EGD
EMG
electromyography
EMG tomorrow
ENG
electronystagmography (electrooculography)
Schedule for an ENG
EPS
electrophysiologic study
EPS today
ERCP
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Schedule for ERCP in am
ICG
impedance cardiography
Place on ICG today
IPG
impedance plethysmogram
IPG today
LOC
leave on chart (when it follows ECG/EKG)
ECG now, LOC
NCS
nerve conduction study
EMG NCS
OSA
obstructive sleep apnea
Sleep study to assess pt for OSA
PFT
pulmonary function test
PFT to evaluate COPD
QEEG
Quantitative electroencephalography
QEEG to evaluate ADHD
RA
room air
ABG on RA
SEP
somatosensory evoked potential
Schedule for SEP
TEE
transesophageal echocardiography
Schedule for TEE this afternoon
TTT
tilt table test
VEP
visual evoked potential
Schedule VEP in am
Electrodiagnostics
Background Information and Overview
Neurodiagnostic Studies (Neurology)
Neurologic and Neuromuscular System Electrodiagnostics
Electroencephalography
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Other Diagnostic Studies
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access