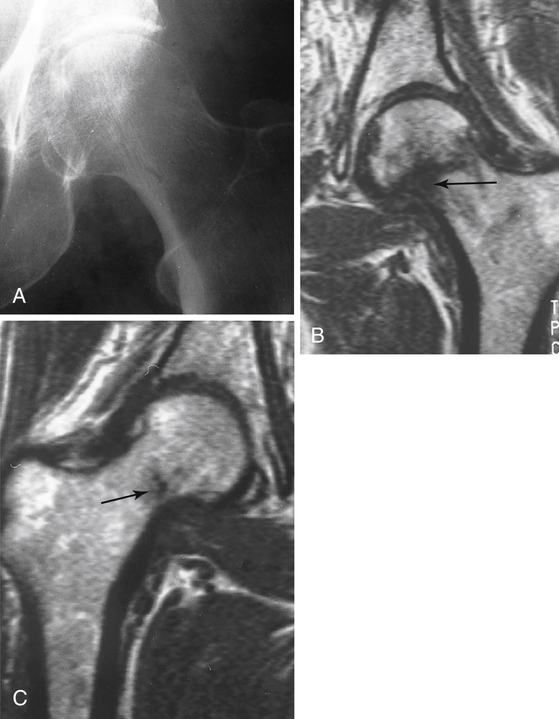
Treat the patient conservatively. Assume that there is a fracture and have the patient rest the injured area. Splinting may be appropriate for distal extremity injuries. Obtain follow-up radiographs 7 to 14 days after the injury if symptoms persist; many occult fractures become visible at that time. The exception to waiting is a suspected hip fracture in an older adult—proceed to computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the hip to allow earlier diagnosis and treatment (Fig. 28-1), which decrease operative morbidity and length of hospital stay compared with delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Orthopedic Surgery
7 How should you treat a patient with severe pain after trauma and negative x-rays?
9 What are the symptoms and signs of compartment syndrome? How is it treated?
 Pain (especially pain on passive movement out of proportion to the injury)
Pain (especially pain on passive movement out of proportion to the injury)
 Paresthesias, hypesthesia, and numbness (decreased sensation and two-point discrimination)
Paresthesias, hypesthesia, and numbness (decreased sensation and two-point discrimination)
 Firm-feeling muscle compartment
Firm-feeling muscle compartment
 Paralysis (late, ominous sign)
Paralysis (late, ominous sign)
10 Cover the right-hand columns of the following table and specify the motor and sensory functions of the following peripheral nerves. In what common clinical scenarios are they often damaged?
NERVE
MOTOR FUNCTION
SENSORY FUNCTION
CLINICAL SCENARIO
Radial
Wrist extension (watch for wrist drop)
Back of forearm, back of hand (first 3 digits)
Humeral fracture
Ulnar
Finger abduction (watch for “claw hand”)
Front and back of last 2 digits
Elbow dislocation or fracture
Median
Pronation, thumb opposition
Palmar surface of hand (first 3 digits)
Carpal tunnel syndrome, humeral fracture
Axillary
Abduction, lateral rotation
Lateral shoulder
Upper humeral dislocation or fracture
Peroneal
Dorsiflexion, eversion (watch for foot drop)
Dorsal foot and lateral leg
Knee dislocation, fibula fracture ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Orthopedic Surgery
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access







