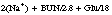O
Opiates, urinary
Basics the nurse needs to know
The opiate screen is used medically to obtain a rapid laboratory result when treating a patient who is suspected of a drug overdose. Morphine, heroin, and codeine are the most frequently abused drugs. If the test is positive, confirmatory tests for the specific opiate are performed, particularly when the case is one involving forensics or medico-legal decisions (see also Drugs of Abuse, p 262; Appendix B, p. 658). If the test result will be part of forensic evidence, the established procedure for chain-of-custody must be followed.
Interfering factors
NURSING CARE
Pretest
• The nurse assesses the patient for signs of opiate use. The patient or parent of the affected patient is asked about the use of any drug or medication in the past 24 hours. The patient who has taken a lower amount of the opiate drug may “nod,” meaning that he or she alternates between drowsiness and alertness. The patient may also appear restless or experience nausea and vomiting. If the dose of the opiate was large, the patient may be unconscious. The patient’s response to the amount of drug taken also varies with the tolerance level. Chronic drug users may have very high levels of the drug in their system, but can tolerate the amount.
Posttest
• Continue to monitor the patient’s vital signs, particularly the respirations. With a respiratory rate of less than 8 breaths per minute, the patient becomes hypoxic. The opioid antagonist naloxone (Narcan) may be given intravenously, as prescribed. Respiratory support with an Ambu bag-mask or intubation and ventilator assistance may be needed also.