Two categories of medications are used for weight control. Appetite suppressants: Block neuronal uptake of norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine, causing a feeling of fullness or satiety. Digestion inhibitors: Reversible lipase inhibitors that block the breakdown and absorption of fats, decreasing appetite and reducing calorie intake. Ophthalmic medications for allergic conjunctivitis
O
Name
Availability
Dosage
Side Effects
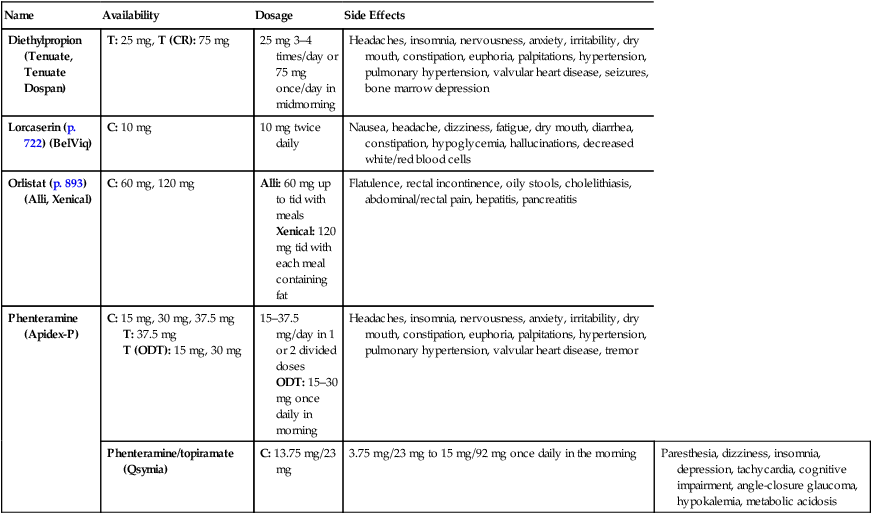
Diethylpropion (Tenuate, Tenuate Dospan)
T: 25 mg, T (CR): 75 mg
25 mg 3–4 times/day or 75 mg once/day in midmorning
Headaches, insomnia, nervousness, anxiety, irritability, dry mouth, constipation, euphoria, palpitations, hypertension, pulmonary hypertension, valvular heart disease, seizures, bone marrow depression
Lorcaserin (p. 722) (BelViq)
C: 10 mg
10 mg twice daily
Nausea, headache, dizziness, fatigue, dry mouth, diarrhea, constipation, hypoglycemia, hallucinations, decreased white/red blood cells
Orlistat (p. 893) (Alli, Xenical)
C: 60 mg, 120 mg
Alli: 60 mg up to tid with meals
Xenical: 120 mg tid with each meal containing fat
Flatulence, rectal incontinence, oily stools, cholelithiasis, abdominal/rectal pain, hepatitis, pancreatitis
Phenteramine (Apidex-P)
C: 15 mg, 30 mg, 37.5 mg
T: 37.5 mg
T (ODT): 15 mg, 30 mg
15–37.5 mg/day in 1 or 2 divided doses
ODT: 15–30 mg once daily in morning
Headaches, insomnia, nervousness, anxiety, irritability, dry mouth, constipation, euphoria, palpitations, hypertension, pulmonary hypertension, valvular heart disease, tremor
Phenteramine/topiramate (Qsymia)
C: 13.75 mg/23 mg
3.75 mg/23 mg to 15 mg/92 mg once daily in the morning
Paresthesia, dizziness, insomnia, depression, tachycardia, cognitive impairment, angle-closure glaucoma, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis
Names
Dosage
Comments/Side Effects
Lodoxamine 0.1% (Alomide)
One to two drops in affected eye(s) 4 times/day
Avoid wearing contact lenses during treatment
Side effects: burning, stinging, or irritation of eyes; watery, itching eyes; blurred vision; headache; dizziness; nausea or stomach discomfort
Nedocromil 2% (Alocril)
One or two drops in affected eye(s) 2 times/day
Remove contact lenses prior to using; may reinsert after 15 min if eyes are not red
Side effects: headache, dizziness, blurring sensation in eye, light intolerance
Pemirolast 0.1% (Alamast)
One or two drops in affected eye(s) 4 times/day
Avoid wearing contact lenses if eyes are red
Remove contact lenses prior to using; may reinsert after 10 min if eyes are not red
Side effects: foreign body sensation, headache, dry eyes, burning sensationRelated
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


