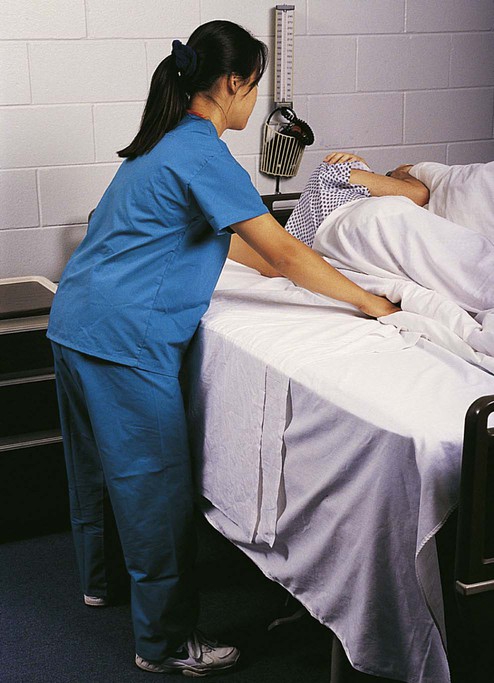
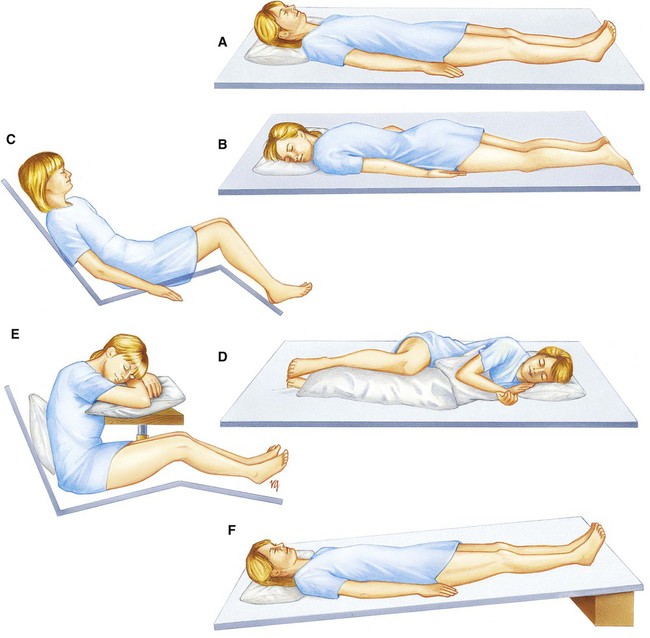
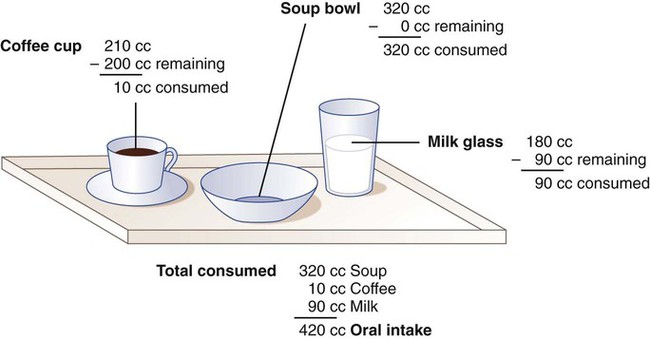
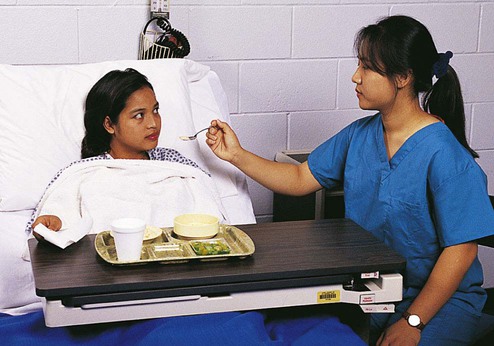
Chapter 24 *A transition syllable or vowel may be added to or deleted from the word parts make the combining form. With more than two million jobs, nurses make up the largest group of health care workers (Box 24-1). Nursing is also among the 10 occupations projected to have the largest number of new jobs in the future (Table 24-1). In fact, the American Nurses Association (ANA) and Bureau of Labor Statistics project that employment for registered nurses will grow by 22% from 2008 to 2018. Levels of workers classified as the registered nurse (RN), licensed practical nurse (LPN), and nursing assistant (NA) give nursing care. Nurses and related caregivers work with their patients in a close, or primary, relationship. The function of the nurse is to promote optimal health and provide care during illness. The duties of the nurse focus on the patient’s physical and mental needs. TABLE 24-1 Nursing Career Educational Cost and Earnings *http://redcrossla.org/classes/nurse-assistant-training. Nurses must have the ability to get along with other people and communicate well. They must provide, without prejudice, the best care possible for all patients. Especially during critical moments, the nurse must be self-controlled and efficient and show problem-solving ability. Health care personnel, including student nurses, may be required to undergo a background check to work in a Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health Care Organization (JCAHO) hospital or health care facility. Chapter 33 provides more information about background checks. LPNs, or vocational nurses, complete a 1- to 2-year program and provide personal care under the direction of a physician, dentist, or RN. Many LPNs work in a hospital, making beds (Fig. 24-1), taking vital signs, positioning (Fig. 24-2), and providing personal hygiene for patients. Other LPNs provide care in long-term care facilities. LPNs may legally administer certain medications, insert catheters, and dress wounds. In some states they may also take orders from the physician and input the orders in a computer for implementation. They may also assist physicians with procedures and train students at some levels. One model for delivery of care that is used by the nursing staff is called the “nursing process” (Box 24-2). It is a goal oriented framework for meeting the patient’s needs. The five steps or phases of the nursing process include assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation or intervention, and evaluation (ADPIE). Data for assessment are gathered by interviewing the patient, physical examination, and observation. The information may be objective (signs) that can be heard, smelt, or felt. It may also be subjective (symptoms) or reported to the nurse by the patient (Fig. 24-3). The nursing process is cyclical (repeating) and ongoing. Oral intake is considered anything that is liquid at room temperature and taken by mouth (Fig. 24-4). This includes foods such as ice cream and Jell-O. The average adult takes in 32 qt (3.3 L) of fluid daily in food and beverages. Intravenous fluids and tube feeding are considered intake. Personal or direct care is usually necessary for the hospitalized patient. Assistance with activities of daily living, as well as treatments, may be necessary if the patient is weak or ill (Fig. 24-5). The manner in which the health care worker provides personal care often determines the patient’s reaction to having someone assist with these activities or treatments. The health care worker should approach direct contact with the patient in a professional, calm, and caring manner. (See Skill List 24-1, Positioning the Patient, p. 392.)
Nursing Careers
 Define at least eight terms relating to nursing careers.
Define at least eight terms relating to nursing careers.
 Specify the role of nurses and related providers, including personal qualities, levels of education, and required credentialing.
Specify the role of nurses and related providers, including personal qualities, levels of education, and required credentialing.
 Differentiate among the roles of the registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and nurse assistant.
Differentiate among the roles of the registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and nurse assistant.
 Identify three items considered to be intake and three to be output.
Identify three items considered to be intake and three to be output.
 Identify three conditions that indicate the need to measure intake and output.
Identify three conditions that indicate the need to measure intake and output.
 Describe methods of maintaining a clean and safe facility or unit.
Describe methods of maintaining a clean and safe facility or unit.
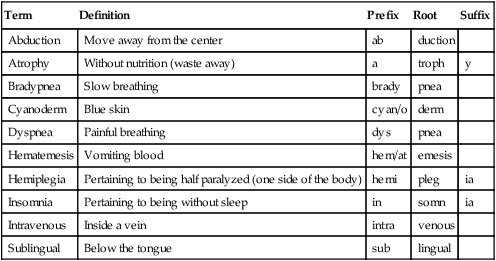
Term
Definition
Prefix
Root
Suffix
Abduction
Move away from the center
ab
duction
Atrophy
Without nutrition (waste away)
a
troph
y
Bradypnea
Slow breathing
brady
pnea
Cyanoderm
Blue skin
cyan/o
derm
Dyspnea
Painful breathing
dys
pnea
Hematemesis
Vomiting blood
hem/at
emesis
Hemiplegia
Pertaining to being half paralyzed (one side of the body)
hemi
pleg
ia
Insomnia
Pertaining to being without sleep
in
somn
ia
Intravenous
Inside a vein
intra
venous
Sublingual
Below the tongue
sub
lingual
Careers
Career
Educational Cost*
Earnings†
Certified nursing assistant
American Red Cross, 171 hours, $1750
Tuition fee includes:
Training books
Uniforms and supplies
Live scan fingerprinting
State examination for certification
Hands-on real life experience
Median annual salary:
Los Angeles, Calif.—$26,060
Licensed Practical Nurse
Content Instruction
Nursing Process
Fluid Balance
Personal Care
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nursing Careers
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access