CHAPTER 15 Persons who are 65 and older are the fastest growing segment of the population, making the elderly a major portion of the health care consumer population. Older persons are in the final stage of development during which many adaptations need to be made by the client because of the physiological changes that occur with aging. The extent or degree of the changes that take place depends on genetic and environmental factors as well as on the client’s previous attention to health maintenance. As a client reaches old age, there may also be many changes in roles, relationships, and ability to maintain his/her usual lifestyle. These factors create psychosocial concerns that need to be addressed. • Decreased cardiac output associated with: • Impaired relaxation and contractility of the heart associated with stiffening of the ventricular walls • Increased cardiac workload resulting from an increase in vascular resistance, thickened and rigid cardiac valves, and stress of current illness • Increased vascular resistance associated with decreased elasticity and increased rigidity of the arterial vessels associated with changes in the proportion of elastin and collagen in the vessel walls and accumulation of substances such as calcium and lipids • Decrease in baroreceptor sensitivity • Peripheral pooling of blood associated with loss of muscle tone in extremities, decreased competency of venous valves, and venous dilation (results from loss of vascular elasticity) DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will maintain adequate tissue perfusion as evidenced by: Ineffective breathing pattern (NDx) • Loss of alveolar elasticity (results in reduced efficiency of air expulsion) • Decreased chest expansion associated with calcification of costal cartilage and weakened respiratory muscles • Decreased responsiveness of chemoreceptors to hypoxia and hypercapnia Ineffective airway clearance (NDx) Related to stasis of secretions associated with decreased activity during illness and an age-related decrease in ciliary activity and cough effectiveness • Loss of effective lung surface associated with a reduced number of alveoli, changes in the alveolar walls, and accumulation of secretions in the bronchioles and alveoli (can result from ineffective airway clearance) • Reduced airflow associated with loss of alveolar elasticity, restricted chest expansion, and premature closure of small airways • Decreased pulmonary blood flow associated with a decrease in the number of capillaries surrounding the alveoli, fibrosis of the pulmonary vessels, and a generalized decrease in tissue perfusion • Age-related decrease in total body water • Decreased fluid intake associated with: • Age-related decline in kidney’s ability to conserve water when a deficit is caused by disease or environmental factors DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will not experience deficient fluid volume as evidenced by: Definition: Intake of nutrients insufficient to meet metabolic needs • Decreased oral intake associated with: • Anorexia resulting from factors such as depression, loneliness, diminished sense of smell and/or taste, early satiety, and dyspepsia • Difficulty chewing and swallowing food resulting from poor dentition, a decreased amount of saliva, and weakened chewing and swallowing muscles • Decreased ability to purchase and/or prepare healthy foods • Decreased utilization of nutrients associated with impaired digestion resulting from: • Decreased ability to chew foods thoroughly • Reduced secretion of digestive enzymes (e.g., salivary ptyalin, hydrochloric acid, pepsin, lipase) • Reduced absorption of nutrients associated with hypochlorhydria, decreased intestinal blood flow, and atrophy of the absorptive surface of the intestine • Increased gastroesophageal sensitivity to irritants associated with thinning of the esophageal and gastric mucosa • Gastroesophageal reflux associated with decreased tone of the lower esophageal sphincter • Impaired digestion of many foods associated with reduced secretion of digestive enzymes (e.g., hydrochloric acid, pepsin, lipase) • Delayed esophageal and gastric emptying associated with decreased gastroesophageal motility • Accumulation of intestinal gas associated with decreased peristalsis Auditory Related to: degenerative changes in the inner ear and eardrum and cerumen accumulation Kinesthetic Related to: a decrease in vestibular sensitivity and ability to perceive movement Tactile Related to: a decreased number of sensory receptors in the skin DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will demonstrate adaptation to disturbed sensory perception as evidenced by: NOC OUTCOMES: Hearing compensation behavior; sensory function: cutaneous; sensory function: hearing; sensory function: proprioception; sensory function: taste and smell; sensory function: vision Definition: At risk for skin being adversely altered • Increased fragility of the skin associated with decreased nutritional status and age-related dryness, loss of elasticity, and thinning of skin • Frequent contact with irritants if urinary incontinence is present • Accumulation of waste products and decreased oxygen and nutrient supply to the skin and subcutaneous tissue associated with decreased blood flow to the skin resulting from: Definition: Disruption of the lips and soft tissue of the oral cavity Irritation and breakdown Related to dryness and thinning of the oral mucosa • Decreased tissue oxygenation associated with diminished functional reserve capacity of the respiratory and cardiac systems during stress/illness • Decrease in strength and endurance associated with the loss of muscle mass that occurs with aging • Inadequate nutritional status • Inadequate rest and sleep associated with age-related changes in sleep pattern and effects of current illness and hospitalization on sleep pattern
Nursing Care of the Elderly Client
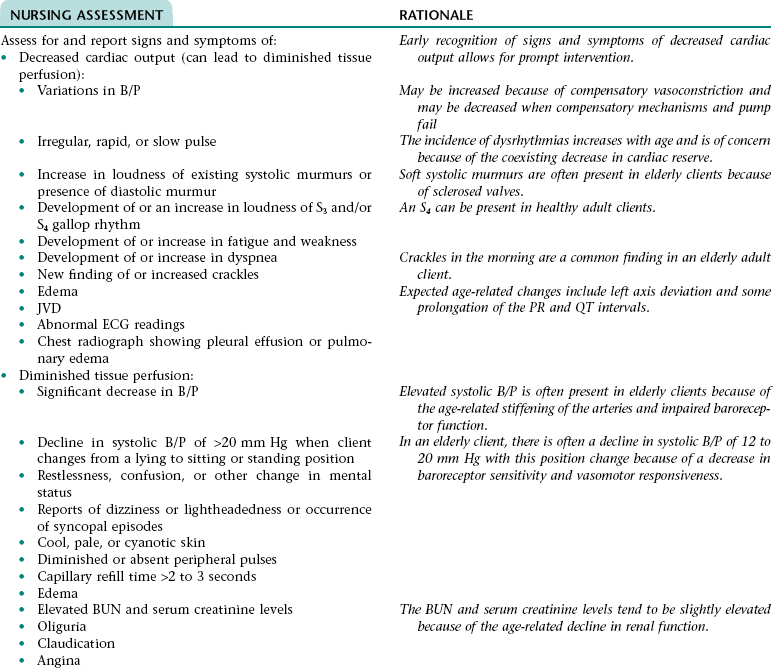
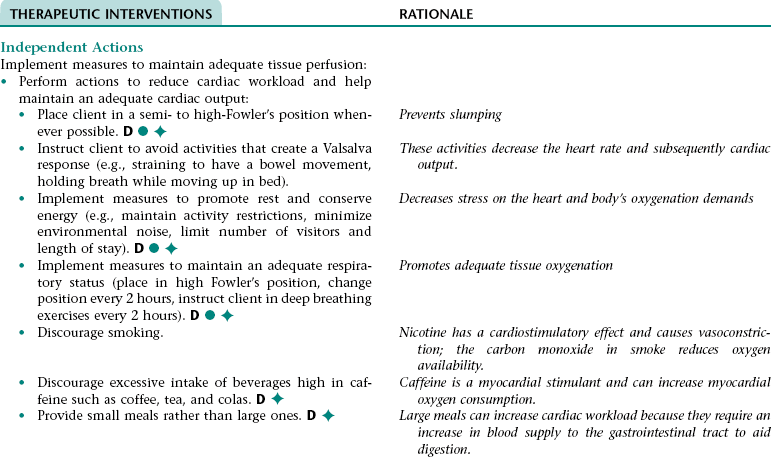
Nursing Diagnosis INEFFECTIVE TISSUE PERFUSION NDx
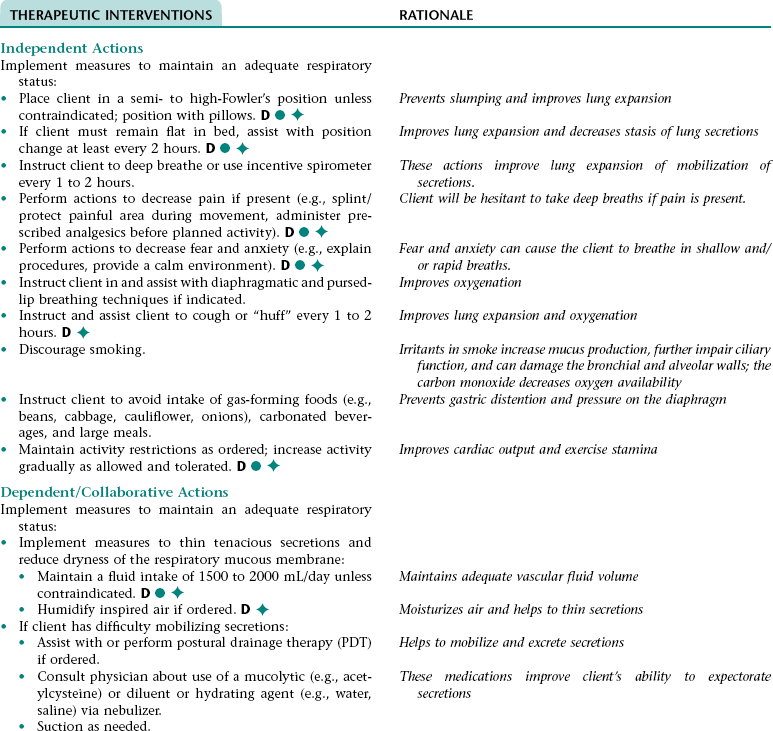
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED RESPIRATORY FUNCTION*
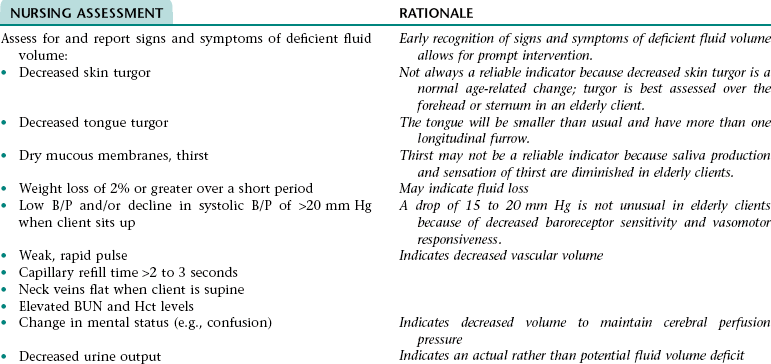
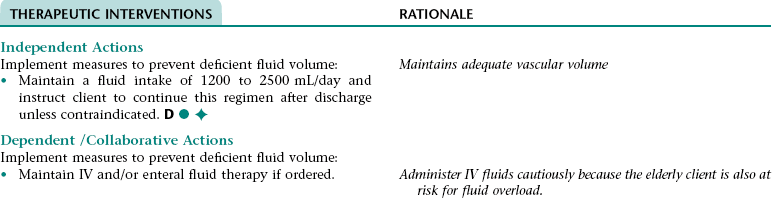
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR DEFICIENT FLUID VOLUME NDx
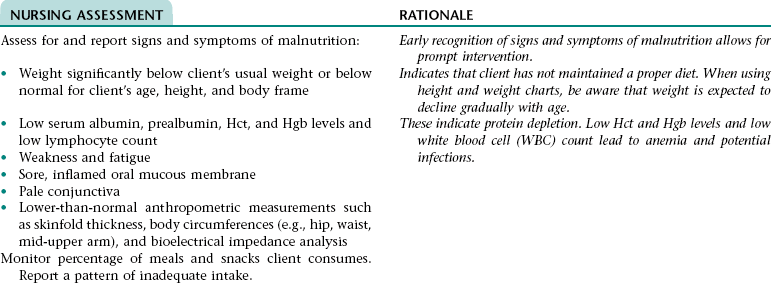
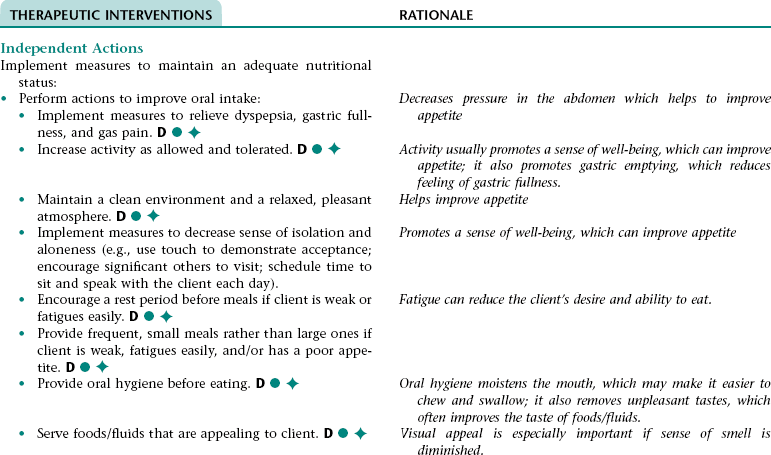
Nursing Diagnosis IMBALANCED NUTRITION: LESS THAN BODYREQUIREMENTS NDx
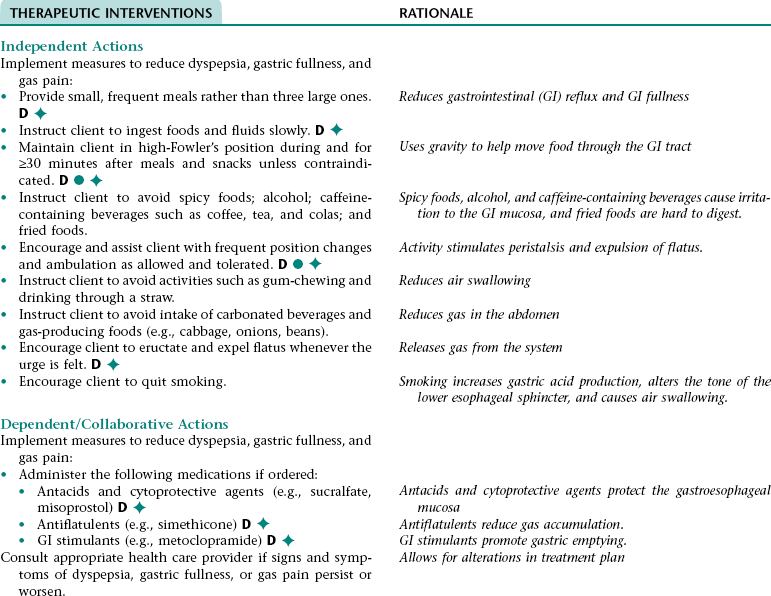
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED COMFORT NDx (DYSPEPSIA, GASTRIC FULLNESS, AND/OR GAS PAIN)
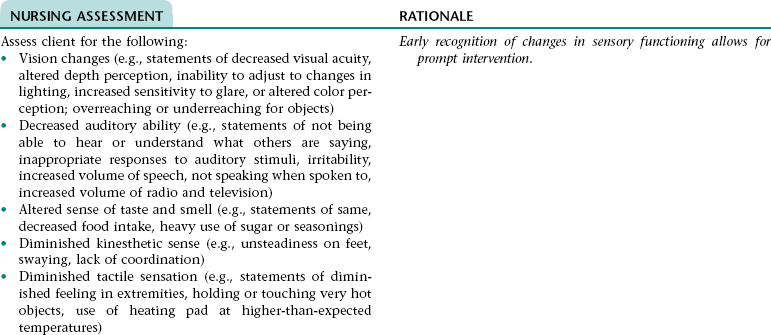
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for signs and symptoms of dyspepsia, gastric fullness, or gas pain (e.g., verbal reports of indigestion, fullness, or gas pain; grimacing; clutching and guarding of abdomen; rubbing epigastric area; restlessness; reluctance to move; frequent eructation; reluctance to eat).
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of dyspepsia, gastric fullness, or gas pain allows for prompt intervention.
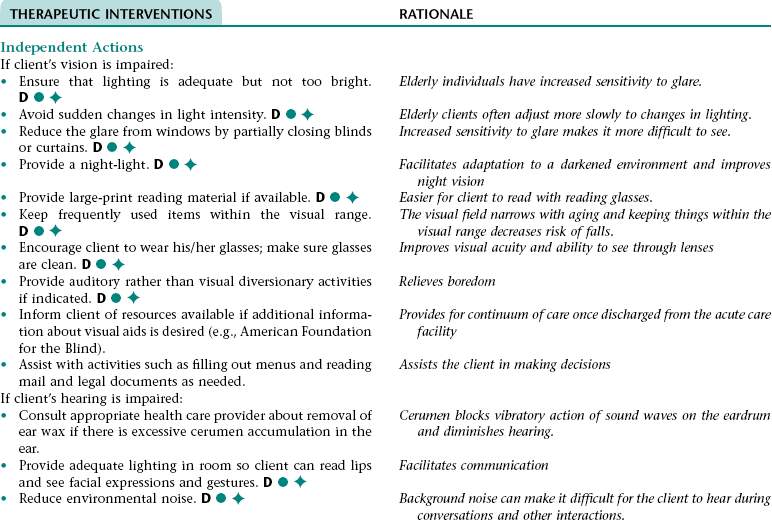
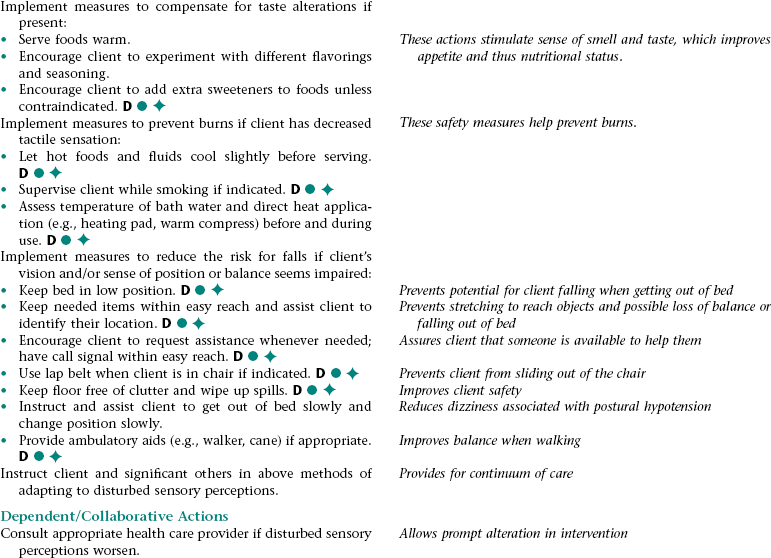
Nursing Diagnosis DISTURBED SENSORY PERCEPTION NDx
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR IMPAIRED SKIN INTEGRITY NDx
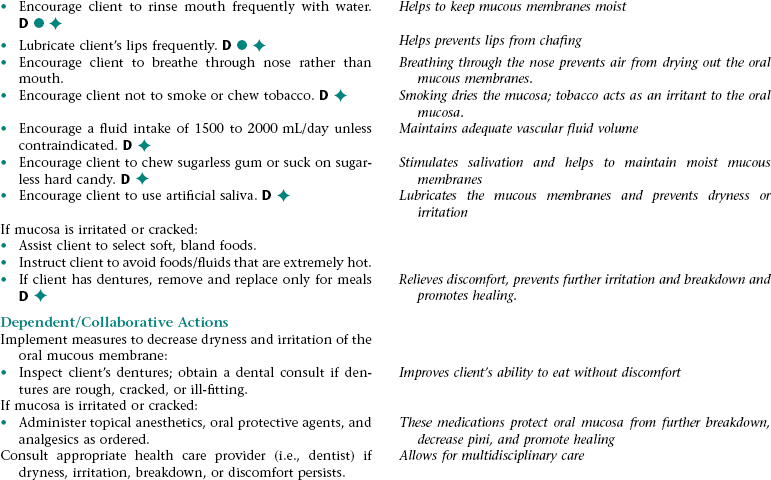
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANE NDx
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess client for dryness, irritation, and breakdown of the oral mucosa.
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of impaired mucous membranes allows for prompt intervention.
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE NDx
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access