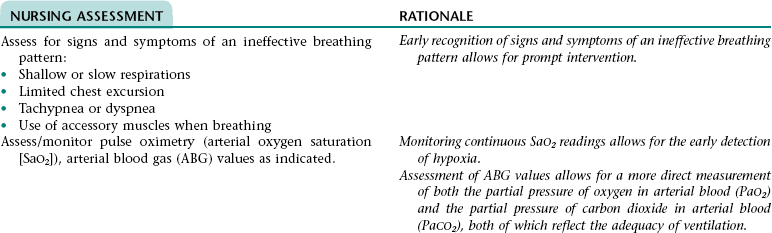
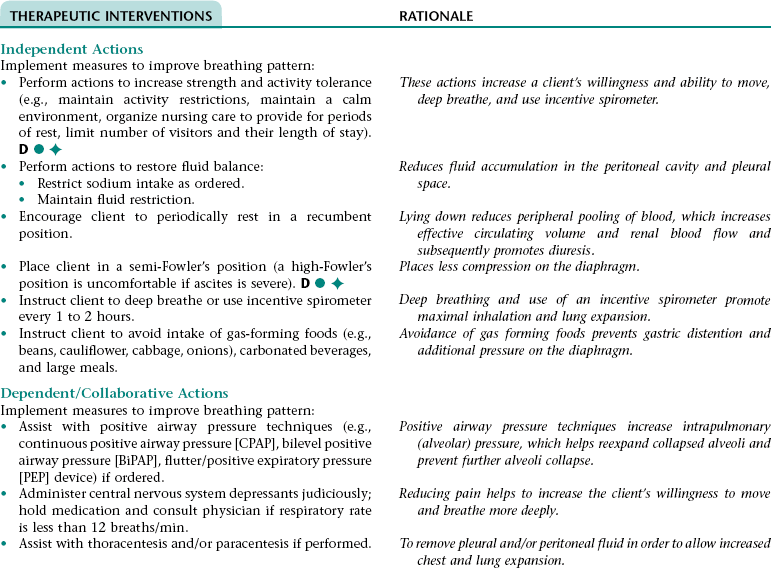
CHAPTER 10 3. Have evidence of normal healing of surgical wound(s) and normal skin integrity around T-tube site 4. Have clear, audible breath sounds throughout lungs 5. Have no signs and symptoms of postoperative complications 6. Demonstrate the ability to appropriately care for T tube and surrounding skin if T tube is present 7. Verbalize an understanding of the rationale for and components of a low- to moderate-fat diet if prescribed 8. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 9. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider, wound care, medications prescribed, and activity level. Definition: Inspiration and/or expiration that does not provide adequate ventilation • Increased rate of respirations associated with fear and anxiety • Decreased rate of respirations associated with the depressant effect of anesthesia and some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics, some antiemetics) • Decreased depth of respirations associated with: • Depressant effect of anesthesia and some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics, some antiemetics) • Reluctance to breathe deeply because of pain • Fear, anxiety, weakness, and fatigue • Restricted chest expansion resulting from positioning and elevation of the diaphragm if abdominal distention is present Definition: An accumulation of pus in any area of the body • Accumulation of drainage in the surgical area and subsequent invasion of the area by microorganisms and neutrophils Definition: Inflammation of the peritoneum Definition: Blockage of bile flow Definition: Absence or deficiency of cognitive information 3. Have no signs and symptoms of complications 4. Verbalize an understanding of ways to reduce the risk for recurrent gallbladder attacks 5. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 6. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider and medications prescribed. For a full, detailed care plan on this topic, go to http://evolve.elsevier.com/Haugen/careplanning/. 1. Have an adequate nutritional intake 2. Perform activities of daily living without extreme fatigue or dyspnea 3. Have a reduction in or resolution of ascites and edema 4. Have no evidence of life-threatening complications 5. Identify ways to prevent further liver damage 6. Verbalize an understanding of the rationale for and components of the recommended diet 7. Identify ways to reduce stress on or trauma to the esophageal blood vessels 8. Identify ways to prevent bleeding 9. Identify ways to reduce the risk of infection 10. Identify ways to relieve pruritus 11. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 12. Identify community resources that can assist with home management and adjustment to lifestyle changes necessary for effective management of cirrhosis 13. Share concerns and feelings about the diagnosis of cirrhosis; prognosis; and effects of the disease process and its treatment on self-concept, lifestyle, and roles 14. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider, medications prescribed, and activity level. Definition: Inspiration and/or expiration that does not provide adequate ventilation • Increased rate of respirations associated with fear and anxiety • Decreased depth of respirations associated with: • Decreased lung compliance (distensibility) resulting from pleural effusion (hepatic hydrothorax) that occurs because of excess fluid volume and passage of ascitic fluid into the pleural space through a probable pressure-related defect in the diaphragm • Restricted chest expansion resulting from positioning and pressure on the diaphragm as a result of ascites • Sodium and water retention associated with an increased serum aldosterone level resulting from: • Inability of the liver to metabolize aldosterone • Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism as a result of decreased renal blood flow (occurs because of a decrease in intravascular volume that results from vasodilation and from third-spacing and sequestration of fluid in the splanchnic system) • Low plasma colloid osmotic pressure associated with hypoalbuminemia (a result of decreased hepatic synthesis of albumin and prolonged inadequate nutrition) DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will experience resolution of fluid and electrolyte imbalance fluid as evidenced by: Definition: Below normal range for serum potassium levels Definition: Below normal range for serum sodium levels Definition: Inadequate intake or insufficient nutrition to meet the body’s metabolic needs • Decreased oral intake associated with dyspepsia, fatigue, dyspnea, dislike of the prescribed diet, and feeling of fullness from ascites • Reduced metabolism and storage of nutrients by the liver associated with a reduction of functional liver tissue • Malabsorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins associated with impaired bile production and flow. • Impaired fat digestion associated with bile flow obstruction • Reflux of gastric contents associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure resulting from ascites • Impaired gastrointestinal functioning associated with venous congestion in the gastrointestinal tract (portal hypertensive gastropathy) • Esophagitis/gastritis associated with the irritant effect of chronic alcohol ingestion on the esophageal and gastric mucosa • Tissue hypoxia associated with anemia resulting from: • Decreased production of red blood cells (RBCs) resulting from a decreased intake and absorption of vitamins and minerals and an inability of the liver to store vitamins and minerals • Excessive RBC destruction resulting from hypersplenism (if venous congestion has resulted in splenomegaly, the spleen will destroy RBCs faster than usual) • Loss of muscle mass, tone, and strength associated with malnutrition and disuse if mobility has been limited for an extended period • Decrease in available energy associated with inability of the liver to metabolize glucose, fats, and proteins properly • Difficulty resting and sleeping associated with dyspnea, discomfort, frequent assessments and treatments, fear, anxiety, and unfamiliar environment NOC OUTCOMES: Cognitive orientation; distorted thought process; neurological status; agitation; sleep level; safety behavior; information processing
Nursing Care of the Client with Disturbances of the Liver, Biliary Tract, and Pancreas
CHOLECYSTECTOMY
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
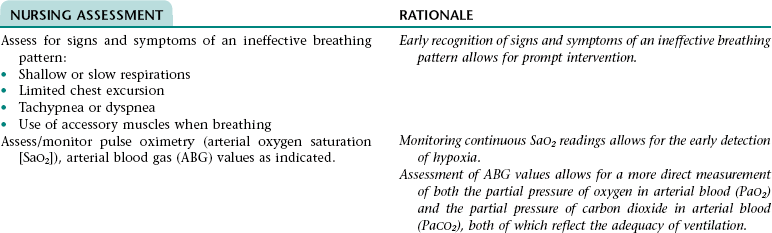
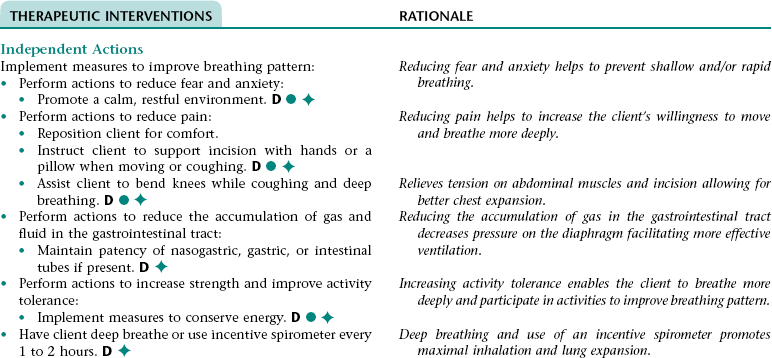
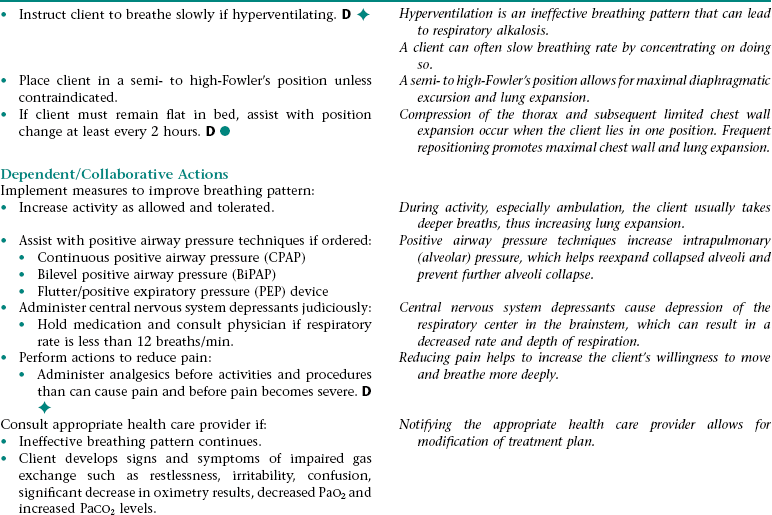
Nursing Diagnosis INEFFECTIVE BREATHING PATTERN NDx
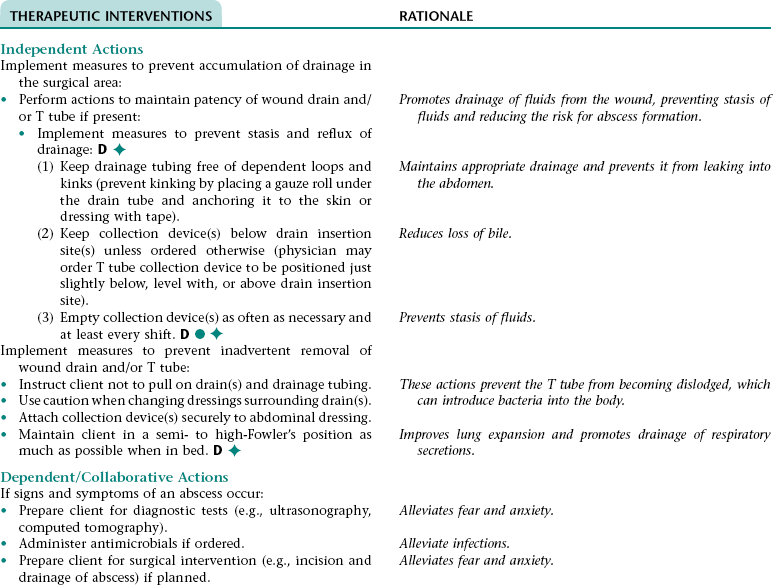
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR ABSCESS FORMATION
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for and report signs and symptoms of an abscess (e.g., increased or more constant abdominal pain, increase in temperature and pulse rate, further increase in WBC count).
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of an abscess allows for prompt intervention.
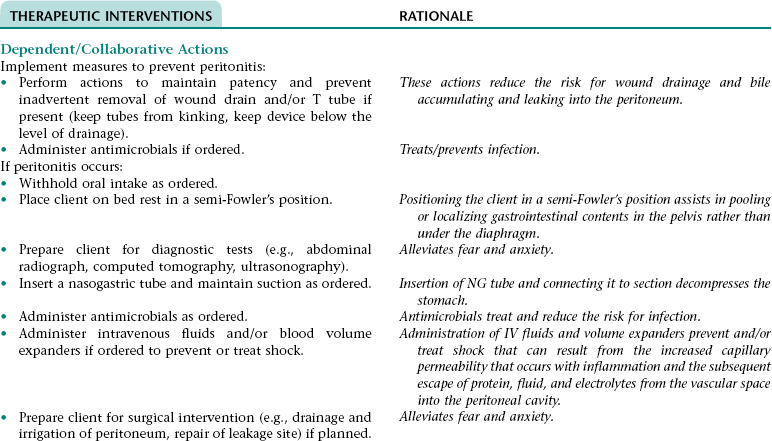
 Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR PERITONITIS
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR PERITONITIS
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for and report signs and symptoms of peritonitis (e.g., increase in severity of abdominal pain; generalized abdominal pain; rebound tenderness; distended, rigid abdomen; increase in temperature; tachycardia; tachypnea; hypotension; nausea; vomiting; continued diminished or absent bowel sounds; WBC count that increases or fails to decline toward normal).
Early recognition of the signs and symptoms of peritonitis allows for prompt intervention.
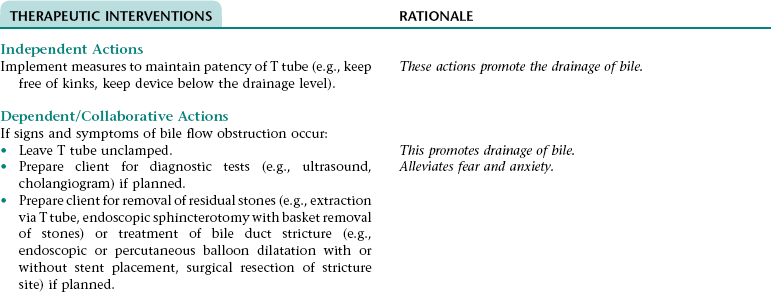
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR CONTINUED OBSTRUCTION OF BILE FLOW
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for and report signs and symptoms of continued bile flow obstruction (e.g., T tube draining more than 1000 mL in 24 hours; a marked increase in T-tube drainage after it has started to decline; persistent pain, nausea, or feeling of fullness when T tube is clamped; jaundice; clay-colored stools; dark amber urine).
Early recognition of the signs and symptoms of bile flow obstruction allows for prompt intervention.
Nursing Diagnosis DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE NDx; INEFFECTIVE FAMILY THERAPEUTIC REGIMEN MANAGEMENT NDx; OR INEFFECTIVE SELF-HEALTH MANAGEMENT* NDx
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
Nursing Diagnosis INEFFECTIVE BREATHING PATTERN NDx
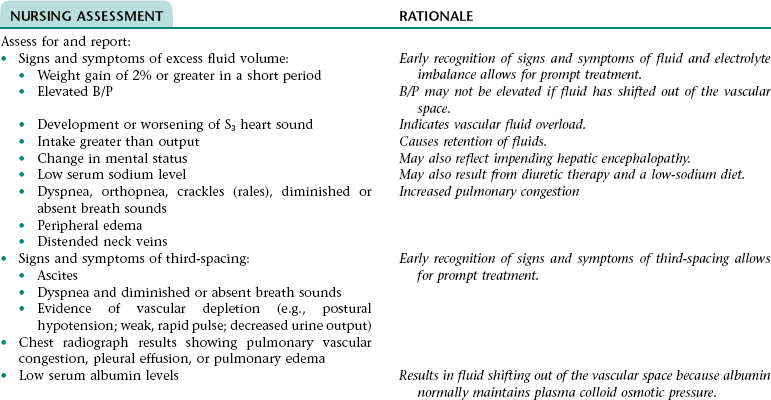
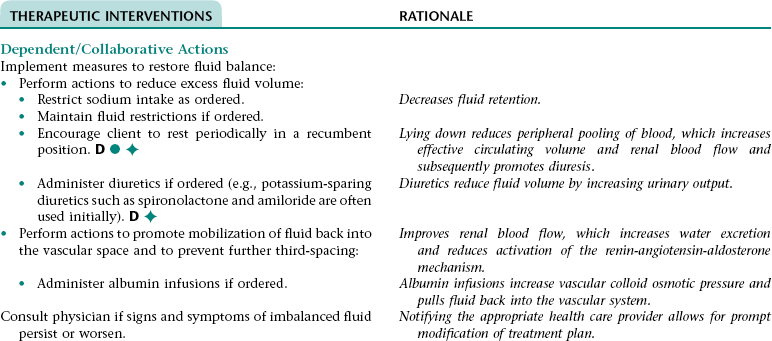
Nursing/Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR EXCESS FLUID VOLUME NDx AND THIRD-SPACING
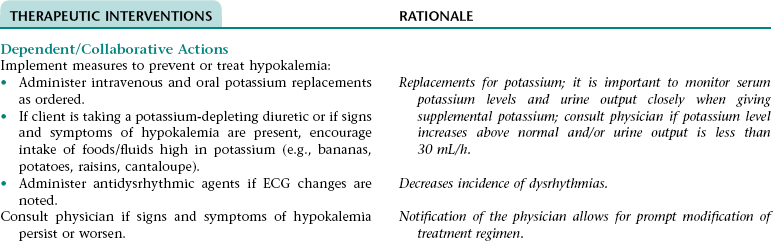
Nursing/Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR HYPOKALEMIA
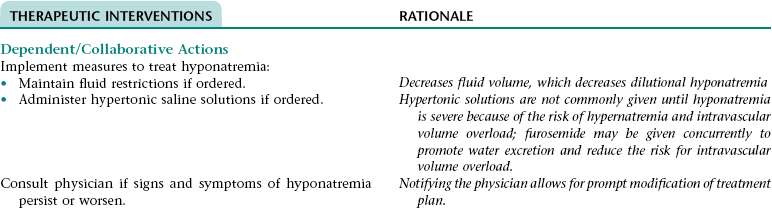
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR HYPONATREMIA
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for and report signs and symptoms of hyponatremia (e.g., nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, lethargy, confusion, weakness, seizures).
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of hyponatremia allows for prompt treatment.
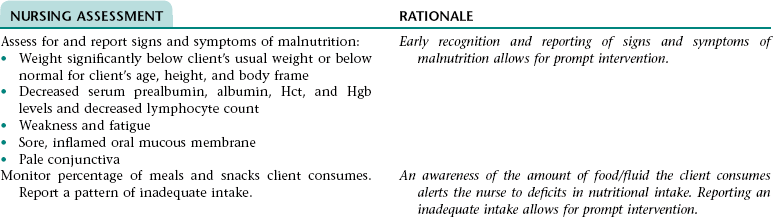
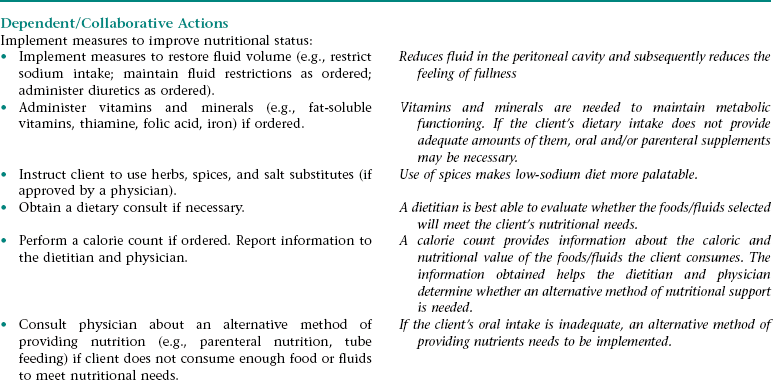
Nursing Diagnosis IMBALANCED NUTRITION: LESS THAN BODY REQUIREMENTS NDx
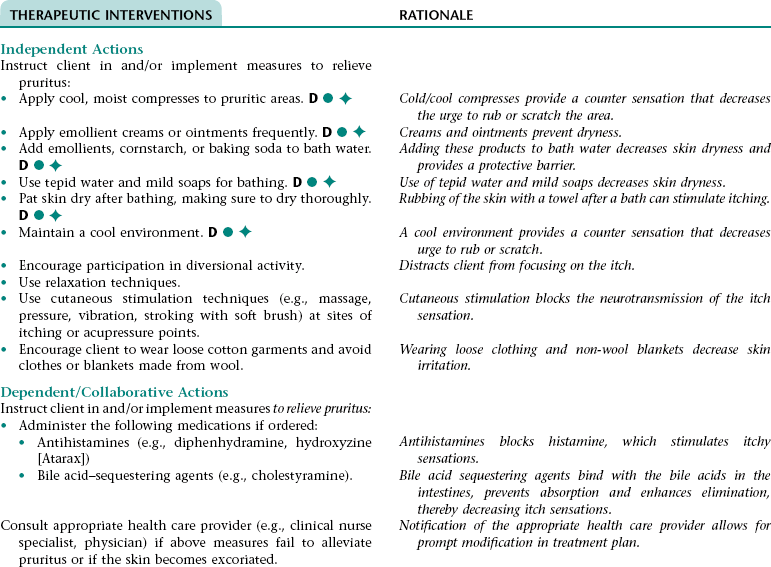
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED COMFORT NDx (PRURITUS)
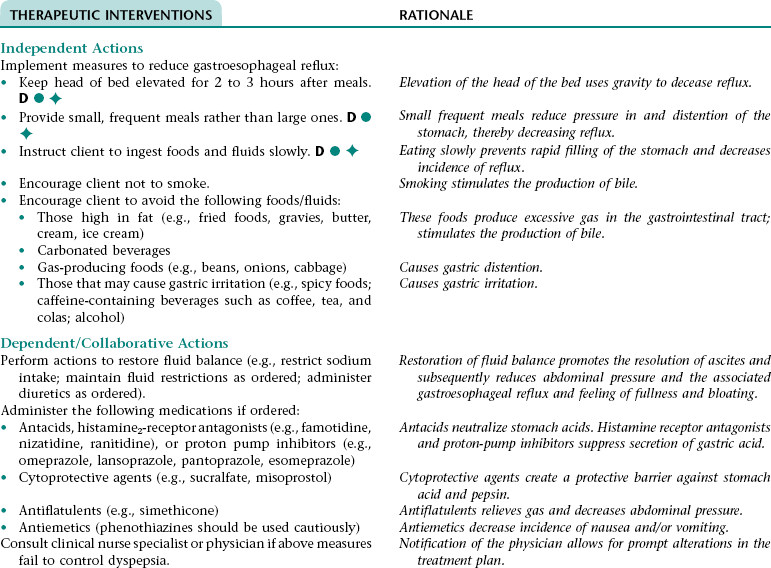
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED COMFORT NDx (DYSPEPSIA)
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess client for signs and symptoms of dyspepsia (e.g., reports of epigastric discomfort, heartburn, nausea, or feeling of fullness or bloating; frequent eructation).
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of dyspepsia allows for prompt intervention.
Assess which foods/fluids contribute to dyspepsia (client usually reports an intolerance of fatty foods).
Helps client determine which foods to avoid.
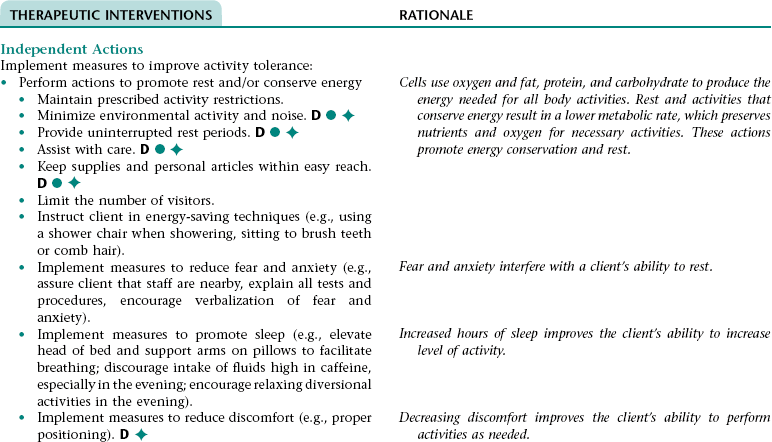
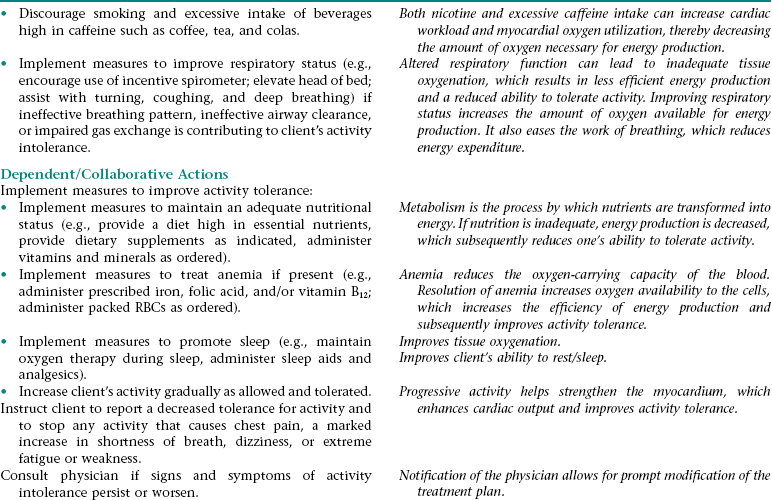
Nursing Diagnosis ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE NDx
Collaborative/Nursing Diagnosis ACUTE AND CHRONIC CONFUSION NDx
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for episodes of disorientation to person, place, and time; episodes of inappropriate behavior; impaired decision-making ability; impaired attention span
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of confusion allows for prompt intervention. ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nursing Care of the Client with Disturbances of the Liver, Biliary Tract, and Pancreas
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access