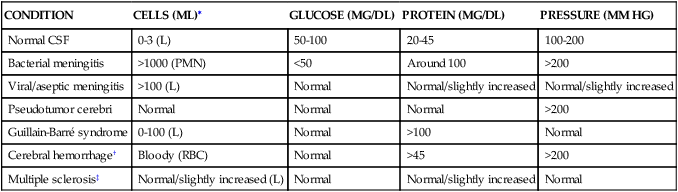
CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; L, lymphocytes; PMN, neutrophils; RBC, red blood cells. ∗Main cell type is in parentheses after number. †Think of subarachnoid hemorrhage, but this pattern may also occur after an intracerebral bleed. ‡On electrophoresis of CSF, look for oligoclonal bands as a result of increased IgG production and an increased level of myelin basic protein in the CSF during active demyelination. Note: Tuberculous and fungal meningitis have low glucose (<50) with increased cells (>100), which are predominantly lymphocytes. In patients with fungal meningitis, a positive India ink preparation equals Cryptococcus neoformans. As many as half of patients have syncope of unknown cause after a standard diagnostic evaluation. ∗The left side is dominant in more than 95% of the population (99% of right-handed people and 60% to 70% of left-handed people).
Neurology
2 Cover all but the left-hand column and describe the classic findings of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis in the following conditions
CONDITION
CELLS (ML)∗
GLUCOSE (MG/DL)
PROTEIN (MG/DL)
PRESSURE (MM HG)
Normal CSF
0-3 (L)
50-100
20-45
100-200
Bacterial meningitis
>1000 (PMN)
<50
Around 100
>200
Viral/aseptic meningitis
>100 (L)
Normal
Normal/slightly increased
Normal/slightly increased
Pseudotumor cerebri
Normal
Normal
Normal
>200
Guillain-Barré syndrome
0-100 (L)
Normal
>100
Normal
Cerebral hemorrhage†
Bloody (RBC)
Normal
>45
>200
Multiple sclerosis‡
Normal/slightly increased (L)
Normal
Normal/slightly increased
Normal
9 What is the most common cause of syncope? What other conditions should you consider?
 Cardiac problems (arrhythmias, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, valvular disease, tamponade). Always check an electrocardiogram (ECG). Further testing with echocardiography or treadmill stress testing can be performed based on the ECG findings and degree of suspicion.
Cardiac problems (arrhythmias, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, valvular disease, tamponade). Always check an electrocardiogram (ECG). Further testing with echocardiography or treadmill stress testing can be performed based on the ECG findings and degree of suspicion.
 Neurologic disorders (e.g., seizures, migraine headache, brain tumor). Consider an electroencephalogram or CT/MRI scan if history suggests seizures or intracranial lesion.
Neurologic disorders (e.g., seizures, migraine headache, brain tumor). Consider an electroencephalogram or CT/MRI scan if history suggests seizures or intracranial lesion.
 Vascular disease (consider transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or carotid stenosis, which can be ruled out with carotid artery ultrasound/duplex scanning, although this is not a common cause of syncope).
Vascular disease (consider transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or carotid stenosis, which can be ruled out with carotid artery ultrasound/duplex scanning, although this is not a common cause of syncope).
 Medication effects (e.g., anticholinergic agents, beta blockers, narcotics, vasodilators, alpha-agonists, antipsychotics).
Medication effects (e.g., anticholinergic agents, beta blockers, narcotics, vasodilators, alpha-agonists, antipsychotics).
10 Cover the right-hand column and localize the neurologic lesion for each of the following symptoms and signs
SYMPTOM/SIGN
AREA
Decreased or no reflexes, fasciculations, atrophy
Lower motor neuron disease (or possibly muscle problem)
Hyperreflexia, clonus, increased muscle tone
Upper motor neuron lesion (cord or brain)
Apathy, inattention, disinhibition, labile affect
Frontal lobes
Broca (motor) aphasia
Dominant frontal lobe∗
Wernicke (sensory) aphasia
Dominant temporal lobe∗
Memory impairment, hyperaggression, hypersexuality
Temporal lobes
Inability to read, write, name, or do math
Dominant parietal lobe∗
Ignoring one side of body, trouble with dressing
Nondominant parietal lobe∗
Visual hallucinations/illusions
Occipital lobes
Cranial nerves III and IV
Midbrain
Cranial nerves V, VI, VII, and VIII
Pons
Cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII
Medulla
Ataxia, dysarthria, nystagmus, intention, tremor, dysmetria, scanning speech
Cerebellum
12 What are the classic differential points between delirium and dementia?
DELIRIUM
DEMENTIA
Onset
Acute and dramatic
Chronic and insidious
Common causes
Illness, toxin, withdrawal
Alzheimer disease, multi-infarct dementia, HIV/AIDS
Reversible
Usually
Usually not
Attention
Poor
Usually unaffected
Arousal level
Fluctuates
Normal
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





