• Familiar objects (coins, keys, paper clip) • Tongue blades (one intact and one broken with pointed and rounded edges) • Tuning forks, 200 to 400 Hz and 500 to 1000 Hz • Test tubes of hot and cold water • Vials of aromatic substances (coffee, orange, peppermint, banana) • Vials of solutions (glucose, salt, lemon or vinegar, quinine) with applicators Assess the neurologic system as the rest of the body is examined. When history and examination findings have not revealed a potential neurologic problem, perform a neurologic screening examination as shown in the box on pp. 218-219, rather than a full neurologic examination. See Chapter 18 for evaluation of muscle tone and strength, because these findings are important for interpreting neurologic system examination findings. The mental status portion of the neurologic system examination can be found in Chapter 3. The following table summarizes the CN examination, and details of examination follow on pp. 220-224. When a sensory or motor loss is suspected, be compulsive about determining the extent of the loss. Procedures for Cranial Nerve Examination Ask patient to close eyes and report if sensation to touch is sharp or dull as you touch each side of face at scalp, cheek, and chin areas, alternately using sharp and rounded edges of tongue blade or paper clip in an unpredictable pattern. Ask patient to report when the stimulus is felt as you stroke same six areas with cotton wisp or brush. Finally, test sensation over buccal mucosa with wooden applicator. Hold card listing tastes in patient’s view. Ask patient to extend tongue. Apply one of four solutions to lateral side of tongue in appropriate taste-bud region. Ask patient to point to taste perceived. Offer patient a sip of water, and repeat with different solution and applicator, testing each side of tongue with each solution. • Accuracy of movement: Finger-to-nose test Position your index finger 40–50 cm from patient. Ask patient to touch his or her nose and your index finger with the index finger of one hand, as shown below. Change location of your index finger several times. Repeat with patient’s other hand. Alternatively ask the patient to close both eyes and touch his or her nose with index finger of each hand while alternating hands and gradually increasing speed.
Neurologic System
Examination
Cranial Nerves I To XII
Cranial Nerve (CN)
Procedure
CN I (olfactory)
Test ability to identify familiar aromatic odors, one naris at a time with eyes closed.
CN II (optic)
Test distance and near vision.
Perform an ophthalmoscopic examination.
Test visual fields by confrontation and extinction of vision.
CN III, CN IV, CN VI (oculomotor, trochlear, abducens)
Test extraocular movement.
Inspect eyelids for drooping.
Inspect pupil size for equality, and direct and consensual response to light and accommodation.
CN V (trigeminal)
Inspect face for muscle atrophy and tremors.
Palpate jaw muscles for tone and strength when patient clenches teeth.
Test superficial pain and touch sensation in each nerve branch.
(Test temperature sensation if findings to pain and touch sensation are unexpected.)
Test corneal reflex.
CN VII (facial)
Inspect symmetry of facial features with various expressions (e.g., smile, frown, puffed cheeks, wrinkled forehead).
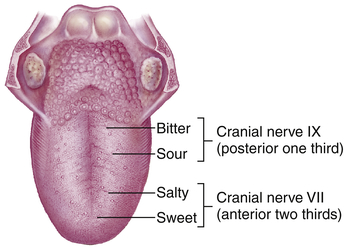
Test ability to identify sweet, salty, sour, and bitter tastes on each side of tongue.
CN VIII (acoustic)
Test sense of hearing with whisper screening tests or by audiometry.
Compare bone and air conduction of sound.
Test for lateralization of sound.
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
Test taste sensation (see CN VII).
Test gag reflex and ability to swallow.
CN X (vagus)
Inspect palate and uvula for symmetry with speech sounds and gag reflex.
Observe for swallowing difficulty.
Evaluate quality of guttural speech sounds (presence of nasal or hoarse quality to voice).
CN XI (spinal accessory)
Test trapezius muscle strength (shrug shoulders against resistance).
Test sternocleidomastoid muscle strength (turn head to each side against resistance).
CN XII (hypoglossal)
Inspect tongue in mouth and while protruded for symmetry, tremors, atrophy.
Inspect tongue movement toward nose and chin.
Test tongue strength with index finger when tongue is pressed against cheek.
Evaluate quality of lingual speech sounds (l, t, d, n).
Technique
Findings
Assess olfactory nerve (CN I)
Ask patient to close eyes. Occlude one naris, hold vial (using least irritating aromatic substances first [e.g., orange or peppermint extract]) under nose, and ask patient to breathe deeply and identify odor. Allow patient to breathe comfortably, then occlude other naris and repeat with different odor. Continue, alternating two or three odors.
EXPECTED: Able to perceive and usually identify odor on each side.
UNEXPECTED: Anosmia, loss of smell or inability to discriminate odors.
Assess optic nerve (CN II)
See tests for near and distance visual acuity and visual fields in Chapter 8.
EXPECTED: Vision 20/20 without or with lenses each eye; full visual fields.
Assess oculomotor, trochlear, abducens nerves (CN III, CN IV, CN VI)
See tests for six cardinal points of gaze, pupil size, shape, response to light and accommodation, and opening of upper eyelids in Chapter 8.
EXPECTED: Equal pupil size, equal and consensual response to light and accommodation, symmetric eye movements in all six cardinal points of gaze.
UNEXPECTED: Absence of lateral gaze. Absence of any expected finding, ptosis.
Assess trigeminal nerve (CN V)
EXPECTED: Symmetric tone.
UNEXPECTED: Muscle atrophy, deviation of jaw to one side, or fasciculations.
EXPECTED: Symmetric discrimination of sensations in each location to all stimuli.
UNEXPECTED: Impaired sensation with identified distribution. If impaired, use test tubes of hot and cold water to evaluate temperature sensation.
EXPECTED: Symmetric blink reflex. May be diminished or absent if patient wears contact lenses.
Assess facial nerve (CN VII)
EXPECTED: Facial symmetry.
UNEXPECTED: Tics, unusual facial movements, or asymmetry of expression (flattened nasolabial fold, lower eyelid sagging, side of mouth drooping).
UNEXPECTED: Difficulty with enunciation of b, m, and p (labial sounds).
EXPECTED: Able to identify sweet, salty, sour, bitter taste bilaterally when placed in appropriate taste-bud region.
Assess acoustic nerve (CN VIII)
EXPECTED: Adequate hearing bilaterally.
Assess glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Assess vagus nerve (CN X)
EXPECTED: Soft palate rises with uvula in midline.
UNEXPECTED: Failure of soft palate to rise or uvula deviates from midline.
EXPECTED: Upward movement of palate and contraction of pharyngeal muscles, with uvula in midline.
UNEXPECTED: Drooping or absence of arch on either side of soft palate; uvula deviates from midline.
EXPECTED: Water easily swallowed.
UNEXPECTED: Retrograde passage of water through nose.
UNEXPECTED: Hoarseness, nasal quality, or difficulty with guttural sounds.
Assess spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
See Chapters 7 and 18 for evaluations of size, shape, strength of trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
EXPECTED: Symmetric size, shape, and strength.
Assess hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
EXPECTED: Tongue midline, symmetric size.
UNEXPECTED: Fasciculations, asymmetry, atrophy, or deviation from midline.
EXPECTED: Able to perform most tongue movements.
EXPECTED: Steady, firm pressure.
UNEXPECTED: Problems with l, t, d, or n (lingual sounds).
Proprioception and Cerebellar Function
Evaluate coordination and fine motor skills
Have patient sit.
EXPECTED: Smooth execution, maintaining rhythm with increasing speed.
UNEXPECTED: Stiff, slowed, nonrhythmic, or jerky clonic movements.
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



Neurologic System
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access