Chapter 22 Note: Thousands of additional practice questions are available on the enclosed companion CD. 1. At what age does Freud’s phallic stage of psychosexual development compare with Erikson’s psychosocial phase of initiative versus guilt? 2. Which relationship is of most concern to the nurse because of its importance in the formation of the personality? 3. A nurse concludes that a client is using displacement. Which behavior has the nurse identified? 1. Ignoring unpleasant aspects of reality 2. Resisting any demands made by others 3. Using imaginative activity to escape reality 4. Directing pent-up emotions to other than the primary source 4. In the process of development the individual strives to maintain, protect, and enhance the integrity of the self. The nurse determines that this usually is accomplished through the use of: 5. A client diagnosed with major depression tells a nurse, “No matter what I do, everything turns out bad.” The nurse concludes that this is an example of: 1. using a cognitive distortion. 2. seeking sympathy from the nurse. 3. regressing to an earlier developmental level. 6. A male college student who is smaller than average and unable to participate in sports becomes the life of the party and a stylish dresser. What defense mechanism should the nurse determine that the client is using? 7. A staff member tells a nurse that an older client gets irritable when asked to assist with activities of daily living. On what general information about older adults should the nurse base a response? 8. The parents of a toddler who was recently diagnosed with moderate retardation discuss their child’s future independent functioning. What should the nurse conclude? 1. They accept the child’s diagnosis. 2. Denial is being used as a defense. 3. They want to explore their child’s limitations. 4. Intellectualization helps them put the diagnosis into perspective. 9. On which generally accepted concept of personality development should a nurse base care? 1. By 2 years of age the personality is firmly set. 2. The personality is capable of modification throughout life. 3. The capacity for personality change decreases rapidly after adolescence. 4. By the end of the first 6 years of life the personality has reached its adult parameters. 10. A 6-year-old child is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Considering the child’s cognitive developmental level, which explanation of the illness is most appropriate? 1. “Diabetes is caused by not having any insulin in your body.” 2. “Diabetes will require you to take insulin shots for the rest of your life.” 3. “You will be taught how to give yourself insulin now that you have diabetes.” 4. “Taking insulin for your diabetes is like getting new batteries for your superhero toys.” 11. Which individual is coping with issues concerning dependence versus independence? 1. “My smoking pot probably caused the leukemia.” 2. “I’m going to do my best to fight this terrible disease.” 3. “Now I can’t go to the prom because I have this stupid illness.” 4. “I know I got sick because I’ve been causing a lot of problems at home.” 5. “This illness is serious, but with treatment I think I will have a chance to get better.” 13. A person mowing the lawn is badly disfigured by the lawn mower blade. According to Erikson’s theory, which age will demonstrate the greatest risk of longer-term psychological effects? 14. A nurse is interviewing an 8-year-old girl who was admitted to the pediatric unit. Which statement by the child needs to be explored? 1. “Wow! This place has bright colors.” 2. “Is my mother allowed to visit me tonight?” 3. “Those boys are so cute. I hope their room is next to mine!” 4. “I am scared about being here. Can you stay with me awhile?” 15. A nurse must consider a child’s cognitive level of development when providing preoperative teaching. At which stage of Piaget’s cognitive theory should the nurse anticipate a child will experience the greatest fear of surgery? 16. After a child’s visit to a health care provider, a parent tells the nurse, “I am very upset. An antidepressant was prescribed for my child.” What is the nurse’s best response? 1. “Tell me more about what’s bothering you.” 2. “Weren’t you told why your child needs an antidepressant?” 3. “You need to speak with the health care provider about your concern.” 4. “Are you sure it’s an antidepressant and not a drug for attention deficit disorder?” 17. A nurse greets a client who had been experiencing delusions of persecution and auditory hallucinations by saying, “Good evening. How are you?” The client, who has been referring to himself as “man,” answers, “The man is bad.” Of what is this an example? 18. A client with a diagnosis of borderline personality disorder has negative feelings toward the other clients on the unit and considers them all to be “bad.” Which defense was the client using when this statement was made? 19. In response to a question posed during a group meeting, the nurse explains that the superego is that part of the self that says: 20. Incidents of child molestation often are revealed years later when the victim is an adult. Which defense mechanism reflects this situation? 21. A client with diabetes mellitus is able to discuss in detail the diabetic metabolic process while eating a piece of chocolate cake. What defense mechanism does the nurse identify when evaluating this behavior? 22. An older adult tells the nurse, “I regret many of the choices I have made during my life.” Which of Erikson’s developmental conflicts does the nurse identify that the client has probably failed to accomplish? 1. Teaching the client relaxation exercises to diminish stress 2. Exploring with the client past experiences that caused distress 3. Providing the client with mastery experiences to boost self-esteem 4. Encouraging the client to replace negative thoughts with positive thoughts 5. Helping the client to modify the belief that anything less than perfection is unacceptable 24. A psychiatric unit uses a behavioral approach to determine a client’s level of privileges. Which factor should a nurse use to determine an increase in privileges? 1. Statements that the depression is lifting 2. An improvement in short-term memory 3. Performing hygiene activities independently 25. A nurse is teaching a class about child abuse. What defense mechanism most often used by the physically abusive individual should the nurse include? 26. A nurse is planning to teach a client about self-care. What level of anxiety will best enhance the client’s learning abilities? 27. A client is scheduled for several diagnostic studies. Which behavior best indicates to the nurse that the client has received adequate preparation? 1. Requests that the tests be reexplained 2. Checks the appointment card repeatedly 3. Arrives early and waits quietly to be called for the tests 28. Before discharge of an anxious client, the nurse should teach the family that anxiety can be recognized as: 2. fears specifically related to the total environment. 3. consciously motivated actions, thoughts, and wishes. 4. a pattern of emotional and behavioral responses to stress. 29. What should a nurse conclude that a client is doing when using the defense mechanism of sublimation? 31. A health care provider orders “Restraints prn” for a client who has a history of violent behavior. What is the nurse’s responsibility concerning this order? 1. Ask that the order indicate the type of restraint. 2. Recognize that prn orders for restraints are unacceptable. 3. Implement the restraint order when the client begins to act out. 4. Ensure that the entire staff is aware of the order for the restraint. 32. A client on the psychiatric unit asks a nurse about psychiatric advance directives (PADs). What information should form the basis of the nurse’s response? 1. The appointment of a surrogate decision maker is unnecessary. 2. A client is permitted to dictate what treatments will be given during future hospitalizations. 3. The need for involuntary admissions is eliminated when a client is a threat to self or others. 4. A client is allowed to consent or refuse potential psychiatric treatments if a future incapacitating mental health crisis occurs. 33. Which statement best describes the practice of psychiatric nursing? 1. Helps people with present or potential mental health problems 2. Ensures clients’ legal and ethical rights by being a client advocate 3. Focuses interpersonal skills on people with physical or emotional problems 4. Acts in a therapeutic way with people who are diagnosed as having a mental disorder 34. A physician is admitted to the psychiatric unit of a community hospital. The client, who was restless, loud, aggressive, and resistive during the admission procedure, states, “I will take my own blood pressure.” What is the nurse’s most therapeutic response? 1. “Right now you are just another client.” 2. “If you would rather, I’m sure you will do it correctly.” 3. “I will get the attendants to assist me if you do not cooperate.” 4. “I am sorry, but I cannot allow that because I must take your blood pressure.” 35. What is the most difficult initial task when developing a nurse-client relationship? 1. Remaining therapeutic and professional 2. Being able to understand and accept a client’s behavior 3. Developing an awareness of self and the professional role in the relationship 4. Accepting responsibility for identifying and evaluating the real needs of a client 36. A parent of a 13-year-old adolescent who was recently diagnosed with Hodgkin disease tells a nurse, “I don’t want my child to know the diagnosis.” How should the nurse respond? 1. “It is best if your child knows the diagnosis.” 2. “Did you know the cure rate for Hodgkin disease is high?” 3. “Would you like someone with Hodgkin disease to talk with you?” 4. “Let’s talk about your feeling regarding your child’s diagnosis.” 37. A male nurse is caring for a client. The client states, “You know, I’ve never had a male nurse before.” What is the nurse’s best reply? 1. “Does it bother you to have a male nurse?” 2. “How do you feel about having a male nurse?” 3. “There aren’t many male nurses. We are a minority.” 4. “You sound upset. I will get a female nurse to care for you.” 38. A nurse reminds a client that it is time for group therapy. The client responds by yelling at the nurse, “You are always telling me what to do, just like my father!” What defense mechanism is the client using? 39. What is the most important tool a nurse brings to the therapeutic nurse-client relationship? 40. A Latino client with schizophrenia is admitted to a mental health unit in an aggravated and disheveled state after failing to take prescribed medications for the last 5 days. When developing a plan of care that incorporates the client’s cultural background, the nurse gives priority to: 1. socioeconomic considerations regarding hospitalization. 2. the meaning and attention the client places on the future. 3. the client’s need to control care to ensure desired outcomes. 4. inclusion of the family in the plan of care with the client’s permission. 1. “I cry all the time, I am so sad.” 2. “Since I retired I have been so depressed.” 3. “I would like to end it all with sleeping pills.” 4. “Voices say it is okay for me to kill all prostitutes.” 42. A nurse encourages a client to join a self-help group after being discharged from a mental health facility. What is the purpose of having people work in a group? 43. As depression begins to lift, a client is asked to join a small discussion group that meets every evening on the unit. The client is reluctant to join because “I have nothing to talk about.” What is the best response by the nurse? 1. “Maybe tomorrow you will feel more like talking.” 2. “Could you start off by talking about your family?” 3. “A person like you has a great deal to offer the group.” 4. “You feel you will not be accepted unless you have something to say?” 44. During a group meeting a client tells everyone, “I am afraid of my impending discharge from the hospital.” What is the most appropriate response by the nurse facilitator? 1. “You ought to be happy that you’re leaving.” 2. “Maybe you’re not ready to be discharged yet.” 3. “Maybe others in the group have similar feelings that they would share.” 4. “How many in the group feel that this member is ready to be discharged?” 45. At a group therapy session a client tearfully tells the other members, “I just lost my job this week.” What is the nurse leader’s most appropriate response? 1. Ask the client to consider the reasons this may have occurred. 2. Quietly observe how the group responds to the client’s statement. 3. Gently suggest that the client check the help-wanted advertisements in the local paper. 4. Request that the group help the client reflect on how the dismissal may have been prevented. 46. A 44-year-old client is unable to function since her husband asked for a divorce 2 weeks ago. She is brought to the crisis intervention center by a friend. What type of crisis reflects this situation? 47. A client with the diagnosis of paranoid schizophrenia throws a chair across the room and starts screaming at the other clients. Several of these clients have frightened expressions, one starts to cry, and another begins to pace. A nurse removes the agitated client from the room. What should the nurse remaining in the room do next? 1. Continue the unit’s activities as if nothing happened. 2. Arrange a unit meeting to discuss what just happened. 3. Refocus clients’ negative comments to more positive topics. 4. Have a private talk with the clients who cried or started to pace. 48. A client with a history of violence is becoming increasingly agitated. Which nursing intervention will most likely increase the risk of acting out behavior? 49. A client is diagnosed with a borderline personality disorder. What is a realistic initial intervention for this client? 1. Establish clear boundaries. 2. Explore job possibilities with the nurse. 3. Initiate discussion of feelings of being victimized. 4. Spend one hour twice a day discussing problems with the nurse. 50. A nurse is aware that a co-worker’s mother died 16 months ago. The co-worker cries every time someone says the word “mother” or if the mother’s name is mentioned. What does the nurse conclude about this behavior? 1. It is an expected response. 2. Most people cry when their mother dies. 3. The co-worker may need help with grieving. 51. A nurse educator is leading a class on supporting middle-aged adults who are experiencing midlife crisis. What should the nurse include as the most significant factor in the development of this type of crisis? 1. The perception of their life situation 2. Many role changes that alter their experiences at this time 3. The anticipation of negative changes associated with old age 4. Lack of support from family members who are busy with their own lives 52. What is the priority goal when planning care for a client in crisis? 1. Referring the client for occupational therapy 2. Restoring the client’s psychologic equilibrium 3. Scheduling the client for follow-up counseling 1. Identify the client’s support systems. 2. Explore the client’s psychotic thoughts. 3. Reinforce the client’s current self-image. 4. Encourage the client to talk about the situation. 5. Suggest that the client explore personal sexual attitudes. 55. Which is the most important assessment data for a nurse to gather from the client in crisis? 2. Any significant physical health data 3. A history of emotional problems in the family 4. The client’s perception of the circumstances surrounding the crisis 56. An extremely anxious client enters a crisis center and asks a nurse for help. Which response best reflects the nurse’s role in crisis intervention? 1. “Tell me what you have done to help yourself.” 2. “I will be here for you to help you figure things out.” 3. “I understand that in the past you have had problems.” 4. “Tell me about the things that are bothering you the most.” 1. ______ Stabilize the client. 2. ______ Intervene immediately. 3. ______ Encourage self-reliance. 4. ______ Use the available resources. 58. A child in the first grade is murdered, and counseling is planned for the other children in the school. What should a nurse identify first before assessing a child’s response to a crisis? 1. Developmental level of the child 2. Quality of the child’s peer relationships 3. Child’s perception of the crisis situation 59. What is an initial client objective in relation to anger management? 1. Expressing remorse over aggressive actions 2. Taking responsibility for the hostile behavior 3. Developing alternative methods to release feelings 4. Teaching others how to avoid triggering the angry behavior 60. A nurse leads an assertiveness training program for a group of clients. Which client statement demonstrates that the treatment has been effective? 1. “I know I should put the needs of others before mine.” 2. “I won’t stand for it, so I told my boss he’s a jerk and to get off my back.” 3. “It annoys me when people call me ‘Dearie,’ so I told him not to do it anymore.” 4. “It is easier for me to agree up front and then just do enough so that no one notices.” 61. A nurse is working with a married woman who has come to the emergency department several times with injuries that appear to be related to domestic violence. While talking with the nurse manager, a nurse expresses disgust that the woman returns to the same situation. What is the nurse manager’s best response? 1. “She must not have the financial resources to leave her husband.” 2. “Most woman attempt to leave about six times before they are able to do so.” 3. “There is nothing the staff can do because people are free to choose their own life.” 4. “These women should be told how foolish they are to remain in their current situation.” 62. What is the most important information a nurse should teach to prevent relapse in a client with a psychiatric illness? 1. Develop close support systems 2. Create a stress-free environment 3. Refrain from activities that cause anxiety 63. A depressed client has been prescribed a tricyclic antidepressant. How long should the nurse inform the client it will take before noticing a significant change in the depression? 64. A nurse is teaching clients about dietary restrictions when taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). What response does the nurse tell them to anticipate if they do not follow these restrictions? 65. A client is receiving lithium. What is an important nursing intervention while this medication is being administered? 1. Restrict the client’s daily sodium intake. 2. Test the client’s urine specific gravity weekly. 3. Monitor the client’s drug blood level regularly. 4. Withhold the client’s other medications for several days. 66. A client in the hyperactive phase of a mood disorder, bipolar type, is receiving lithium. A nurse identifies that the client’s lithium blood level is 1.8 mEq/L. What is the most appropriate nursing action? 1. Continue the usual dose of lithium and note any adverse reactions. 2. Discontinue the drug until the lithium serum level drops to 0.5 mEq/L. 3. Ask the health care provider to increase the dose of lithium because the blood lithium level is too low. 4. Hold the drug and notify the health care provider immediately because the blood lithium level may be toxic. 67. A nurse administers an antipsychotic to a client. For which common manageable side effect should the nurse assess the client? 68. What medication should the nurse expect to administer to actively reverse the overdose sedative effects of benzodiazepines? 69. A nurse is caring for a client who abruptly withdrew from barbiturate use. What should the nurse anticipate that the client may experience? 70. Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) 100 mg PO per hour is prescribed for a client with a Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment (CIWA) score of 25. The client had 300 mg in 3 hours and is still displaying acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms. What is the next nursing action? 1. Inform the client that the limit of chlordiazepoxide has been reached. 2. Administer chlordiazepoxide as indicated by the client’s CIWA score. 3. Request a prescription for another medication to replace the chlordiazepoxide. 4. Inform the health care provider that the maximum dose of chlordiazepoxide has been reached. 3. There is more interest shown in unit activities. 4. The client reports that the hallucinations have stopped. 5. The client performs activities of daily living independently. 72. A client with a diagnosis of schizophrenia is discharged from the hospital. At home the client forgets to take the medication, is unable to function, and must be rehospitalized. What medication may be prescribed that can be administered on an outpatient basis every 2 to 3 weeks? 73. A client is scheduled for a 6-week electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) treatment program. What intervention is important during the 6-week course of treatment? 1. Provision of tyramine-free meals 2. Avoidance of exposure to the sun 3. Maintenance of a steady sodium intake 74. Imipramine (Tofranil), 75 mg three times per day, is prescribed for a client. What nursing action is appropriate when administering this medication? 1. Tell the client that barbiturates and steroids will not be prescribed. 2. Warn the client not to eat cheese, fermenting products, and chicken liver. 3. Monitor the client for increased tolerance and report if the dosage is no longer effective. 4. Have the client checked for increased intraocular pressure and teach about symptoms of glaucoma. 75. A health care provider prescribes haloperidol (Haldol) for a client. What should the nurse teach the client to avoid while taking this medication? 76. A nurse is evaluating the medication regimens of a group of clients to determine whether the therapeutic level has been achieved. For which medication should the nurse review the client’s serum blood level? 77. A client with depression is to receive fluoxetine (Prozac). What precaution should the nurse consider when initiating treatment with this drug? 1. It must be given with milk and crackers to avoid hyperacidity and discomfort. 2. Eating cheese or pickled herring or drinking wine may cause a hypertensive crisis. 3. Blood levels may not be sufficient to cause noticeable improvement for 2 to 4 weeks. 4. Blood levels should be obtained weekly for 3 months to monitor for appropriate levels. 78. A client with type 1 diabetes is diagnosed with a psychosis and is to receive haloperidol (Haldol). Which response should a nurse anticipate with this drug combination? 79. In conjunction with which classification of medication are trihexyphenidyl, biperiden (Akineton), or benztropine (Cogentin) often prescribed? 80. A nurse is educating a client who is taking clozapine (Clozaril) for paranoid schizophrenia. What should the nurse emphasize about the side effects of clozapine? 81. A nurse is teaching clients in a medication education group about side effects of medications. Which drug will cause a heightened skin reaction to sunlight? 82. A primary nurse observes that a client has become jaundiced after 2 weeks of antipsychotic drug therapy. The primary nurse continues to administer the antipsychotic until the health care provider can be consulted. What does the nurse manager conclude concerning this situation? 1. Jaundice is sufficient reason to discontinue the antipsychotic. 2. The blood level of antipsychotics must be maintained once established. 3. Jaundice is a benign side effect of antipsychotics that has little significance. 4. The prescribed dose for the antipsychotic should have been reduced by the nurse. 84. A client with chronic undifferentiated schizophrenia is receiving an antipsychotic medication. For which potentially irreversible extrapyramidal side effect should a nurse monitor the client? 85. A monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) is prescribed. What should the nurse include in the teaching plan about what to avoid when taking this drug? 86. A client has been receiving escitalopram (Lexapro) for treatment of a major depressive episode. On the fifth day of therapy the client refuses the medication stating, “It doesn’t help, so what’s the use of taking it?” What is the nurse’s best response? 1. “Sometimes it takes 1 to 4 weeks to see an improvement.” 2. “It takes 6 to 8 weeks for this medication to have an effect.” 3. “I’ll talk to your health care provider about increasing the dose. That may help.” 4. “You should have felt a response by now. I’ll notify your health care provider immediately.” 87. A client is receiving doxepin (Silenor). For which most dangerous side effect of tricyclic antidepressants should a nurse monitor the client? 88. A client with schizophrenia is actively psychotic, and a new medication regimen is prescribed. A student nurse asks the primary nurse, “Which of the prescribed medications will be most helpful for reducing psychotic signs and symptoms?” What should the nurse respond? 89. A client with a psychosis is receiving olanzapine (Zydis). What is important for a nurse to consider when administering this drug? 1. It can be given intramuscularly. 2. A special tyramine-free diet is required. 3. It dissolves instantly after oral administration.
Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing
Review Questions with Answers and Rationales
 Denotes alternate format question.
Denotes alternate format question.
Foundations of Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing
 12. A 17-year-old teenager is diagnosed with leukemia. Which statements by the teenager reflect Piaget’s cognitive processes associated with adolescence? Select all that apply.
12. A 17-year-old teenager is diagnosed with leukemia. Which statements by the teenager reflect Piaget’s cognitive processes associated with adolescence? Select all that apply.
 23. A client states, “I get down on myself when I make a mistake.” When a cognitive therapy approach is used, which nursing interventions are most appropriate? Select all that apply.
23. A client states, “I get down on myself when I make a mistake.” When a cognitive therapy approach is used, which nursing interventions are most appropriate? Select all that apply.
The Practice of Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing
 30. Among members of the nursing team, which functions are registered nurses legally permitted to perform in a mental health hospital? Select all that apply.
30. Among members of the nursing team, which functions are registered nurses legally permitted to perform in a mental health hospital? Select all that apply.
 41. A family member brings a relative to the local community hospital because the relative “has been acting strange.” Which statements meet involuntary hospitalization criteria? Select all that apply.
41. A family member brings a relative to the local community hospital because the relative “has been acting strange.” Which statements meet involuntary hospitalization criteria? Select all that apply.
 53. An adult who has been in a gay relationship for 3 years arrives at the emergency department in a near panic state. The client states, “My partner just left me. I am a wreck.” What should the nurse do to help the client cope with this loss? Select all that apply.
53. An adult who has been in a gay relationship for 3 years arrives at the emergency department in a near panic state. The client states, “My partner just left me. I am a wreck.” What should the nurse do to help the client cope with this loss? Select all that apply.
 54. Which approaches should a nurse use during crisis intervention? Select all that apply.
54. Which approaches should a nurse use during crisis intervention? Select all that apply.
 57. When assisting clients to cope with a crisis, the health care provider should follow the principles of intervention. Place the following interventions in order of their priority.
57. When assisting clients to cope with a crisis, the health care provider should follow the principles of intervention. Place the following interventions in order of their priority.
 71. A client with schizophrenia who has type II (negative) symptoms is prescribed risperidone (Risperdal). Which outcomes indicate that the medication has minimized these symptoms? Select all that apply.
71. A client with schizophrenia who has type II (negative) symptoms is prescribed risperidone (Risperdal). Which outcomes indicate that the medication has minimized these symptoms? Select all that apply.
 83. A client has been receiving fluphenazine for several months. For which side effects should the nurse assess the client? Select all that apply.
83. A client has been receiving fluphenazine for several months. For which side effects should the nurse assess the client? Select all that apply.
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



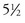 years
years