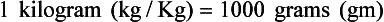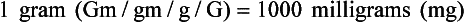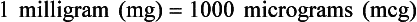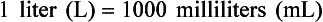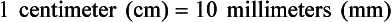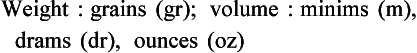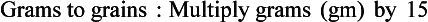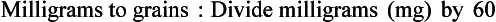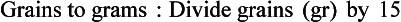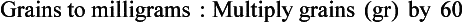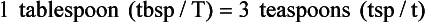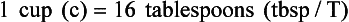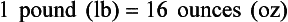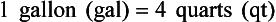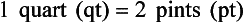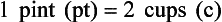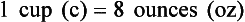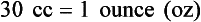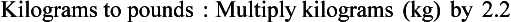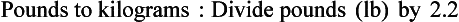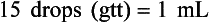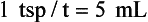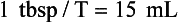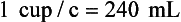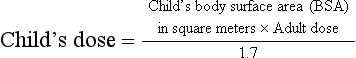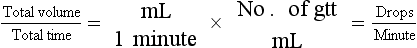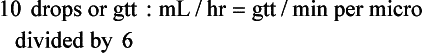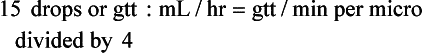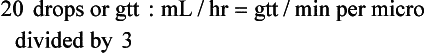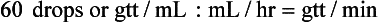Chapter 2 Clayton BC, Stock YN: Basic pharmacology for nurses, ed 15, St. Louis, 2010, Mosby. Skidmore-Roth L: Mosby’s 2012 nursing drug reference, ed 25, St. Louis, 2012, Mosby. Workman ML et al: Understanding pharmacology: essentials for medication safety, St. Louis, 2011, Mosby. Absorption The passage of drug molecules into the blood Abuse A maladaptive pattern of drug usage Allergic reaction An unpredictable response to a drug Biotransformation Drug metabolism from an active to an inactive state Classification Indicates the effect on a body system Distribution How a drug is absorbed into the body tissues Duration Length of time in the body Excretion The exit of the drug from the body Form Determines the routes of administration Genetic difference The makeup by which a person’s genetic background may affect a drug’s actions in the body Half-life Time of elimination from body Idiosyncratic Drugs that are overactive or underactive Interactions When one drug modifies the actions of another Medication A substance used in the treatment, cure, relief, or prevention of disease Onset First response of drug in the body Peak Highest level of drug in the body Pharmacokinetics The study of how drugs enter the body, reach their site of action, are metabolized, and exit the body Physiologic variables The normal difference between men and women and differences in weight may affect the metabolism of a drug Plateau Concentration of scheduled doses Side effects Unintended secondary effects Standards Guidelines for purity and quality of a drug Therapeutic Beneficial level of drug Tolerance Low response to a drug Toxic Not beneficial or lethal level of drug
Medications
Calculations and Administration
Calculations
Common Drug Terminology
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Medications: Calculations and Administration
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue