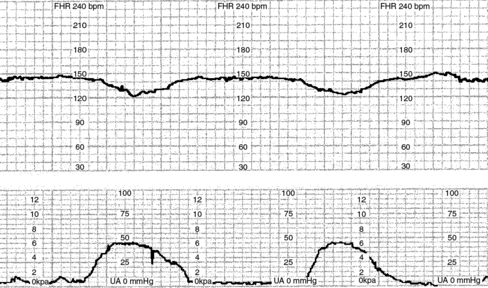
1. What is important to note in the initial assessment? 2. You find a boggy fundus during your assessment. What corrective measures can be instituted? 3. The patient complains of pain and discomfort in her perineal area. How will you respond? 4. The nurse reviews the hospital security guidelines with T.N. The nurse points out that her baby has a special identification bracelet that matches a bracelet worn by T.N. and reviews other security procedures. Which statement by T.N. indicates a need for more teaching? a. “If I have a question about someone’s identity, I can ask about it.” b. “If someone comes to take my baby for an exam, that person will usually carry my baby to the exam room.” c. “Nurses on this unit all wear the same purple uniforms.” d. “Each staff member who takes my baby somewhere should have a picture identification badge.” 5. An hour after admission, you recheck T.N.’s perineal pad and find that there is a very small amount of drainage on the pad. What will you do next? a. Ask T.N. to change her perineal pad. b. Check her perineal pad again in 1 hour. c. Check the pad underneath T.N.’s buttocks. 6. That evening, the NAP assesses T.N.’s vital signs. Which vital signs would be of concern at this time? 8. T.N.’s condition is stable and you prepare to provide patient teaching. What patient teaching is vital after delivery? 9. T.N. tells you she must go back to work in 6 weeks and is not sure she can continue breastfeeding. What options are available to her? 1. What are the two most important questions to ask to determine possible pregnancy? 2. You ask whether she has ever been pregnant, and she tells you she has never been pregnant. How would you record this information? 3. What additional information would be needed to complete the TPAL record? 4. It is important to complete the intake interview. What categories will you address with P.M.? 5. Do any of these vital signs cause concern? What should you do? 6. P.M. tells you that the date of her last menstrual period (LMP) was February 2. How would you calculate her due date? What is her due date? 7. What is the significance of a gynecoid pelvis? 8. What specimens are important to obtain when the pelvic examination is done? 9. A psychological assessment is done to determine P.M.’s feelings and attitudes regarding her pregnancy. How do attitudes, beliefs, and feelings affect pregnancy? 10. P.M. asks you whether there are any foods that she should avoid while pregnant. She lists some of her favorite foods. Which foods, if any, should she avoid eating while she is pregnant? (Select all that apply.) 11. As the nurse, you know that assessment and teaching are vital in the prenatal period to ensure a positive outcome. What information is important to include at every visit and at specific times during the pregnancy? 12. After her examination, P.M. states that she is worried because her sister had an ectopic pregnancy and had to have surgery. She asks you, “What are the signs of an ectopic pregnancy?” Which of these are correct? (Select all that apply.) a. Fullness and tenderness in her abdomen, near the ovaries b. Pain, either unilateral, bilateral, or diffuse over the abdomen d. Dark red or brown vaginal bleeding 13. P.M. asks the nurse about what should be reported to her doctor. List at least six of the “danger signs of pregnancy.” 14. Changes in the body caused by pregnancy include relaxation of joints, alteration to center of gravity, faintness, and discomforts. These changes can lead to problems with coordination and balance. In teaching P.M. about safety during pregnancy, what will you include in your teaching? 15. P.M. asks, “Is a vaginal exam done at every visit?” What is your response? Explain your answer. 1. What three initial questions will you ask, and why? 2. D.H. has contractions 2 to 3 minutes apart and lasting 45 seconds. It is her third pregnancy (gravida 3, para 2002). Her bag of waters is intact at this time. She states that her due date is 2 days away. You determine that it is appropriate to ask for further information before a vaginal exam is done. What information do you need? 3. What assessment should you make to gain further information from D.H.? 4. Upon examination, D.H. is 80% effaced and 4 cm dilated. The fetal heart rate (FHR) is 150 beats/min and regular. She is admitted to a labor and delivery room on the unit. What nursing measures should be done at this time? 5. As part of your assessment, you review the fetal heart strip pictured below. What will you do?
Maternal and Obstetric Disorders
Scenario
Scenario
Case Study Progress
Case Study Progress
Scenario
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Maternal and Obstetric Disorders
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
