Chapter 24 Management of quality in dialysis care
What is the medicare improvements for patients and providers act?
The composite rate is a fixed rate that Medicare pays for each dialysis treatment. This fixed or composite rate covers all services rendered, including supplies, equipment, and medications associated with the dialysis treatment. Since the composite rate was established, many new treatment-related pharmaceuticals have become part of the standard dialysis treatment. These additional drugs, such as erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, vitamin D, and iron, were not included in the original composite rate and have been billed for separately, over and above the composite rate. Additionally, many new laboratory studies and supplies did not exist when the composite rate went into effect, so these too have been billed separately. With the increase in Medicare use for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) services, MIPPA has charged the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to develop a new bundled payment that will include the additional drugs and laboratory services. This new rule will also align dialysis facility payments based on quality performance measures. The new payment system is being phased in over a period of three years, beginning in January 2011.
What is quality assessment and performance improvement?
Quality Assessment and Performance Improvement (QAPI) is the name given by CMS to an internal program that ESRD facilities must develop to promote continuous improvement and outcomes (Box 24-1).
Box 24-1 V626 QAPI Condition Statement
From The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Interpretive Guidance, April 2008.
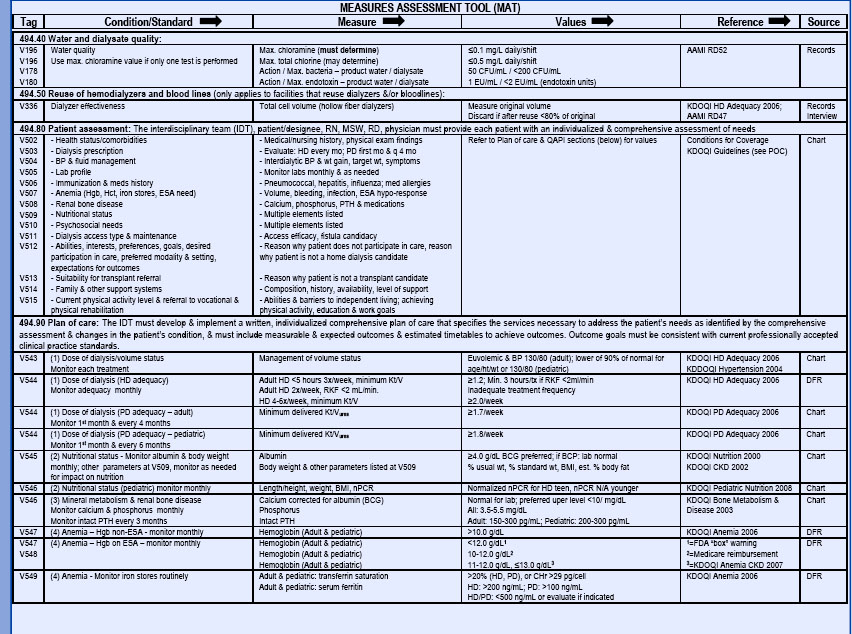
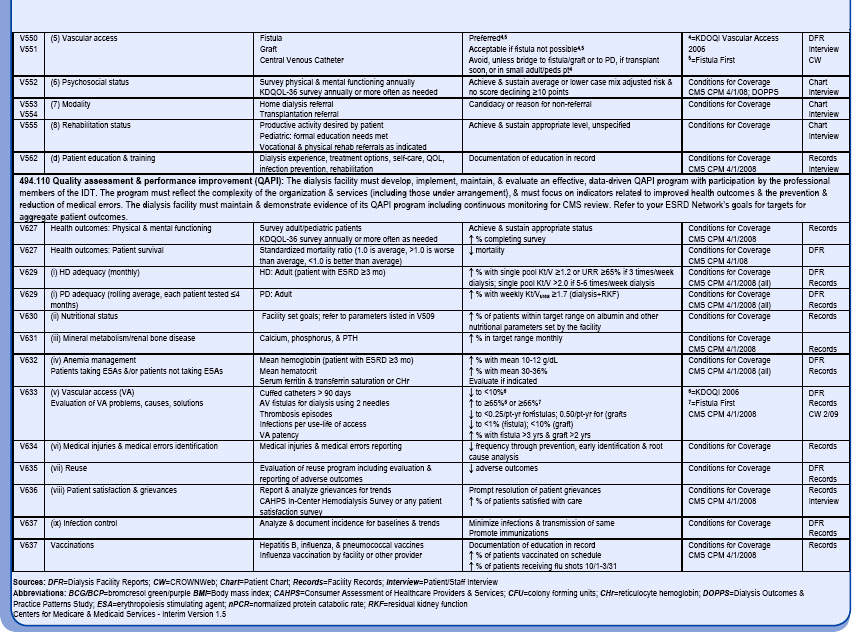
Quality of care issues to address include, but are not limited to, dialysis adequacy, dialyzer reuse program, nutritional status, anemia management, vascular access, bone disease management, infection control, medical injuries and errors, patient education, patient survival, vaccinations, and physical and mental functioning. Facilities are expected to prioritize those areas affecting patient safety. The Measures Assessment Tool is a reference list of acceptable standards and values for clinical and quality outcomes (Table 24-1). CMS requires that all facilities have a written plan describing their QAPI program. Facilities are also required to constantly monitor their performance and to make performance improvements as needed using quality indicators or performance measures. Action plans must be prioritized and action that results in performance improvement must be taken.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree