Magnesium
QUICK LOOK AT THE CHAPTER AHEAD
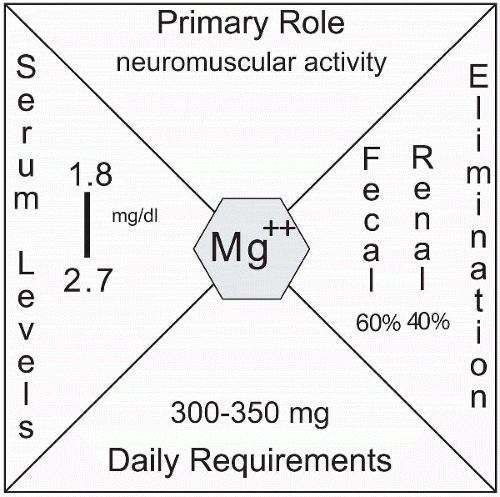
After potassium, magnesium is the second most prevalent cation in the intracellular fluid. The normal concentration of magnesium is 1.8 to 2.7 mEq/L. A well-balanced diet supplies the necessary daily requirement (300-350 mg) for the body. In this chapter we discuss the function, regulation, and balance of magnesium in the body.
After potassium, magnesium is the second most prevalent cation in the intracellular fluid. The normal concentration of magnesium is 1.8 to 2.7 mEq/L with very little found in the extracellular fluid and approximately 60% located in the bones. Magnesium is similar to calcium in that it is found either ionized in a physiologically active form (approximately two-thirds) or bound, primarily with albumin, and considered physiologically inactive (one-third).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree