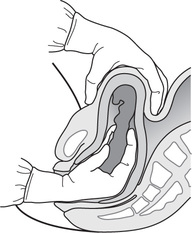
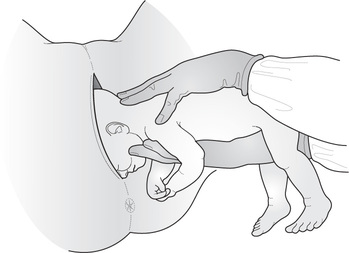
Mackenrodt’s ligaments transverse or cardinal ligaments supporting uterus in pelvic cavity. macro- prefix meaning ‘large’. macroscopic discernible with naked eye. macrosomia large baby, birthweight above 97th centile for gestation or over 4–4.5 kg at term. malaise feeling of general discomfort and illness. malar pertaining to malar bone of face or adjacent area. malformation congenital or acquired anatomical abnormality or deformity. malnutrition defective quantity or quality of nutrition, causing deficiency syndromes. Malpighian body glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule of kidney. Malström vacuum extractor See vacuum extractor. maltose sugar (disaccharide) formed when starch is hydrolysed by amylase. mammary pertaining to breasts. mandelic acid ketoacid used as urinary antiseptic in nephritis, pyelitis and cystitis. mandible bone forming lower jaw. manipulation using hands, e.g. to change position of fetus. manometer instrument used to measure pressure or tension of liquids or gases. See sphygmomanometer. mask of pregnancy See chloasma. McRobert’s manoeuvre manoeuvre to rotate angle of symphysis pubis anteriorly, in which mother brings knees up to chest, in order to release impacted fetal shoulders in shoulder dystocia. See also appendix 4. measles highly infectious notifiable viral disease; rubeola or morbilli. See immunisation.
M
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access