(Apo-Labetalol (Epivir, Epivir-HBV, Heptovir Do not confuse Epivir with Combivir, or lamivudine with lamotrigine. Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance. (Apo-Lamotrigine Do not confuse Lamictal with Lamisil or Lomotil, or lamotrigine with labetalol or lamivudine.
L
labetalol
![]() , Normodyne
, Normodyne ![]() , Trandate)
, Trandate)
lamivudine
![]() )
)
Indications/routes/dosage
HIV infection
Dosage in renal impairment
Creatinine Clearance
Dosage HIV
Dosage Hepatitis B
30–49 ml/min
150 mg once a day
100 mg first dose, then 50 mg once a day
15–29 ml/min
150 mg first dose, then 100 mg once a day
100 mg first dose, then 25 mg once a day
5–14 ml/min
150 mg first dose, then 50 mg once a day
35 mg first dose, then 15 mg once a day
Less than 5 ml/min
50 mg first dose, then 25 mg once a day
35 mg first dose, then 10 mg once a day
lamotrigine
![]() , Lamictal, Lamictal ODT, Lamictal XR, Novo-Lamotrigine
, Lamictal, Lamictal ODT, Lamictal XR, Novo-Lamotrigine ![]() )
)
L
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 classification
classification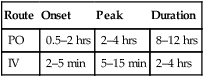
 classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification

