11 Joints or articulations
Fibrous joints
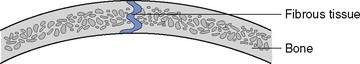
One type of fibrous joint (Fig. 11.1) occurs where the margins of two bones meet and dovetail accurately into one another, separated only by a thin band of fibrous tissue. Joints such as these, which do not normally permit movement, are found between the bones of the cranium and are called sutures. In the infant at birth, there is a definite line of fibrous tissue between two adjoining bones, which allows the edges to glide over one another, enabling the head to be moulded to ease its passage through the birth canal. Other fibrous joints occur where the roots of the teeth articulate with the upper and lower jaws and where there is an interosseous ligament, as in the tibiofibular joint.
Cartilaginous joints
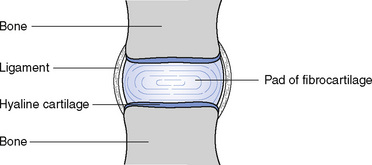
A cartilaginous joint (Fig. 11.2) occurs where the two bony surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage and are connected by a pad of fibrocartilage and by ligaments, which do not form a complete capsule round the joint. A limited degree of movement is possible because the cartilaginous pad can be compressed. The joints between the bodies of the vertebrae and between the manubrium and the body of the sternum are cartilaginous joints.
Synovial joints
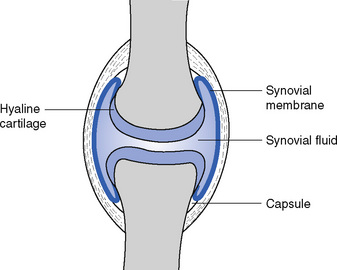
A synovial joint (Fig. 11.3) consists of two or more bones, the ends of which are covered with articular hyaline cartilage. There is a joint cavity, containing synovial fluid, which nourishes the avascular articular cartilage, and the joint is completely surrounded by a fibrous capsule, lined with synovial membrane, which lines the whole of the interior of the joint with the exception of the bone ends, menisci and discs. The bones are also connected by several ligaments, and some movement is always possible in a synovial joint even though it may be limited, as in the gliding movement between the adjoining metacarpal bones.
Types of synovial joint
The synovial joints are divided into several classes according to the type of movement that occurs:
Joint movements
Joint movements are of three kinds: gliding, angular and circular:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree