Chapter 23 *A transition syllable or vowel may be added to or deleted from the word parts to make the combining form. The careers in diagnostic imaging include workers with a broad range of interests, abilities, and training (Box 23-1). The career opportunities in this area include radiography and related occupations (Table 23-1). The radiology department of most health care facilities provides additional radiography procedures, such as monitoring of the heart (electrocardiography) and the brain (electroencephalography). TABLE 23-1 Imaging Career Educational Cost and Earnings *(2009-2010) http://www.uams.edu/chrp/imaging/.
Imaging Careers
 Define at least seven terms relating to careers in medical imaging.
Define at least seven terms relating to careers in medical imaging.
 Specify the role of selected diagnostic medical health care workers, including personal characteristics, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
Specify the role of selected diagnostic medical health care workers, including personal characteristics, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
 Discuss three important developments in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Discuss three important developments in the field of diagnostic imaging.
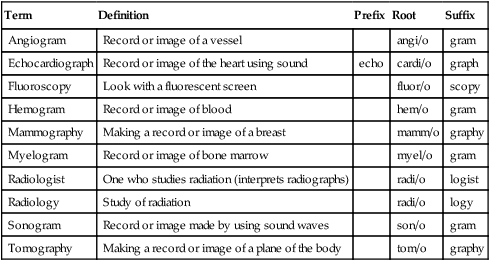
Term
Definition
Prefix
Root
Suffix
Angiogram
Record or image of a vessel
angi/o
gram
Echocardiograph
Record or image of the heart using sound
echo
cardi/o
graph
Fluoroscopy
Look with a fluorescent screen
fluor/o
scopy
Hemogram
Record or image of blood
hem/o
gram
Mammography
Making a record or image of a breast
mamm/o
graphy
Myelogram
Record or image of bone marrow
myel/o
gram
Radiologist
One who studies radiation (interprets radiographs)
radi/o
logist
Radiology
Study of radiation
radi/o
logy
Sonogram
Record or image made by using sound waves
son/o
gram
Tomography
Making a record or image of a plane of the body
tom/o
graphy
Careers
Career
Educational Cost*
Earnings†
Radiologist assistant
Radiologist assistant; University of Arkansas for medical sciences (UAMS);
Tuition (in state) $12,980
Books and supplies $732
Technology fee $176
Student health fee $374
Program fee $150
Graduation fee $58
Median annual salary: Little Rock, Ark.—$47,590
Imaging Careers
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access













