iatrogenic caused by treatment. ICSI See intracytoplasmic sperm injection. ideology science of development of ideas; body of ideas characteristic of individual or social unit. ileocaecal valve valve at junction of the ileum and the caecum. ileum last part of small intestine, terminating at caecum. ilium upper broad part of innominate bone. imaging production of diagnostic images, e.g. radiography, ultrasonography, scintigraphy. immature not mature, insufficiently developed. Immunisation Schedule For Children From Birth To Age 18 Years impacted driven into, wedged, lodged in narrow strait, e.g. impacted shoulder presentation. implant introduction into body tissues of drugs or tissue. impregnate 1. to saturate or instil. 2. to render pregnant. incompatibility state of being incompatible, applied to blood or chemicals, etc. incomplete abortion See abortion.
I
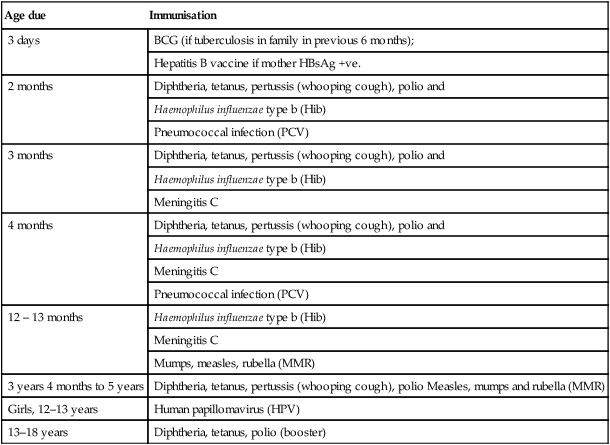
Age due
Immunisation
3 days
BCG (if tuberculosis in family in previous 6 months);
Hepatitis B vaccine if mother HBsAg +ve.
2 months
Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), polio and
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
Pneumococcal infection (PCV)
3 months
Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), polio and
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
Meningitis C
4 months
Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), polio and
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
Meningitis C
Pneumococcal infection (PCV)
12 – 13 months
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
Meningitis C
Mumps, measles, rubella (MMR)
3 years 4 months to 5 years
Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), polio Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR)
Girls, 12–13 years
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
13–18 years
Diphtheria, tetanus, polio (booster)
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
