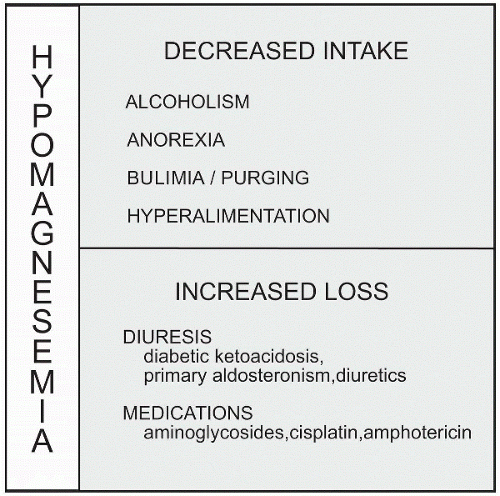
Hypomagnesmia
 Hypomagnesemia is a condition that results in a magnesium blood level of <1.5 mEq/L, but many patients do not experience symptoms until the serum level reaches 1.0 mEq/L.
Hypomagnesemia is a condition that results in a magnesium blood level of <1.5 mEq/L, but many patients do not experience symptoms until the serum level reaches 1.0 mEq/L.alcohol use also causes an increased loss through a high urine output or emesis. Anorexic patients suffer from multiple electrolyte imbalances, including hypomagnesemia. Patients who require long-term intravenous therapy during extended hospitalizations or hyperalimentation that are not supplemented with magnesium may suffer from hypomagnesemia.
Table 25-1 Causes of Hypomagnesemia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
such as the thiazide or loop diuretics, results in an increased loss of fluid and therefore an increased loss and exchange of electrolytes, including magnesium. Patients suffering from serious burns or wounds also lose magnesium through the injured area. The use of certain antibiotics such as cyclosporine, amphotericin B, and aminoglycoside antibiotics may contribute to the loss of magnesium through increased urinary excretion. Cisplatin, used in chemotherapy, or digitalis and insulin are other commonly used drugs that affect the magnesium level.
 Magnesium is lost through the renal system and affects anyone suffering from excessive diuresis.
Magnesium is lost through the renal system and affects anyone suffering from excessive diuresis. Depleting the intracellular level of magnesium leaves the cell weak, contributing to weakened skeletal muscles and hyperirritable nerves and muscles. Hypomagnesemia + hypokalemia + hypocalcemia = neuromuscular problems and cardiac dysrhythmias.
Depleting the intracellular level of magnesium leaves the cell weak, contributing to weakened skeletal muscles and hyperirritable nerves and muscles. Hypomagnesemia + hypokalemia + hypocalcemia = neuromuscular problems and cardiac dysrhythmias.Table 25-2 Manifestations of Hypomagnesemia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
 Compared with hypermagnesemia, where the muscles become weak, in hypomagnesemia the muscles become hyperactive, developing tremors, twitching, spasticity, and hyperactive deep tendon reflexes.
Compared with hypermagnesemia, where the muscles become weak, in hypomagnesemia the muscles become hyperactive, developing tremors, twitching, spasticity, and hyperactive deep tendon reflexes.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree