10 Haematology, oncology and immunology
Haematology: anatomy and physiology
The haematology system consists of the blood and the bone marrow.
Haematopoiesis
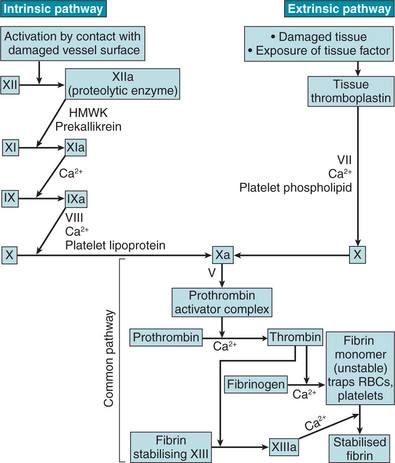
Clotting factors
| I | Fibrinogen |
| II | Prothrombin |
| III | Thromboplastin (tissue factor) |
| IV | Calcium ions |
| V | Proaccelerin |
| VI | Proconvertin |
| VII | Antihaemophilic factor |
| VIII | Plasma thromboplastin component |
| IX | Stuart-Prower factor |
| X | Plasma thromboplastin antecedent |
| XI | Hageman factor |
| XII | Fibrin stabilising factor |
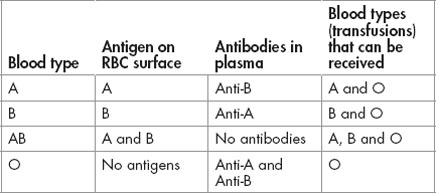
Haematology disorders
Anaemia
Decreased circulating red blood cells (RBC).
Types
 Pernicious
Pernicious• Decreased intrinsic factor and production of hydrochloric acid (required for vitamin B12 absorption)
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
 Circulating thrombi activate fibrinolysis, which causes microthrombi to break down, leading to haemorrhage.
Circulating thrombi activate fibrinolysis, which causes microthrombi to break down, leading to haemorrhage.Signs and symptoms
 Abnormal bleeding within a significant past history, e.g. bleeding from GI tract and IV/injection sites
Abnormal bleeding within a significant past history, e.g. bleeding from GI tract and IV/injection sitesHaemophilia
A genetic (X-linked recessive) bleeding disorder due to a deficiency of clotting factors.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access