C, Capsules; DT, disintegrating tablets; I, injection; L, liquid; OS, oral suspension; T, tablets. Hormones can be local or general: • Local hormones have specific local effects (e.g., acetylcholine, which is secreted at parasympathetic and skeletal nerve endings). • General hormones are mostly secreted by specific endocrine glands (e.g., epinephrine/norepinephrine are secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to sympathetic stimulation), transported in the blood to all parts of the body, causing many different reactions. Altered cell permeability, which causes a change in protein structure of the receptor, usually opening or closing a channel for one or more ions. The movement of these ions causes the effect of the hormone. Activation of intracellular enzymes immediately inside the cell membrane (e.g., hormone combines with receptor that then becomes the activated enzyme adenyl cyclase, which causes formation of cAMP). • Endocrine gland oversecretes. • Hormone exerts more and more of its effect. • Target organ performs its function. • Too much function in turn feeds back to endocrine gland to decrease secretory rate. • Adrenocorticotropin (corticotropin) • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) (TSH) • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) • Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) releasing thyroid-stimulating hormone • Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) releasing adrenocorticotropin • Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) releasing growth hormone and growth hormone inhibitory hormone (GHIH) (same as somatostatin) • Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) releasing the two gonadotropic hormones LH and FSH • Prolactin inhibitory factor (PIF) causing inhibition of prolactin and prolactin-releasing factor
H
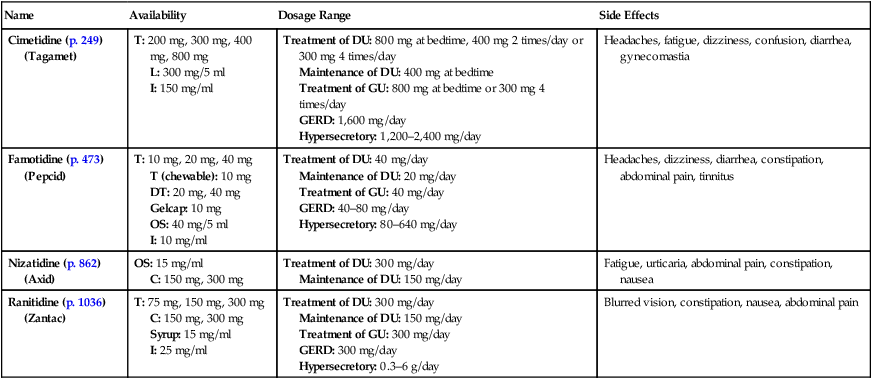
Name
Availability
Dosage Range
Side Effects
Cimetidine (p. 249) (Tagamet)
T: 200 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg
L: 300 mg/5 ml
I: 150 mg/ml
Treatment of DU: 800 mg at bedtime, 400 mg 2 times/day or 300 mg 4 times/day
Maintenance of DU: 400 mg at bedtime
Treatment of GU: 800 mg at bedtime or 300 mg 4 times/day
GERD: 1,600 mg/day
Hypersecretory: 1,200–2,400 mg/day
Headaches, fatigue, dizziness, confusion, diarrhea, gynecomastia
Famotidine (p. 473) (Pepcid)
T: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg
T (chewable): 10 mg
DT: 20 mg, 40 mg
Gelcap: 10 mg
OS: 40 mg/5 ml
I: 10 mg/ml
Treatment of DU: 40 mg/day
Maintenance of DU: 20 mg/day
Treatment of GU: 40 mg/day
GERD: 40–80 mg/day
Hypersecretory: 80–640 mg/day
Headaches, dizziness, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, tinnitus
Nizatidine (p. 862) (Axid)
OS: 15 mg/ml
C: 150 mg, 300 mg
Treatment of DU: 300 mg/day
Maintenance of DU: 150 mg/day
Fatigue, urticaria, abdominal pain, constipation, nausea
Ranitidine (p. 1036) (Zantac)
T: 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg
C: 150 mg, 300 mg
Syrup: 15 mg/ml
I: 25 mg/ml
Treatment of DU: 300 mg/day
Maintenance of DU: 150 mg/day
Treatment of GU: 300 mg/day
GERD: 300 mg/day
Hypersecretory: 0.3–6 g/day
Blurred vision, constipation, nausea, abdominal pain
Name
Availability
Side Effects
Ferrous fumarate (p. 486) (Femiron, Feostat)
T: 63 mg, 200 mg, 324 mg
Constipation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain/cramps
Ferrous gluconate (p. 486) (Fergon)
T: 240 mg, 325 mg
Same as ferrous fumarate
Ferrous sulfate (p. 486) (Fer-In-Sol)
T: 325 mg
Liquid: 300 mg/5 ml
E: 220 mg/5 ml
D: 75 mg/ml
Same as ferrous fumarate
Ferrous sulfate exsiccated (Slow-Fe)
T: 200 mg
Same as ferrous fumarate
Related
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


