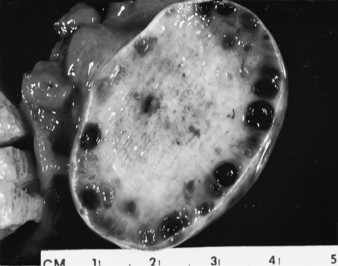
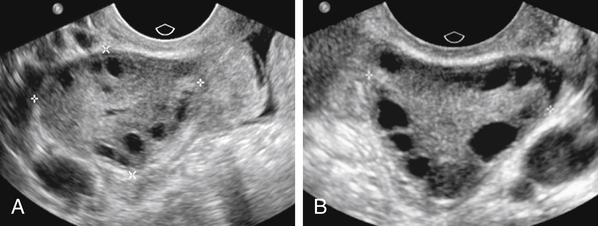
KOH, Potassium hydroxide; STD, sexually transmitted disease; HPV, Human papillomavirus. ∗Chlamydia can be treated with erythromycin if the patient is pregnant. If compliance is an issue (alcoholic, drug abuse, homeless, or unreliable patient), give azithromycin 1 g orally in a single dose so that you can watch the patient take it. Patients with gonorrhea should be treated for presumed chlamydial co-infection (but the opposite is not true). Fibroids (i.e., leiomyomas) are benign uterine tumors (Fig. 16-1). They are the most common tumors in women and the most common indication for hysterectomy (when they grow too large or cause symptoms). Up to 40% of women have fibroids by age 40 years. Malignant transformation is rare (<1%). PCOS is an endocrine imbalance characterized by androgen excess as well as a ratio of leuteinizing hormone (LH) to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) greater than 2:1. Patients also frequently develop enlarged ovaries with multiple peripherally oriented cysts, which can be seen on ultrasound (Figs. 16-2 and 16-3). On the Step 2 exam, watch for an overweight woman who has acne, hirsutism, amenorrhea, and/or infertility.
Gynecology
8 Cover the right-hand columns and specify the findings and treatment for the following vaginal infections:
INFECTIOUS AGENT
FINDINGS
TREATMENT
Candida sp.
“Cottage cheese” appearance; pseudohyphae seen on KOH preparation; history of diabetes, antibiotic treatment, or pregnancy
Topical or oral antifungal
Trichomonas vaginalis
Trichomonads can be seen swimming under microscope; pale green, frothy, watery discharge; “strawberry” cervix
Metronidazole
Gardnerella vaginalis
Malodorous discharge; fishy smell on KOH preparation; clue cells
Metronidazole
HPV
Venereal warts, koilocytosis on Pap smear
Many (acid, cryo therapy, laser, podophyllin)
Herpes virus
Multiple shallow, painful ulcers; recurrence and resolution
Acyclovir, valacyclovir
Syphilis (stage I)
Painless chancre, spirochete on dark-field microscopy
Penicillin
Syphilis (stage II)
Condyloma lata, maculopapular rash on palms, serology
Penicillin
Chlamydia trachomatis
Most common STD; dysuria, positive culture and antibody tests
Doxycycline or azithromycin∗
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Mucopurulent cervicitis; gram-negative bacteria on Gram stain
Ceftriaxone
Molluscum
Characteristic appearance of lesions, intracellular inclusions
Curette, cryotherapy, or electrocauterization/coagulation
Pediculosis
“Crabs”; look for itching; lice can be seen on pubic hairs
Permethrin cream (or malathion)
12 What are fibroids? How common are they? How often do they become malignant?
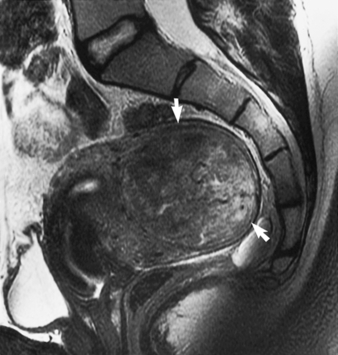
18 Define PCOS. How do you recognize it?
Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access