CHAPTER 1 General Concepts in Caring for Medical-Surgical Patients
Section One Perioperative Care
Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Preoperatively
Postoperatively
Risk for injury
Desired outcome
Patient does not experience injury or untoward effects of pharmacotherapy or other external factors.
Nursing Interventions
Desired outcome
Patient’s airway is clear as evidenced by normal breath sounds to auscultation, respiratory rate (RR) 12-20 breaths/min with normal depth and pattern (eupnea), normothermia, normal skin color, and O2 saturation greater than 92% on room air.
Nursing Interventions
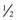 hr before deep breathing, coughing, or ambulation to promote adherence.
hr before deep breathing, coughing, or ambulation to promote adherence.Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
TABLE 1-1 NONPHARMACOLOGIC MEASURES TO PROMOTE SLEEP
| ACTIVITY | EXAMPLES |
|---|---|
| Mask or eliminate environmental stimuli | Use eye shields or ear plugs; play soothing music; dim lights at bedtime; mask odors from dressings/drainage; change dressing or drainage container as indicated |
| Promote muscle relaxation | Encourage ambulation as tolerated throughout the day; teach and encourage in-bed exercises and position changes; perform back massage at bedtime; if not contraindicated, use heating pad |
| Reduce anxiety | Ensure adequate pain control; keep patient informed of progress and treatment measures; avoid overstimulation by visitors or other activities immediately before bedtime; avoid stimulant drugs (e.g., caffeine) |
| Promote comfort | Encourage patient to use own pillows and bed clothes if not contraindicated; adjust bed; rearrange linens; regulate room temperature |
| Promote usual presleep routine | Offer oral hygiene at bedtime; provide warm beverage at bedtime; encourage reading or other quiet activity |
| Minimize sleep disruption | Maintain quiet environment throughout the night; plan nursing activities to allow long periods (at least 90 min) of undisturbed sleep; use dim lights when checking on patient during the night |
Impaired physical mobility
related to postoperative pain, decreased strength and endurance secondary to CNS effects of anesthesia or blood loss, musculoskeletal or neuromuscular impairment secondary to disease process or surgical procedure, perceptual impairment secondary to disease process or surgical procedure (e.g., ocular surgery, neurosurgery), or cognitive deficit secondary to disease process or effects of opioid analgesics and anesthetics
Nursing Interventions
Risk for trauma
related to weakness, balancing difficulties, and reduced muscle coordination secondary to anesthetics and postoperative opioid analgesics
Nursing Interventions
Risk for impaired skin integrity
related to presence of secretions/excretions around percutaneous drains and tubes
Desired outcome
Patient’s skin around percutaneous drains and tubes remains intact and nonerythematous.
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Interventions
Section Two Pain
Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions
Chronic pain
related to disease process, injury, or surgical procedure
Desired outcome
As reported by patient (subjective) or family pain is at an acceptable level, documented through use of a pain scale. Behavioral (BOX 1-1) and physiologic (BOX 1-2) indicators of pain are absent.
Nursing Interventions
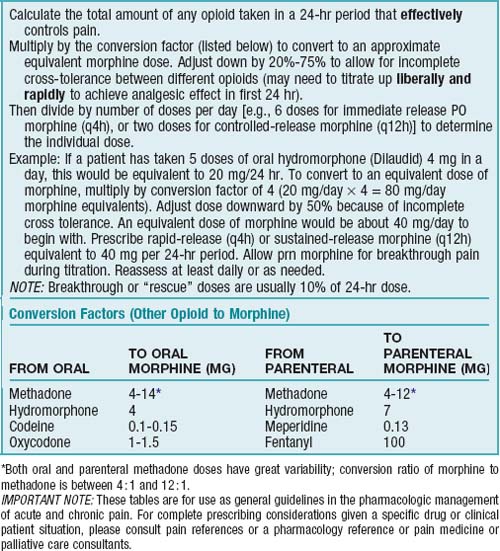
BOX 1-5 NALOXONE (NARCAN)
 Adult dosage range for respiratory depression secondary to opioid intoxication is 0.4-2 mg intravenously (preferred route), intramuscularly, or subcutaneously.
Adult dosage range for respiratory depression secondary to opioid intoxication is 0.4-2 mg intravenously (preferred route), intramuscularly, or subcutaneously. Maximum dose is 10 mg. If no response after 10 mg, another cause of respiratory depression is considered.
Maximum dose is 10 mg. If no response after 10 mg, another cause of respiratory depression is considered.TABLE 1-5 METHADONE CONVERSION CHART
| ORAL MORPHINE EQUIVALENT DAILY DOSE (mg/day) | INITIAL DOSE RATIO (ORAL MORPHINE : ORAL METHADONE) |
|---|---|
| 30-90 | 4 : 1 |
| 90-300 | 8 : 1 |
| More than 300 | 12 : 1 |
Data from Pereira J, Lawlor P, Vigano A et al: Equianalgesic dose ratios for opioids: a critical review and proposals for long-term dosing, J Pain Symptom Manage 22(2):672-687, 2001; and Anderson R, Saiers JH, Abram S, Schlicht C: Accuracy in equianalgesic dosing: conversion dilemmas, J Pain Symptom Manage 21(5):397-406, 2001.