Chapter 4 Note: Thousands of additional practice questions are available on the enclosed companion CD. 1. A nurse is caring for a client who has paraplegia as a result of a spinal cord injury. Which rehabilitation plan will be most effective for this client? 1. Arrangements will be made by the client and the client’s family. 2. The plan is formulated and implemented early in the client’s care. 3. The rehabilitation is minimal and short term because the client will return to former activities. 4. Arrangements will be made for long-term care because the client is no longer capable of self-care. 2. What is a basic concept associated with rehabilitation that the nurse should consider when formulating discharge plans for clients? 1. Rehabilitation needs are best met by the client’s family and community resources. 2. Rehabilitation is a specialty area with unique methods for meeting clients’ needs. 3. Immediate or potential rehabilitation needs are exhibited by clients with health problems. 4. Clients who are returning to their usual activities following hospitalization do not require rehabilitation. 3. A nurse is teaching a client how to use the call bell system. Which level of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs does this nursing action address? 4. A nurse is supportive of a child receiving long-term rehabilitation in the home rather than in a health care facility. Why is living with the family so important to a child’s emotional development? 1. It provides rewards and punishment. 2. The child’s development is supported. 3. It reflects the mores of a larger society. 5. A nurse is discussing Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) with a client. What behavior expected of members of AA should the nurse include in the discussion? 1. Speaking aloud at weekly meetings 2. Promising to attend at least 12 meetings yearly 3. Maintaining controlled drinking after 6 months 6. A nurse discusses the philosophy of Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) with the client who has a history of alcoholism. What need must self-help groups such as AA meet to be successful? 7. A daughter of a Chinese-speaking client approaches a nurse and asks multiple questions while maintaining direct eye contact. What culturally related concept does the daughter’s behavior reflect? 8. A nurse manager works on a unit where the nursing staff members are uncomfortable taking care of clients from cultures that are different from their own. How should the nurse manager address this situation? 1. Assign articles about various cultures so that they can become more knowledgeable. 2. Relocate the nurses to units where they will not have to care for clients from a variety of cultures. 3. Rotate the nurses’ assignments so they have an equal opportunity to care for clients from other cultures. 4. Plan a workshop that offers opportunities to learn about the cultures they might encounter while at work. 9. A nurse is teaching a parenting class. What should the nurse suggest about managing the behavior of a young school-age child? 10. A nurse in the health clinic is counseling a college student who was recently diagnosed with asthma. On what aspect of care should the nurse focus? 1. Teaching how to make a room allergy-free 2. Referring to a support group for individuals with asthma 3. Arranging with the college to ensure a speedy return to classes 4. Evaluating whether the necessary lifestyle changes are understood 11. Nurses are held responsible for the commission of a tort. The nurse understands that a tort is: 1. the application of force to the body of another by a reasonable individual. 2. an illegality committed by one person against the property or person of another. 3. doing something that a reasonable person under ordinary circumstances would not do. 4. an illegality committed against the public and punishable by the law through the courts. 12. A client is placed on a stretcher and restrained with straps while being transported to the x-ray department. A strap breaks, and the client falls to the floor, sustaining a fractured arm. Later the client shows the strap to the nurse manager, stating, “See, the strap is worn just at the spot where it snapped.” What is the nurse’s accountability regarding this incident? 1. Exempt from any lawsuit because of the doctrine of respondeat superior 2. Totally responsible for the obvious negligence because of failure to report defective equipment 3. Liable, along with the employer, for misapplication of equipment or use of defective equipment that harms the client 4. Exonerated, because only the hospital, as principal employer, is responsible for the quality and maintenance of equipment 13. A 2-year-old child admitted with a diagnosis of pneumonia was administered antibiotics, fluids, and oxygen. The child’s temperature increased until it reached 103° F. When notified, the health care provider determined that there was no need to change treatment, even though the child had a history of febrile seizures. Although concerned, the nurse took no further action. Later, the child had a seizure that resulted in neurologic impairment. Legally, who is responsible for the child’s injury? 1. Health care provider, because this decision took precedence over the nurse’s concern 2. Health care provider, because of total responsibility for the child’s health and treatment regimen 3. Nurse, because failure to further question the health care provider about the child’s status placed the child at risk 4. Neither, because high fevers are common in children and the health care provider had little cause for concern 14. A graduate nurse is preparing to apply to the State Board of Nursing for licensure to practice as a registered professional nurse. What group primarily is protected under the regulations of the practice of nursing? 15. A client with coronary artery disease has a sudden episode of cyanosis and a change in respirations. The nurse starts oxygen administration immediately. Legally, should the nurse have administered the oxygen? 1. The oxygen had not been ordered and therefore should not have been administered. 2. The symptoms were too vague for the nurse to determine a need for administering oxygen. 3. The nurse’s observations were sufficient, and therefore oxygen should have been administered. 4. The health care provider should have been called for an order before the nurse administered the oxygen. 16. An adolescent is taken to the emergency department of the local hospital after stepping on a nail. The puncture wound is cleansed and a sterile dressing applied. The nurse asks about having had a tetanus immunization. The adolescent responds that all immunizations are up to date. Penicillin is administered, and the client is sent home with instructions to return if there is any change in the wound area. A few days later, the client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of tetanus. Legally, what is the nurse’s responsibility in this situation? 1. The nurse’s judgment was adequate, and the client was treated accordingly. 2. The possibility of tetanus was not foreseen because the client was immunized. 3. Nurses should routinely administer immunization against tetanus after such an injury. 4. Assessment by the nurse was incomplete, and as a result the treatment was insufficient. 17. When being interviewed for a position as a registered professional nurse, the applicant is asked to identify an example of an intentional tort. What is the appropriate response? 18. Several recently licensed registered nurses are discussing whether they should purchase personal professional liability insurance. Which statement indicates the most accurate information about professional liability insurance? 1. “If you have liability insurance, you are more likely to be sued.” 2. “Your employer provides you with the liability insurance you will need.” 3. “Liability insurance is not available for nursing professionals working in a hospital.” 4. “Personal liability insurance offers representation if the State Board of Nursing files charges against you.” 19. A 3-year-old child with eczema of the face and arms has disregarded the nurse’s warnings to “stop scratching, or else!” The nurse finds the toddler scratching so intensely that the arms are bleeding. The nurse then ties the toddler’s arms to the crib sides, saying, “I’m going to teach you one way or another.” How should the nurse’s behavior be interpreted? 1. These actions can be construed as assault and battery. 2. The problem was resolved with forethought and accountability. 3. Skin must be protected, and the actions taken were by a reasonably prudent nurse. 4. The nurse had tried to reason with the toddler and expected understanding and cooperation. 20. A nurse is teaching a group of parents about child abuse. What definition of assault should the nurse include in the teaching plan? 1. Assault is a threat to do bodily harm to another person. 2. It is a legal wrong committed by one person against the property of another. 3. It is a legal wrong committed against the public that is punishable by state law. 4. Assault is the application of force to another person without lawful justification. 21. A nurse is teaching staff members about the legal terminology used in child abuse. What definition of battery should the nurse include in the teaching? 1. Maligning a person’s character while threatening to do bodily harm 2. A legal wrong committed by one person against property of another 3. The application of force to another person without lawful justification 4. Behaving in a way that a reasonable person with the same education would not 22. A toddler screams and cries noisily after parental visits, disturbing all the other children. When the crying is particularly loud and prolonged, the nurse puts the crib in a separate room and closes the door. The toddler is left there until the crying ceases, a matter of 30 or 45 minutes. Legally, how should this behavior be interpreted? 1. Limits had to be set to control the child’s crying. 2. The child had a right to remain in the room with the other children. 3. The child had to be removed because the other children needed to be considered. 4. Segregation of the child for more than half an hour was too long a period of time. 23. A pregnant woman is admitted with a tentative diagnosis of placenta previa. The nurse implements orders to start an IV infusion, administer oxygen, and draw blood for laboratory tests. The client’s apprehension is increasing, and she asks the nurse what is happening. The nurse tells her not to worry, that she is going to be all right, and that everything is under control. What is the best interpretation of the nurse’s statement? 1. Adequate, because the preparations are routine and need no explanation 2. Effective, because the client’s anxieties would increase if she knew the danger involved 3. Questionable, because the client has the right to know what treatment is being given and why 4. Incorrect, because only the health care provider should offer assurances about management of care 24. What should the nurse do initially when obtaining consent for surgery? 1. Describe the risks involved in the surgery. 2. Explain that obtaining the signature is routine for any surgery. 3. Witness the client’s signature, which the nurse’s signature will document. 4. Determine whether the client’s knowledge level is sufficient to give consent. 25. A client who has been told she needs a hysterectomy for cervical cancer is upset about being unable to have a third child. What is the next nursing action? 1. Evaluate her willingness to pursue adoption. 2. Encourage her to focus on her own recovery. 3. Emphasize that she does have two children already. 4. Ensure that other treatment options for her will be explored. 26. The family of an older adult who is aphasic reports to the nurse manager that the primary nurse failed to obtain a signed consent before inserting an indwelling catheter to measure hourly output. What should the nurse manager consider before responding? 1. Procedures for a client’s benefit do not require a signed consent. 2. Clients who are aphasic are incapable of signing an informed consent. 3. A separate signed informed consent for routine treatments is unnecessary. 4. A specific intervention without a client’s signed consent is an invasion of rights. 27. The spouse of a comatose client who has severe internal bleeding refuses to allow transfusions of whole blood because they are Jehovah’s Witnesses. What action should the nurse take? 1. Institute the ordered blood transfusion because the client’s survival depends on volume replacement. 2. Clarify the reason why the transfusion is necessary and explain the implications if there is no transfusion. 3. Phone the health care provider for an administrative order to give the transfusion under these circumstances. 4. Give the spouse a treatment refusal form to sign and notify the health care provider that a court order can now be sought. 28. A client is voluntarily admitted to a psychiatric unit. Later, the client develops severe pain in the right lower quadrant and is diagnosed as having acute appendicitis. How should the nurse prepare the client for the appendectomy? 1. Have two nurses witness the client signing the operative consent form. 2. Ensure that the surgeon and the psychiatrist sign for the surgery because it is an emergency procedure. 3. Ask the client to sign the operative consent form after the client has been informed of the procedure and required care. 4. Inform the client’s next of kin that it will be necessary for one of them to sign the consent form because the client is on a psychiatric unit. 29. What should the nurse consider when obtaining an informed consent from a 17-year-old adolescent? 1. If the client is allowed to give consent 2. The client cannot make informed decisions about health care. 3. If the client is permitted to give voluntary consent when parents are not available 4. The client probably will be unable to choose between alternatives when asked to consent. 1. Clients have a right to refuse treatment. 2. Nurses are required to answer clients truthfully. 3. The health care provider should have been notified. 4. The client had insufficient knowledge to make such a decision. 5. Legally prescribed medications are administered despite a client’s objections. 31. A client using fentanyl (Duragesic) transdermal patches for pain management in late-stage cancer dies. What should the hospice nurse who is caring for this client do about the patch? 1. Tell the family to remove and dispose of the patch. 2. Leave the patch in place for the mortician to remove. 3. Have the family return the patch to the pharmacy for disposal. 4. Remove and dispose of the patch in an appropriate receptacle. 1. Count the client’s respirations. 2. Document the intensity of the client’s pain. 3. Withhold the medication if the client reports pruritus. 4. Verify the number of doses in the locked cabinet before administering the prescribed dose. 5. Discard the medication in the client’s toilet before leaving the room if the medication is refused. 33. Which nursing behavior is an intentional tort? 1. Miscounting gauze pads during a client’s surgery 2. Causing a burn when applying a wet dressing to a client’s extremity 3. Divulging private information about a client’s health status to the media 4. Failing to monitor a client’s blood pressure before administering an antihypertensive 34. Twenty-four hours after a cesarean birth, a client elects to sign herself and her baby out of the hospital. Staff members are unable to contact her health care provider. The client arrives at the nursery and asks that her infant be given to her to take home. What is the most appropriate nursing action? 1. Give the infant to the client and instruct her regarding the infant’s care. 2. Explain to the client that she can leave, but her infant must remain in the hospital. 3. Emphasize to the client that the infant is a minor and legally must remain until orders are received. 4. Tell the client that hospital policy prevents the staff from releasing the infant until ready for discharge. 35. A client is hospitalized because of severe depression. The client refuses to eat, stays in bed most of the time, does not talk with family members, and will not leave the room. The nurse attempts to initiate a conversation by asking questions but receives no answers. Finally the nurse tells the client that if there is no response, the nurse will leave and the client will remain alone. How should the nurse’s behavior be interpreted? 1. A system of rewards and punishment is being used to motivate the client. 2. Leaving the client alone allows time for the nurse to think of other strategies. 3. This behavior indicates the client’s desire for solitude that the nurse is respecting. 4. This threat is considered assault, and the nurse should not have reacted in this manner. 36. During a newborn assessment the nurse identifies that the temperature, pulse, respirations, and other physical characteristics are within the expected range. The nurse records these findings on the clinical record. Legally, how should the nurse’s action be interpreted? 1. The nurse met the requirements set forth in the Nurse Practice Act. 2. This is a medical diagnosis and the nurse overstepped the legal boundary. 3. Nursing assessments are not equivalent to a health care provider’s assessments. 4. The initial assessment of the infant’s physical status is the responsibility of the client’s health care provider. 37. Which nursing action is protected from legal action? 1. Providing health teaching regarding family planning 2. Offering first aid at the scene of an automobile collision 3. Reporting incidents of suspected child abuse to the appropriate authorities 4. Administering resuscitative measures to an unconscious child pulled from a swimming pool 39. A weak, dyspneic, terminally ill client is visited frequently by the spouse and teenage children. What should the client’s plan of care include? 1. Foster self-activity whenever possible. 2. Plan care to be completed at one time followed by a long rest. 3. Teach family members how to assist with the client’s basic care. 4. Limit visiting to evening hours before the client goes to sleep. 40. A nurse is evaluating a client’s knowledge of ambulating with crutches. The nurse identifies the need for further teaching when the client states, “I must practice: 1. sitting down and standing up.” 2. ambulating several hours a day.” 3. standing and maintaining balance.” 41. A nurse educator is presenting information about the nursing process to a class of nursing students. What definition of the nursing process should be included in the presentation? 1. Procedures used to implement client care 2. Sequence of steps used to meet the client’s needs 3. Activities employed to identify a client’s problem 4. Mechanisms applied to determine nursing goals for the client 1. ______ Identify goals for care. 2. ______ Develop a plan of care. 3. ______ State client’s nursing needs. 4. ______ Obtain client’s nursing history. 43. A nurse is explaining the nursing process to a nursing assistant. Which step of the nursing process should include interpretation of data collected about the client? 44. Which nurse collaborates directly with the client to establish and implement a basic plan of care after admission? 45. A newly oriented home health nurse on a first visit checks the client’s vital signs and obtains a blood sample for an international normalization ratio (INR). After completion of these tasks, the client asks the nurse to straighten the blankets on the bed. What is the nurse’s most appropriate response? 1. “I would, but my back hurts today.” 2. “OK. It will be my good deed for the day.” 3. “Of course. I want to do whatever I can for you.” 46. A nurse is reviewing a client’s plan of care. What is the determining factor in the revision of the plan? 2. “What will my friends think?” 3. “How do I give myself an injection?” 4. “Can you tell me how the glucose monitor works?” 5. “How do I get the insulin from the vial into the syringe?” 48. A nurse is caring for a client with hemiplegia who is frustrated. How can the nurse motivate the client toward independence? 1. Establish long-range goals for the client. 2. Identify errors that the client can correct. 3. Reinforce success in tasks accomplished. 49. A client is receiving an antihypertensive drug intravenously for control of severe hypertension. The client’s blood pressure is unstable and is 160/94 mm Hg before the infusion. Fifteen minutes after the infusion is started, the blood pressure increases to 180/100 mm Hg. Which type of response is the client demonstrating? 50. A client has an anaphylactic reaction after receiving intravenous penicillin. What does the nurse conclude is the cause of this reaction? 1. An acquired atopic sensitization occurred. 2. There was passive immunity to the penicillin allergen. 3. Antibodies to penicillin developed after a previous exposure. 4. Potent antibodies were produced when the infusion was instituted. 51. At the conclusion of visiting hours, the parent of a 14-year-old adolescent scheduled for orthopedic surgery the next day hands the nurse a bottle of capsules and says, “These are for my child’s allergy. Will you be sure my child takes one about 9 tonight?” What is the nurse’s best response? 1. “I will give one capsule tonight before bedtime.” 2. “I will get a prescription so that the medicine can be taken.” 3. “Does your health care provider know about your child’s allergy?” 4. “Did you ask your health care provider if your child should have this tonight?” 55. Based on the client’s reported pain level, the nurse administers 8 mg of the prescribed morphine. The medication is available in a 10 mg syringe. Wasting of the remaining 2 mg of morphine should be done by the nurse and a witness. Who should be the witness? 56. A nurse is instructing a group of volunteer nurses on the technique of administering the smallpox vaccine. What injection method should the nurse teach? 58. A client is scheduled to receive phenytoin (Dilantin) 100 mg orally at 6 PM but is having difficulty swallowing capsules. What method should the nurse use to help the client take the medication? 1. Sprinkle the powder from the capsule into a cup of water. 2. Insert a rectal suppository containing 100 mg of phenytoin. 3. Administer 4 mL of phenytoin suspension containing 125 mg/5 mL. 4. Obtain a change in the administration route to allow an IM injection. 60. A pregnant client is now in the third trimester. The client tells the nurse, “I want to be knocked out for the birth.” How should the nurse respond? 1. “You are worried about too much pain.” 2. “You don’t want to be awake during the birth.” 3. “I can understand that because labor is uncomfortable.” 4. “I will tell your health care provider about this request.” 61. What should a nurse consider when trying to promote affective learning in a client with a newly diagnosed disease?
Foundations of Nursing Practice
Review Questions with Answers and Rationales
 Denotes alternate format question.
Denotes alternate format question.
 30. A client with rheumatoid arthritis does not want the prescribed cortisone and informs the nurse. Later, the nurse attempts to administer cortisone. When the client asks what the medication is, the nurse gives an evasive answer. The client takes the medication and later discovers that it was cortisone. The client states an intent to sue. What factors in this situation must be considered in a legal action? Select all that apply.
30. A client with rheumatoid arthritis does not want the prescribed cortisone and informs the nurse. Later, the nurse attempts to administer cortisone. When the client asks what the medication is, the nurse gives an evasive answer. The client takes the medication and later discovers that it was cortisone. The client states an intent to sue. What factors in this situation must be considered in a legal action? Select all that apply.
 32. What is a nurse’s responsibility when administering prescribed opioid analgesics? Select all that apply.
32. What is a nurse’s responsibility when administering prescribed opioid analgesics? Select all that apply.
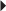 38. A nurse is assigned to care for a newly admitted client. The nurse performs a physical assessment and reviews the admission form and the health care provider’s orders. What should the nurse identify as the priorities in this client’s plan of care?
38. A nurse is assigned to care for a newly admitted client. The nurse performs a physical assessment and reviews the admission form and the health care provider’s orders. What should the nurse identify as the priorities in this client’s plan of care?
 42. Place each step of the nursing process in the order that they should be used.
42. Place each step of the nursing process in the order that they should be used.
 47. A nurse is teaching an adolescent about type 1 diabetes and self-care. Which client questions indicate a need for additional teaching in the cognitive domain? Select all that apply.
47. A nurse is teaching an adolescent about type 1 diabetes and self-care. Which client questions indicate a need for additional teaching in the cognitive domain? Select all that apply.
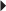 52. Filgrastim (Neupogen) 5 mcg/kg/day by injection is prescribed for a client who weighs 132 lb. The vial label reads filgrastim 300 mcg/mL. How many milliliters should the nurse administer? Record your answer using a whole number.
52. Filgrastim (Neupogen) 5 mcg/kg/day by injection is prescribed for a client who weighs 132 lb. The vial label reads filgrastim 300 mcg/mL. How many milliliters should the nurse administer? Record your answer using a whole number.
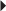 53. A child is to receive 60 mg of phenytoin (Dilantin). The medication is available as an oral suspension that contains 125 mg/5 mL. How many milliliters should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal place.
53. A child is to receive 60 mg of phenytoin (Dilantin). The medication is available as an oral suspension that contains 125 mg/5 mL. How many milliliters should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal place.
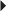 54. A health care provider prescribes an IV infusion ampicillin 375 mg every 6 hours. The drug is supplied as 500 mg of powder in a vial. The directions are to mix the powder with 1.8 mL of diluent, which yields 250 mg/mL. How much prepared solution should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal place.
54. A health care provider prescribes an IV infusion ampicillin 375 mg every 6 hours. The drug is supplied as 500 mg of powder in a vial. The directions are to mix the powder with 1.8 mL of diluent, which yields 250 mg/mL. How much prepared solution should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal place.
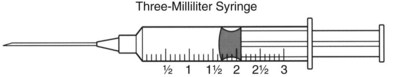
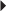 57. A primary care provider prescribes cefazolin (Kefzol) 125 mg IM for a client. The vial contains 0.5 gm of Kefzol in powdered form. The instructions indicate to add 2 mL of sterile water to provide a solution that contains 225 mg per mL. Draw a line on the syringe to indicate the volume of medication to the nearest tenth the nurse should administer.
57. A primary care provider prescribes cefazolin (Kefzol) 125 mg IM for a client. The vial contains 0.5 gm of Kefzol in powdered form. The instructions indicate to add 2 mL of sterile water to provide a solution that contains 225 mg per mL. Draw a line on the syringe to indicate the volume of medication to the nearest tenth the nurse should administer.
 59. What are the desired outcomes that the nurse expects when administering a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID)? Select all that apply.
59. What are the desired outcomes that the nurse expects when administering a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID)? Select all that apply.
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Foundations of Nursing Practice: Review Questions with Answers and Rationales
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access