Chapter 34 *A transition syllable or vowel may be added to or deleted from the word parts to make the combining form. Environmental careers create a supportive environment for the patient. Support services or ancillary health workers are necessary in all aspects of health care (Table 34-1). Most ancillary workers are not seen by the person receiving the service (Box 34-1). Many of the assistant-level environmental workers provide care in other career areas by maintaining the equipment and supplies necessary for optimal care. In addition to the specific skills and knowledge necessary in each specialty area, ancillary workers must know basic medical terminology and principles of asepsis. TABLE 34-1 Environmental Career Educational Cost and Earnings *http://www.uky.edu/Registrar/feesgen.htm. Dietary technicians complete a 2-year associate degree program. They plan menus and supervise the production of food. Food service workers or dietary assistants prepare and deliver the meal trays to patients or prepare the dining area (Fig. 34-1). They may also help the patient select a menu and process the order. Food service workers may prepare food and beverages. Collecting the empty meal trays and washing the dishes are also duties of the food service worker. On-the-job training is available for some of the entry-level dietary positions. Dietitians are assisted by others in the facility to distribute meal requisitions to patients early in the day (Fig. 34-2). The type of meal plan is determined by the physician’s order, preferences, and special needs of the patient. When the diet menus are completed, they are collected, and the amount of food portions necessary to complete the meals may be determined and prepared. In some cases, the meals may be served using “a la carte” room service. Patients are allowed to request their meals and snacks from a personal diet menu at any time. (See Skill List 34-1, Planning Menus, and Skill List 34-2, Preparing the Dining Area, p. 555.) Environmental health technicians collect and analyze air and water samples under the supervision of the sanitarian (Fig. 34-3). Training for the environmental health care technician is available in postsecondary vocational programs. Training may also be offered in the community college and result in an associate degree. Certification is available for the environmental health technician through the National Environmental Health Association. Environmental health assistants perform routine tasks under the supervision of the sanitarian. Environmental health assistants learn on the job. Public health microbiologists conduct tests and study the relationship of people to organisms that cause pollution, disease, or epidemics to prevent the same problems in the future. Microbiologists in public health usually work for some level of government. Some examples of the work done by microbiologists include testing foods, monitoring the sludge from sewage treatment, and identifying organisms that cause widespread disease. Microbiologists must have at least a bachelor’s degree in biological or life science. However, most microbiology study is completed on the graduate level. Some states require public health microbiologists to be licensed. Certification as a Specialist in Public Health may be granted by the Academy of Microbiology. (See Skill List 34-3, Using the Epidemiological Approach, p. 556.)
Environmental Careers
 Define at least eight terms relating to environmental health care.
Define at least eight terms relating to environmental health care.
 Describe the function of the environmental health care team.
Describe the function of the environmental health care team.
 Specify the role of the environmental health care team members, including personal qualities, educational requirements, responsibilities, and credentialing requirements.
Specify the role of the environmental health care team members, including personal qualities, educational requirements, responsibilities, and credentialing requirements.
 Identify at least five areas of pollution control that are monitored and regulated by environmental health services.
Identify at least five areas of pollution control that are monitored and regulated by environmental health services.
 List at least five health conditions that are affected by environmental pollution.
List at least five health conditions that are affected by environmental pollution.
 Describe the natural recycling process or chain of life in an ecosystem.
Describe the natural recycling process or chain of life in an ecosystem.
Term
Definition
Prefix
Root
Suffix
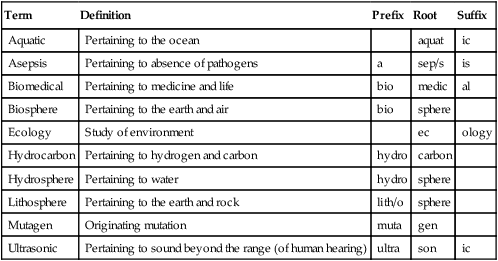
Aquatic
Pertaining to the ocean
aquat
ic
Asepsis
Pertaining to absence of pathogens
a
sep/s
is
Biomedical
Pertaining to medicine and life
bio
medic
al
Biosphere
Pertaining to the earth and air
bio
sphere
Ecology
Study of environment
ec
ology
Hydrocarbon
Pertaining to hydrogen and carbon
hydro
carbon
Hydrosphere
Pertaining to water
hydro
sphere
Lithosphere
Pertaining to the earth and rock
lith/o
sphere
Mutagen
Originating mutation
muta
gen
Ultrasonic
Pertaining to sound beyond the range (of human hearing)
ultra
son
ic
Careers
Career
Educational Cost*
Earnings†
Dietitian
University of Kentucky, bachelor’s degree, 128 credit hours
Fees include:
Tuition $4305/semester
Fees $477/semester
Median annual salary: Lexington, Ky.—$51,110
Nutrition Services
Environmental Control
Environmental Careers
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access





