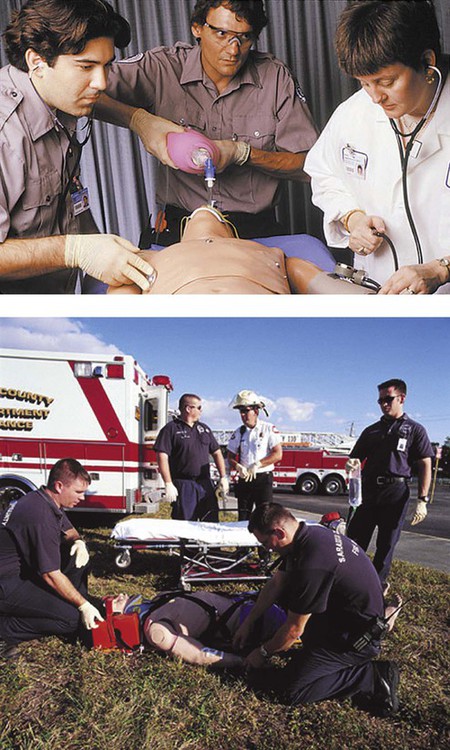
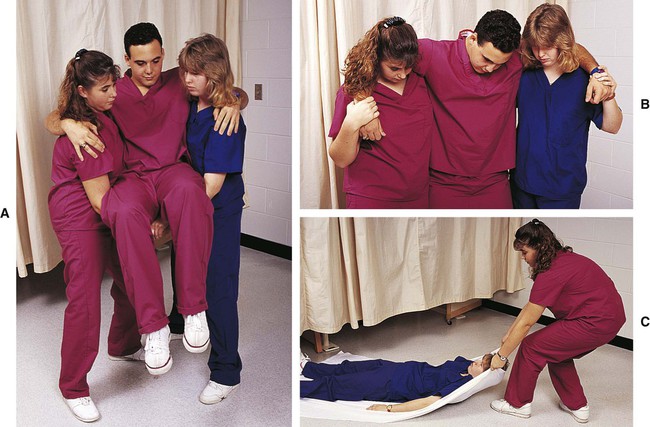
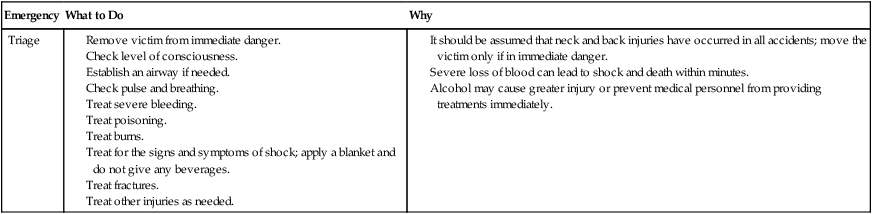
Chapter 32 Emergency Health Careers Terminology* *A transition syllable or vowel may be added to or deleted from the word parts make the combining form. Accidents are one of the five leading causes of death in the United States. They account for 50% of the fatalities of those 15 to 24 years of age. Injuries can result from automobile and home accidents, falls, fires, explosions, natural disasters, and industrial mishaps. Snow, water, and other athletic sports also account for injuries that require emergency care. Common injuries caused by accidents include bone fractures, cuts, poisoning, reactions to heat and cold, problems associated with medical conditions, and loss of vital functions. The goal of modern emergency care is immediate aid, or first aid, at the scene of injury rather than just the transportation of the victim to a medical facility. Levels of care have developed to provide this immediate care (Table 32-1). These include the bystanders or first responders with knowledge of first aid and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), emergency medical technicians (EMTs), and advanced emergency personnel (Box 32-1). Emergency medical services (EMS) are present in many communities. The EMS system is a coordinated response by all levels of practitioners to accidents and sudden illness. In most areas of the United States, EMS are initiated by the use of the 9-1-1 telephone call. Personnel answering 9-1-1 calls are trained to determine the type of rescue personnel needed, the location of the emergency, and other pertinent information. In some instances EMS personnel may even be able to direct the caller on methods for giving aid to the victim. TABLE 32-1 Emergency Health Career Educational Cost and Earnings *http://www.occc.edu/admissions/Tuition-Fees.html#educational. The role of the EMT-First Responder is to provide care in cases of acute illness and injury until more qualified personnel are available. Skills such as CPR, first aid for fractures and bleeding, treatment of shock, and assistance with childbirth are included in the training (Fig. 32-1). The first-aid rescuer assesses the scene of injury or illness to determine the necessary action (Table 32-2). The first priority of the rescuer is to remove the victim from any immediate danger (Fig. 32-3). The level of consciousness of the victim is the second consideration. The EMS system is activated at the earliest moment, and then hands-on CPR is started. In most areas of the United States, the 9-1-1 emergency number may be used to summon help. When reporting an incident, the rescuer states the location, his or her name, the number of victims involved, and the nature of the incident. The rescuer waits for the EMS to disconnect the phone first. Because the rescuer may be visiting in the victim’s home, all homeowners should place their name and address on each phone. TABLE 32-2 Emergency Assessment and Treatment
Emergency Health Careers
 Define at least 10 terms related to emergency health care.
Define at least 10 terms related to emergency health care.
 Specify the role of the emergency medical technician and emergency department personnel, including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
Specify the role of the emergency medical technician and emergency department personnel, including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
 Identify three levels of care that have been developed to provide first aid.
Identify three levels of care that have been developed to provide first aid.
 Identify at least six types of external wounds and first-aid treatment for each.
Identify at least six types of external wounds and first-aid treatment for each.
 Identify at least three types of burns and first-aid treatment for each.
Identify at least three types of burns and first-aid treatment for each.
 Describe at least five ways in which poisoning may occur and first-aid treatment for each.
Describe at least five ways in which poisoning may occur and first-aid treatment for each.
 Describe at least five causes of shock and the physical reaction to and first-aid treatment for each.
Describe at least five causes of shock and the physical reaction to and first-aid treatment for each.
 Identify three types of fractures and first-aid treatment for each.
Identify three types of fractures and first-aid treatment for each.
 Describe the effects of extreme cold and heat on the body and first-aid treatment for each.
Describe the effects of extreme cold and heat on the body and first-aid treatment for each.
 Describe the signs, symptoms, and treatment for a stroke and seizure activity.
Describe the signs, symptoms, and treatment for a stroke and seizure activity.
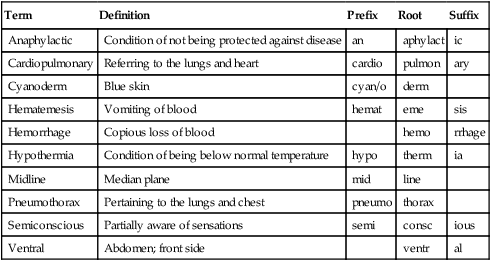
Term
Definition
Prefix
Root
Suffix
Anaphylactic
Condition of not being protected against disease
an
aphylact
ic
Cardiopulmonary
Referring to the lungs and heart
cardio
pulmon
ary
Cyanoderm
Blue skin
cyan/o
derm
Hematemesis
Vomiting of blood
hemat
eme
sis
Hemorrhage
Copious loss of blood
hemo
rrhage
Hypothermia
Condition of being below normal temperature
hypo
therm
ia
Midline
Median plane
mid
line
Pneumothorax
Pertaining to the lungs and chest
pneumo
thorax
Semiconscious
Partially aware of sensations
semi
consc
ious
Ventral
Abdomen; front side
ventr
al
Careers

Emergency Medical Technician
Content Instruction
Emergency Procedures
Emergency Assessment and Treatment
Emergency
What to Do
Why
Triage
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Emergency Health Careers
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access