CHAPTER 14 Earache
Otalgia, or ear pain, is generally caused by an inflammatory process. In children, inflammation most commonly occurs in the middle ear. Adults more often have an earache from external ear conditions or from referred pain from other head and neck structures. Acute otitis media (AOM) refers to any inflammation of the middle ear and encompasses a variety of clinical conditions. Otitis media with effusion is a collection of fluid in the middle ear. This condition is also known as serous otitis media, secretory otitis, or nonsuppurative otitis. External or middle ear disorders can often be distinguished after a brief history and physical examination. If the physical findings are normal, referred pain is a likely cause. About 50% of referred pain is caused by dental problems, although other causes may include temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder, parotitis, pharyngitis, or cervical, mouth, or facial disorders. The most serious, although least common, cause of referred pain is nasopharyngeal cancer, a condition more common in Asians. Figure 14-1 illustrates the structures of the ear.
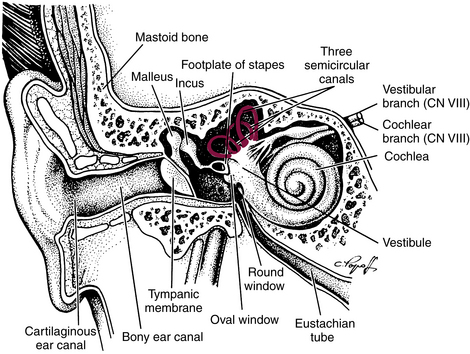
FIGURE 14-1 External auditory canal, middle ear, inner ear.
(From Barkauskas VH, Baumann L, Darling-Fisher C: Health and physical assessment, ed 3, St Louis, 2002, Mosby.)
Diagnostic reasoning: focused history
Family history
Having a sibling or parent with chronic otitis media makes it twice as likely for the illness to develop in the child. The presence of chronic otitis media may also be related to child-care practices, such as bottle propping, or environmental exposures, such as second-hand cigarette smoke.
Airplane travelers, divers
Barotrauma is a cause of acute serous otitis related to pressure changes from flying or scuba diving. This is often aggravated by recent upper respiratory tract infection or nasal congestion. Failure of the eustachian tube to open and equilibrate during descent results in a collection of serosanguineous fluid in the middle ear. This may be felt as ear pressure that can lead to pain, tinnitus, and temporary deafness. Swallowing, chewing, or blowing out the nose with the mouth and nose occluded can relieve symptoms.
Cleft palate
Itching or drainage
Itching or drainage from the ear usually indicates an infection or inflammation of the external canal. Itching can also be a precursor to herpes zoster of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). Drainage may also be present after the TM ruptures from increased middle ear pressure, or it may be from exudate secondary to mastoiditis. Cholesteatoma is an epidermal inclusion cyst of the middle ear or mastoid. A perforation of the TM and associated foul-smelling discharge may occur.
What does a history of trauma or injury tell me?
Key questions
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree































