Chapter 13 For in-depth study of the digestive system, consult the following publications: Lewis SM, et al: Medical-surgical nursing, ed 8, St. Louis, 2011, Mosby. Nugent P, Green J, Hellmer Saul MA, Pelikan P: Mosby’s comprehensive review of nursing for the NCLEX-RN examination, ed 20, St. Louis, 2012, Mosby. Patton K, Thibodeau G: Structure and function of the human body, ed 14, St. Louis, 2012, Mosby. Potter PA, Perry AG, Stockert PA, Hall A: Fundamentals of nursing, ed 8, St. Louis, 2013, Mosby Weilitz P, Potter PA: Pocket guide for health assessment, ed 6, St. Louis, 2007, Mosby Caloric Increase Needed For Select Injury Factors
Digestive System
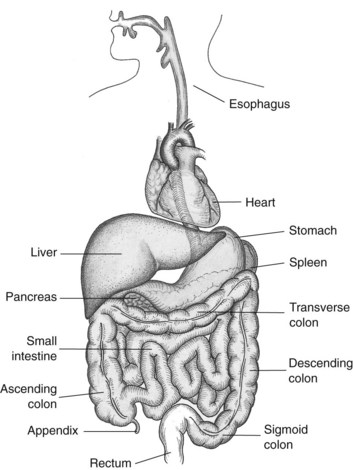
Digestive System and Associated Structures
Type
Description
Patient Complaint
Regular
Has all essentials; no restrictions
No special diet needed
Clear liquid
Broth, tea, clear soda, strained juices, gelatin
Recovery from surgery or very ill
Full liquid
Clear liquids plus milk products, eggs
Transition from clear to regular diet
Soft
Soft consistency and mild spice
Difficulty swallowing
Mechanical soft
Regular diet but chopped or ground
Difficulty chewing
Bland
No spicy food
Ulcers or colitis
Low residue
No bulky food, apples, or nuts
Rectal disease
High calorie
High protein, vitamin, and fat
Malnourished
Low calorie
Decreased fat, no whole milk, cream eggs, complex carbohydrates
Obese
Diabetic
Balance of protein, carbohydrates, fat
Insulin–food imbalance
High protein
Meat, fish, milk, cheese, poultry, eggs
Tissue repair, underweight
Low fat
Little butter, cream, whole milk, or eggs
Gallbladder, liver, or heart disease
Low cholesterol
Little meat or cheese
Need to decrease fat intake
Low sodium
No salt added during cooking
Heart or renal disease
Salt free
No salt
Heart or renal disease
Tube feeding
Formulas or liquid food
Oral surgery, oral or esophageal cancers, inability to eat or swallow
Type
Function
Food Sources
Carbohydrate
Energy, body temperature
Simple: sugars, fruits, nuts
Complex: grains, potatoes milk
Protein
Tissue growth, tissue repair
Meat, fish, eggs, milk, poultry, beans, peas, nuts
Fat
Energy and repair, carries vitamins A and D
Animal fat, meat, nuts, milk, fish, poultry
Water
Carries nutrients, regulates body processes, lubricates joints
Liquids, most fruits and vegetables
Type
Function
Food Sources
Calcium
Renews bones and teeth, regulates heart and nerves
Milk, green vegetables, cheese, salmon, legumes
Phosphorus
Renews bones and teeth, maintains nerve function
Cheese, oats, meat, milk, fish, poultry, nuts
Iron
Renews hemoglobin
Meat, eggs, liver, flour, yellow or green vegetables
Iodine
Regulates thyroid
Table salt, seafood
Magnesium
Component of enzymes
Grains, green vegetables
Sodium
Maintains water balance, nerve function
Salt, cured meats
Potassium
Maintains nerve function
Meat, milk, vegetables
Chloride
Formation of gastric juices
Salt
Zinc
Component of enzymes
Meat, seafood
Type
Function
Food Sources
A (retinol)
Helps eyes, skin, hair; fights infection
Yellow fruits and vegetables, liver, kidneys, fish
B1 (thiamine)
Maintains nerves, aids carbohydrate function
Bread, cereal, beans, peas, pork, liver, eggs, milk
B2 (riboflavin)
Maintains skin, mouth, nerve functions
Milk, cheese, eggs, cereal, dark green vegetables
B3 (niacin)
Oxidation of proteins and carbohydrates
Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, nuts, bread, cereal
B12
Aids muscles, nerves, heart, metabolism
Organ meats, milk
C (ascorbic acid)
Maintains integrity of cells, repairs tissue
Citrus fruits, tomatoes, green vegetables, potatoes
D
Enables body to use calcium and phosphorus
Milk, margarine, fish, liver, eggs
F
Antioxidant
Peanuts, vegetable oils
K
Aids in blood clotting
Green leafy vegetables
Injury
% Caloric Increase
Minor surgery
10
Mild infection
20
Moderate infection
40
Severe infection
60
Congestive heart failure
30
Cancer therapy
30
Pulmonary disease
30
Wound healing
20–60
Long bone fracture
30–50 ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree