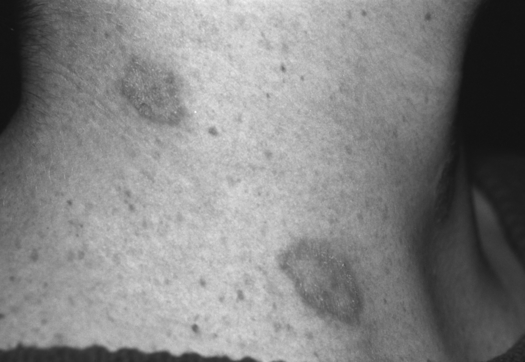
Chapter 6 Contact dermatitis is usually caused by a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, although it may be result from an irritating or toxic substance. Look for a new exposure to a classic offending agent, such as poison ivy, nickel earrings, or deodorant. The rash is well circumscribed and occurs only in the area of exposure. The skin is red and itchy and often has vesicles or bullae (Fig. 6-1; Plate 3). The causal agent should be avoided. Patch testing may determine the antigen. Known as dermatophytosis, tinea, and ringworm, fungal infections include the following: Tinea corporis (body/trunk): Look for red ring-shaped lesions with raised borders that tend to clear centrally while expanding peripherally (Fig. 6-2; Plate 4). Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot): Look for macerated, scaling web spaces between the toes that often itch and may be associated with thickened, distorted toenails (onychomycosis). Good foot hygiene is part of treatment. Tinea unguium (onychomycosis): thickened, distorted nails with debris under the nail edges. Tinea capitis (scalp): Mainly affects children (highly contagious), who have scaly patches of hair loss and may have an inflamed, boggy granuloma of the scalp (known as a kerion) that usually resolves on its own. Tinea cruris (jock itch): More common in obese males; usually is found in the crural folds of the upper, inner thighs.
Dermatology
1 Cover the two right-hand columns in the following table and define the common terms used in dermatology to describe skin findings:
TERM
DEFINITION
EXAMPLES
Macule
<1 cm; flat spot (nonpalpable, just visible)
Freckles, tattoos
Patch
>1 cm; otherwise, same as macule
Port-wine birthmarks
Papule
<1 cm; solid, elevated (palpable)
Wart, acne, lichen planus
Plaque
>1 cm; otherwise, same as papule and flat-topped
Psoriasis
Nodule
>1 cm; palpable, solid lesion; not flat-topped
Small lipoma, erythema nodosum
Vesicle
<5 mm; elevated, circumscribed lesion containing clear fluid (small blister)
Chickenpox, genital herpes
Bulla
>5 mm; otherwise, same as vesicle (large blister)
Contact dermatitis, pemphigus
Wheal
Itchy, transiently edematous area
Allergic reaction
4 Define contact dermatitis. How do you recognize it? What are the classic causes?
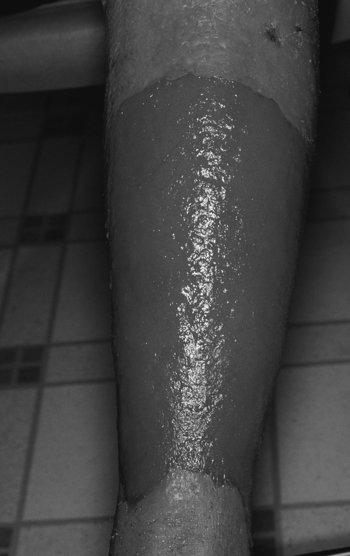
7 Name the various dermatologic fungal infections
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


