Chapter 36 1. What should the nurse do to assess the neurovascular status of an extremity casted from the ankle to the thigh? 1. Palpate the femoral artery. 2. Assess for a positive Homan sign. 3. Compress and release the client’s toenails. 3. A client who has breast cancer had postlumpectomy chemotherapy and is now scheduled for radiation on an outpatient basis. What is an important nursing intervention while the client is receiving radiation? 1. Assess the radiated site daily for redness or irritation. 2. Rinse the radiated site with an antibacterial solution after each treatment. 3. Instruct the client to apply lotion twice daily to the skin on the radiated area. 4. Encourage the client to wear a snug-fitting bra between radiation treatments. 4. A client’s problem with ineffective control of type 1 diabetes is identified when a sudden decrease in blood glucose level is followed by rebound hyperglycemia. What should the nurse do when this event occurs? 1. Give the client a glass of orange juice. 2. Seek an order to increase the insulin dose at bedtime. 3. Encourage the client to eat smaller, more frequent meals. 4. Collaborate with the health care provider to alter the insulin prescription. 5. A client with the diagnosis of personality disorder with antisocial behavior is hospitalized. The client is openly discussing interpersonal difficulties with family members and the boss at work from whom money has been stolen. The client presently is facing criminal charges. Which behavior indicates that the client is meeting treatment goals? 1. Expression of feelings of resentment toward the employer 2. Discussion of plans for each of the possible outcomes of a trial 3. Expression of resignation about difficult spousal and children relationships 4. Discussion of the decision to file a grievance against the employer after discharge from the hospital 6. A client with severe preeclampsia is hospitalized. What should a nurse do first to ensure her physical safety? 1. Decrease environmental stimuli. 2. Place her on seizure precautions. 3. Administer the prescribed sedatives. 7. Which statement by a client with type 2 diabetes indicates to the nurse that additional teaching about the diet is needed? 1. “I can eat as much dietetic fruit as I want.” 2. “I can have a lettuce salad whenever I want it.” 3. “I know that half of my diet should be carbohydrates.” 4. “I need to reduce the amounts of saturated fats in my diet.” 8. A child is found to be allergic to dust. The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for the parents. What should the nurse include in the plan? 1. Housework must be done by professional house cleaners. 2. Damp-dusting the house will help limit dust particles in the air. 3. The condition must be accepted because dust in a house cannot be limited. 4. The house must be redecorated because the environment must be dust-free. 9. A client who has just started on a regimen of haloperidol (Haldol) is observed pacing and shifting weight from one foot to another. What side effect does the nurse document in the client’s chart? 10. A client who has been on a psychiatric unit for several weeks continually talks about delusional material. What response by the nurse is most therapeutic? 1. Ask the client to explain the delusion. 2. Allow the client to maintain the delusion. 3. Encourage the client to focus on reality issues. 11. A client has a tonic-clonic seizure. What is the priority nursing intervention during the tonic-clonic stage of the seizure? 12. A nurse admits an adolescent to the psychiatric unit with the diagnosis of anorexia nervosa. What is the primary gain a client with anorexia achieves from this disorder? 1. Reduction of anxiety through control over food 2. Separation from parents secondary to hospitalization 3. Release from school responsibilities because of illness 4. Increased parental attentiveness related to massive weight loss 13. A nurse is caring for a newborn with a myelomeningocele. What should immediate nursing care for this infant include? 1. Changing diapers immediately when moist 2. Placing the infant in the reverse Trendelenburg position 3. Applying sterile, moist, nonadherent dressings to the sac 4. Positioning the infant prone with the legs slightly adducted 2. Turn the client on her side. 3. Notify the health care provider. 4. Verify the length of contractions. 15. The cervix of a client in labor is dilated 8 cm. She tells a nurse that she has a desire to push and is becoming increasingly uncomfortable. She requests pain medication. How should the nurse respond? 1. Help her to take panting breaths. 2. Prepare the birthing bed for the birth. 3. Assist her out of bed to the bathroom. 16. A nurse administers an intramuscular injection of vitamin K to a newborn. What is the purpose of the injection? 1. Maintains the intestinal floral count 2. Promotes proliferation of intestinal flora 3. Stimulates vitamin K production in the baby 4. Provides protection until intestinal flora is established 17. A child with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis requests a snack. Which is the most therapeutic selection of food the nurse can provide? 18. A client reports experiencing nausea, dyspnea, and right upper quadrant pain unrelieved by antacids. The pain occurs most often after eating in fast-food restaurants. Which diet should the nurse instruct the client to follow? 19. A person sustains deep partial-thickness burns while working on a boat in a town marina and seeks advice from the nurse in the first aid station. The nurse encourages the client to seek medical attention, but the client refuses. The nurse advises the person to go to a health care provider if: 20. A client with a history of gambling has legal difficulties for embezzling money and is required to obtain counseling. During an intake interview, the client says, “I never would have done this if I had been paid what I am worth.” What factor will create the greatest difficulty when assisting this client to develop insight? 1. Feelings of boredom and emptiness 2. Grandiosity related to personal abilities 3. Projection of reasons for difficulties onto others 22. A client has a urinary retention catheter in place after surgery. What should the nurse do when planning for the client’s safety needs in relation to this device? 1. Empty the bag every six hours. 2. Maintain the tension on the tubing. 3. Keep the system closed at all times. 23. What is the most important test the nurse should check to determine whether a transplanted kidney is functioning? 24. A pregnant adolescent at 10 weeks’ gestation visits the prenatal clinic for the first time. The nutrition interview indicates that her dietary intake consists mainly of soft drinks, candy, French fries, and potato chips. Why does the nurse consider this diet inadequate? 1. Caloric content will result in too great a weight gain. 2. Ingredients in soft drinks and candy can be teratogenic in early pregnancy. 3. Salt in this diet will contribute to the development of gestational hypertension. 4. Nutritional composition of the diet places her at risk for a low-birth-weight infant. 25. A nurse in the prenatal clinic is assessing a woman at 34 weeks’ gestation. The client’s blood pressure is 166/100 mm Hg and her urine is +3 for protein. She states that she has a severe headache and occasional blurred vision. Her baseline blood pressure was 100/62 mm Hg. What is the priority nursing action? 1. Arrange transportation to the hospital. 2. Obtain a prescription for an antihypertensive. 3. Recheck the blood pressure within half an hour. 4. Obtain a prescription for acetaminophen to relieve the headache. 26. A child has cystic fibrosis. Which statement by the parents about their plan for the child’s dietary regimen provides evidence that they understand the nurse’s instructions? 1. “I will restrict fluids during mealtimes.” 2. “I will discontinue the use of salt when cooking.” 3. “I should provide high-calorie foods between meals.” 27. A nurse is caring for a client with glaucoma. What rationale associated with the need for treatment of this condition should the nurse include in a teaching program? 1. Total blindness is inevitable. 2. Lost vision cannot be restored. 3. Use of both eyes usually is restricted. 28. A nurse is caring for a client with a below-the-knee amputation. What should the nurse encourage the client to do to prepare the residual limb for a prosthesis? 1. Abduct the residual limb when ambulating. 2. Dangle the residual limb off the bed frequently. 3. Soak the residual limb in warm water twice a day. 4. Press the end of the residual limb against a pillow periodically. 29. A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of an exacerbation of asthma. What should the nurse plan to do to best help this client? 1. Determine the client’s emotional state. 2. Give prescribed drugs to promote bronchiolar dilation. 3. Provide education about the impact of a family history. 4. Encourage the client to use an incentive spirometer routinely. 30. A health care provider orders daily sputum specimens to be collected from a client. When is the most appropriate time for the nurse to collect these specimens? 31. Which factor is essential to consider when a nurse evaluates whether a unit environment is conducive to psychologic safety for a confused client with dementia? 32. A client is extubated in the postanesthesia care unit after surgery. For which common response should the nurse be alert when monitoring the client for acute respiratory distress? 34. An IV infusion of magnesium sulfate is prescribed for a client with severe preeclampsia. The dose is twice the usual adult dose. When a nurse questions the dosage, the health care provider insists that it is the desired dose and directs the nurse to administer the medication. How should the nurse respond to this directive? 1. Administer the dose and monitor the client. 2. Withhold the dose and notify the nurse manager. 3. Administer the dose and document it on the client’s record. 4. Withhold the dose and notify the director of the obstetric department. 2. Turn the client on the side. 3. Increase the rate of infusion. 4. Discontinue the oxytocin infusion. 5. Request a prescription for an antibiotic. 36. Which nursing action should be included in the plan of care for a child with acute poststreptococcal glome-rulonephritis? 37. A nurse is caring for an older adult who is taking acetaminophen (Tylenol) for the relief of chronic pain. Which substance is most important for the nurse to determine the client is taking because it intensifies the most serious adverse effect of acetaminophen? 38. The parents of a child who is dying of cancer ask the nurse whether they should tell their 7-year-old son that his sister is dying. What is the most appropriate response by the nurse? 1. “Your child cannot comprehend the real meaning of death, so don’t tell him until the last moment.” 2. “Your son probably fears separation most and wants to know that you will care for him, rather than what will happen to his sister.” 3. “You should talk this over with your health care provider, who probably knows best what is happening in terms of your daughter’s prognosis.” 4. “Your son probably doesn’t understand death as we do but fears it just the same. He should be told the truth to let him prepare for his sister’s possible death.” 40. A client with major depression is admitted to the hospital. What is the most therapeutic initial nursing intervention? 1. Introducing the client to one other client 2. Requiring participation in therapy sessions 3. Encouraging interaction with others in small groups 41. During the first trimester, a client tells a nurse at the prenatal clinic that she frequently feels nauseated. What should the nurse teach her about reducing the nausea? 42. A nurse is caring for a client with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). What complications are most commonly associated with COPD? 43. A new parent asks a nurse how to care for the baby’s umbilical cord stump. What should the nurse include in the teaching? 1. Expect a moderate amount of drainage. 2. Keep the area moist with sterile normal saline. 3. Provide sponge baths until the stump falls off. 4. Cover the site with a small sterile dressing twice a day. 44. After resection of a lower lobe of the lung, a client has excessive respiratory secretions. Which independent nursing action should the nurse implement? 45. A health care provider explains a cystectomy and an ileal conduit to a client with invasive carcinoma of the bladder. Later the client expresses concerns about the possibility of offensive odors associated with this procedure. What is the best response by the nurse? 1. “Tell me more about what you are thinking.” 2. “Products are available to limit this problem.” 3. “This is a problem, but the surgery is necessary.” 4. “Most people who have this surgery share this same concern.” 46. Using Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, what should the nurse expect a 6-month-old infant to demonstrate? 47. An internal fetal monitor is applied while a client is in labor. What should the nurse explain about positioning while the monitor is in place? 1. The most comfortable position can be assumed. 2. Monitoring is more accurate in the side-lying position. 3. The monitor leads can be detached when sitting on the bedpan. 4. Maintaining a supine position holds the internal electrode in place. 48. During a newborn assessment a nurse reports a sign of respiratory distress. What clinical manifestation did the nurse identify? 49. On the third postpartum day, a woman who is breastfeeding calls the nurse at the clinic and asks why her breasts are tight and swollen. What should the nurse consider before explaining why her breasts are engorged? 1. There is an overabundance of milk. 2. Breastfeeding probably is ineffective. 3. The breasts have been inadequately supported. 50. A person on the beach sustains a deep partial-thickness burn because of a severe sunburn. What is the best first-aid measure that a nurse should instruct the person to apply before seeking health care? 51. A nurse is assessing a newborn. What finding indicates the need for follow-up care? 52. A nurse is assessing a group of older adults. Which should the nurse consider to be least likely to be affected by aging? 54. What should be the initial nursing action after the birth of a preterm infant with an Apgar score of 6? 1. Check and clamp the umbilical cord. 2. Dry the infant and place in a warm environment. 3. Obtain a footprint and apply an identification band. 4. Get resuscitative equipment and assist the health care provider. 55. Which is most important for the nurse to do when providing care to a client who has had a transurethral resection of the prostate? 1. Maintain patency of the cystostomy tube. 2. Ensure patency of the indwelling catheter. 3. Keep the abdominal dressing clean and dry. 57. A client on a psychiatric unit who has been hearing voices is receiving a neuroleptic medication for the first time. The client takes the cup of water and the pill and stares at them. What is the most therapeutic statement the nurse can make? 1. “You have to take your medicine.” 2. “Your doctor wants you to have this medicine. Swallow it.” 3. “There must be a reason why you don’t want to take your medicine.” 4. “This is the medication that your doctor ordered for you to make you well.” 58. After a therapy session with a health care provider in the mental health clinic, a client tells the nurse that the therapist is uncaring and impersonal. What is the nurse’s best response? 1. “Your therapist is really very good.” 2. “I hope that the rest of the staff is caring.” 3. “The therapist is there to help you; try to cooperate.” 4. “You have strong feelings about your therapy session and your therapist.” 59. A client who has just had a kidney transplant is transferred from the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) to the intensive care unit (ICU). How often should the nurse in the ICU monitor the client’s urinary output? 60. A client who uses ritualistic behavior taps other clients on the shoulders three times while going through the ritual. The nurse infers that this client has a: 61. A pregnant client with severe preeclampsia is receiving IV magnesium sulfate. What should the nurse keep at the bedside to prepare for the possibility of magnesium sulfate toxicity? 62. A person who is hospitalized for alcoholism becomes boisterous and belligerent and verbally threatens the nurse. What is the most appropriate response by the nurse? 1. Place the client in restraints. 2. Sedate and place the client in a controlled environment. 3. Encourage the client to play Ping Pong with another client. 4. Set firm limits on the client’s behavior and enforce adherence to them. 63. A family of a client with myasthenia gravis asks the nurse whether the client will be an invalid. What is the nurse’s best response? 1. “Medications will mask the signs of the disease.” 2. “With continuous treatment, the progression of the disease usually can be controlled.” 3. “There will be periods when bed rest will be necessary and times when regular activity will be possible.” 4. “The progression generally is slow, so people with myasthenia will spend their younger life with few problems.” 64. A parent of a 2-year-old child who was just diagnosed with cystic fibrosis expresses concern about the child’s frailty and low weight. What is the nurse’s most appropriate reply? 1. “Digestive enzymes will be given to help your child digest food.” 2. “Your child’s appetite will improve once respiratory therapy is initiated.” 3. “Your child’s coughing and shortness of breath prevent adequate chewing of food.” 4. “I suggest that you offer baby foods to your child because they are more easily digested.” 65. During the first well-baby visit after discharge from the hospital, the parents inform the nurse that their baby has difficulty sucking and swallowing and tires easily. What should the nurse consider when assessing this infant? 1. Newborns tend to tire easily, especially when feeding. 2. Decreased sucking is insignificant in the absence of cyanosis. 3. Difficulty when feeding may be an early indication of a heart defect. 4. Some infants retain mucus for several days that may interfere with feeding. 66. For which clinical indicator should the nurse monitor a child with chronic hypoxia? 67. A nurse is caring for a client with a fracture of the head of the femur. The health care provider places the client in a Buck extension. What explanation does the nurse give the client for why the traction is being used? 68. A client has a total hip arthroplasty. What should the nurse do when caring for this client after surgery? 1. Use a pillow to keep the legs abducted. 2. Elevate the client’s affected limb on a pillow. 3. Turn the client using the log-rolling technique. 69. Which client in a psychiatric unit needs immediate therapeutic intervention from the nurse? 1. 50-year-old woman who is pacing around the dayroom and picking fights with other clients 2. 25-year-old man who is making sounds and actions like a machine gun in front of the nurse’s station 3. 45-year-old man who sits quietly in the corner of the room, watching the movements of other clients 4. 33-year-old woman who wanders aimlessly around the unit, saying, “I just don’t know what to do. I feel so lost.” 70. A client in a psychiatric hospital with the diagnosis of major depression is tearful and refuses to eat dinner after a visit with a friend. What is the most therapeutic nursing action? 1. Allow the client to skip the meal. 2. Offer an opportunity to discuss the visit. 3. Reinforce the importance of adequate nutrition. 71. A person with a history of alcoholism states, “I have been drinking since last Friday to celebrate my son’s graduation from college.” What defense mechanism does the nurse identify the client is using? 73. The parents of a child with spasmodic croup ask why their child is receiving humidified oxygen. What effect of humidified oxygen should the nurse include in the explanation? 2. Provides a mode for giving inhalant drugs 3. Increases the surface tension of the respiratory tract 74. A client has a surgical creation of a colostomy. What is the most effective nursing intervention to initially help the client accept the colostomy? 1. Introduce equipment needed to care for the colo-stomy. 2. Provide literature containing factual data about colostomies. 3. Ask a member of a support group to come to speak with the client. 4. Point out the number of important people who have had colostomies. 75. When planning care for a child with autism, the nurse understands that given a choice, the child with autism usually enjoys playing: 76. A client who is at 26 weeks’ gestation arrives at the clinic for her scheduled examination. Her blood pressure is 150/86. She tells the nurse that she has gained 5 pounds in the last 2 weeks. What is the priority nursing action? 1. Test the client’s urine for albumin. 2. Take the client’s body temperature. 3. Prepare the client for a vaginal examination. 77. What behavior does a nurse expect of a newborn about 1 hour after birth? 78. A client who has a phobia about dogs is about to begin systematic desensitization. The client asks what the treatment will involve. What is the nurse’s best response? 1. “You will be exposed to dogs until you no longer feel anxious.” 2. “Rewards will be given when you do not become anxious around dogs.” 3. “Your contact with dogs will increase while using relaxation techniques.” 4. “There will be in-depth discussions to identify what caused your phobia.” 79. A nurse is providing dietary teaching for a client who is receiving a high-protein diet while recovering from an acute episode of colitis. What should the nurse include is the rationale for this diet? 80. A nurse is caring for a client experiencing an acute episode of bronchial asthma. What outcome should be achieved? 1. Raising mucous secretions from the chest 2. Curing the client’s condition permanently 3. Limiting pulmonary secretions by decreasing fluid intake 4. Convincing the client that the condition is emotionally based 81. When a developmental appraisal is performed on a 6-month-old infant, which observation is most important to the nurse in light of a diagnosis of hydrocephalus? 82. A new mother refuses to look at her newborn who has a severe birth defect. What is the nurse’s most therapeutic approach? 1. Request that the family try to distract her. 2. Clarify why she should stop blaming herself for the baby’s handicap. 3. Reinforce the explanation of the handicap and allow time for her to discuss her fears. 4. Wait until she has sufficiently recovered from the stress of birth and then bring the baby to her again. 83. When teaching a class about parenting, the nurse asks the participants what they do when their toddlers have a temper tantrum. Which statement demonstrates one parent’s understanding of the origin of temper tantrums? 1. “After a temper tantrum, I discipline my child by restricting a favorite food or activity.” 2. “When a temper tantrum begins, I isolate and ignore my child until the behavior improves.” 3. “During a temper tantrum, I partially gives in to my child before the tantrum becomes excessive.” 4. “I try to prevent a temper tantrum by allowing my child to choose between two reasonable alternatives.” 84. A nursing assistant interrupts the performance of a ritual by a client with obsessive-compulsive disorder. What is the most likely client reaction? 85. When a nurse is working with a client with psychiatric problems, a primary goal is the establishment of a therapeutic nurse-client relationship. What is the major purpose of this relationship? 1. Increase nonverbal communication 2. Present an outlet for suppressed hostile feelings 3. Assist the client in acquiring more effective behavior 86. An African-American woman is diagnosed with primary hypertension. She asks, “Is hypertension a disease of African-American people?” What is the nurse’s best response? 1. “The prevalence of hypertension is about equal for women of all races.” 2. “The higher-risk population is composed of African-American men and women.” 3. “The highest-risk population consists of older Caucasian-American men and women.” 4. “The prevalence of hypertension is greater for African-American women than for African-American men.” 87. A health care provider prescribes a diuretic for a client with hypertension. What should the nurse include in the teaching when explaining how diuretics reduce blood pressure? 88. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving a thiazide diuretic for hypertension. Which food selected by the client indicates to the nurse that dietary teaching about thiazide diuretics was effective? 89. A 20-year-old college student comes to the college health clinic reporting increasing anxiety, loss of appetite, and an inability to concentrate. What is the most appropriate response by the nurse? 1. “With whom have you shared your feelings of anxiety?” 2. “What have you identified as the cause of your anxiety?” 3. “It has been difficult for you. How long has this been going on?” 4. “Let’s talk about your problems. Are you having difficulty adjusting?” 90. A nurse is caring for a client who attempted suicide. What is the most desirable short-term client outcome during this crisis situation? 1. Strengthening coping skills 2. Establishing a no-suicide contract 3. Learning problem-solving techniques 91. A 92. A client with adrenal insufficiency reports feeling weak and dizzy, especially in the morning. What should the nurse determine is the most probable cause of these symptoms? 93. A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of chronic kidney failure. For signs of what electrolyte imbalance should the nurse monitor the client? 94. During her sixth month of pregnancy, a woman visits the prenatal clinic for the first time. As part of the initial assessment, a CBC and a urinalysis are performed. Which laboratory finding should alert the nurse that further assessment is required? 95. Two hours after an uneventful labor and birth, a client’s uterus is four fingerbreadths above the umbilicus. After urinary catheterization, the fundus remains firm and four fingerbreadths above the umbilicus. What is the priority nursing action? 1. “I have ringing in my ears.” 2. “It improves when I lie down.” 3. “Bright lights really bother my eyes.” 4. “It gets better as soon as I walk a while.” 5. “My head hurts more when I am sitting watching TV.” 6. “My head hurts more when I am lying on my side breastfeeding.” 97. A client has a history of hypothyroidism. Which skin condition should the nurse expect when performing a physical assessment? 98. A nurse is caring for a client who has had an open reduction internal fixation of a fractured hip. Which nursing assessment of the affected leg is most important after this surgery? 99. A nurse is caring for a client with myxedema who has undergone abdominal surgery. What should the nurse consider when administering opioids to this client? 1. Tolerance to the drug develops readily. 2. One third to one half the usual dose should be prescribed. 3. Opioids may interfere with the secretion of thyroid hormones. 4. Sedation will have a paradoxical effect, causing hyperactivity. 100. A nurse is caring for a child with spasmodic croup. Which clinical finding alerts the nurse that immediate nursing intervention is required? 101. What must the nurse emphasize to the family when preparing a child with persistent asthma for discharge? 1. A cold, dry environment is desirable. 2. Limits should not be placed on the child’s behavior. 3. The health problem is gone when symptoms subside. 102. An older adult with dementia is admitted to a nursing home. The client is confused, agitated, and at times unaware of the presence of others. What is the best nursing approach to help this client adapt to the unit? 1. Initiate a program of planned interaction. 2. Explain the nature and routines of the unit. 3. Explore in depth the reasons for the admission. 103. The parents of a child with a fever, headache, and stiff neck express concern that the child be tested for meningitis. Which test should the nurse explain to the parents is used to confirm the diagnosis of meningitis? 104. A nurse is caring for a client after a left pneumonectomy for cancer. The nurse palpates the client’s trachea routinely. What is the rationale for this nursing intervention? 1. A mediastinal shift may have occurred. 2. Nodular lesions may demonstrate metastasis. 3. Tracheal edema may lead to an obstructed airway. 105. A CBC, urinalysis, and x-ray examination of the chest are ordered for a client before surgery. The client asks why these tests are done. Which is the best reply by the nurse? 1. “Don’t worry; these tests are routine.” 2. “They are done to identify other health risks.” 3. “They determine whether surgery will be safe.” 106. A client is scheduled for emergency abdominal surgery. What is the priority preoperative nursing objective when caring for this client? 1. Recording accurate vital signs 2. Alleviating the client’s anxiety 3. Teaching about early ambulation 107. An infant born with hydrocephalus is to be discharged after insertion of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Which common complication of this type of surgery should the nurse explain to the parents to prepare them for their child’s discharge? 1. Violent involuntary muscle contractions 2. Eyes with sclerae visible above the irises 3. Excessive fluid accumulation in the abdomen 108. Parents are considering a bone marrow transplant for their child who has recurrent leukemia. The parents ask the nurse for clarification about the procedure. What is the best response by the nurse? 1. “It is rarely performed in children.” 2. “The immune system must be destroyed before a transplant can take place.” 3. “The hematopoietic stem cells are surgically implanted in the bone marrow.” 4. “It is a simple procedure with little preparation needed, and the stem cells are infused as in a blood transfusion.” 109. What is most important for a nurse to do when helping a new mother on the postpartum unit develop her parenting role? 1. Teach her how to care for the infant. 2. Provide time for her and her infant to be together. 3. Respond to any questions she has about her infant’s behavior. 4. Demonstrate infant care and evaluate her return demonstration. 110. When performing a newborn assessment after a vaginal birth, a nurse observes a swelling on one side of the top of the head. What clinical manifestation did the nurse identify? 1. Caput succedaneum that will spread across the scalp and then resolve 2. Fontanel that bulges when the infant cries and will close in eighteen months 3. Cephalohematoma that does not cross the suture line and will resolve in several weeks 4. Molding that results from the skull taking the shape of the vagina and will disappear in several days 111. A health care provider prescribes famotidine (Pepcid) for a client with dyspepsia. What is important to include about this medication in a teaching program for this client? 112. Although a nurse is unable to identify any obvious signs or symptoms of bleeding, a client repeatedly has tested positive for occult blood in the stool. Which laboratory result is a concern considering this client’s history? 113. A nurse is caring for a client with severe gastritis who vomited a large amount of blood. A lavage is ordered by the health care provider. Which response does the nurse expect when using a room temperature irrigating solution? 114. A blood transfusion is initiated after a client has had emergency surgery. What should the nurse do first when the client develops fever, chills, and low back pain? 1. Notify a health care provider. 2. Stop the blood and infuse saline. 3. Obtain a prescription for an antihistamine. 4. Slow the rate of the transfusion and inform the blood bank. 115. When entering a room, a nurse finds new parents looking at their newborn, who is lying in the bassinet with eyes wide open. What action should the nurse take in response to this infant’s behavior? 1. Turn on the lights in the room. 2. Begin the physical assessment. 3. Position the infant on the right side. 116. A nurse determines that a postpartum client is gravida 1 and para 1. Her blood type is B negative, and her baby’s blood type is O positive. What should the nurse include in the plan of care? 117. While changing a newborn’s diaper, a client expresses concern about a small spot of red vaginal discharge on the diaper. How should the nurse respond to this concern? 1. Assess for other signs of bleeding. 2. Obtain an order for vaginal cultures. 3. Explain that this is an expected finding. 119. What concept of death should a nurse expect a preschool-age child to have? 120. A nurse is assessing a client with major depression. Which clinical manifestation reflects a disturbance in affect related to depression? 121. A client is admitted to the birthing unit in active labor. An amniotomy is performed. What physiologic change does the nurse expect to occur after the procedure? 1. Diminished vaginal bleeding 2. Less discomfort with contractions 3. Progressive dilation and effacement 122. A nurse is caring for a client in labor. What client response indicates that the transition phase of labor probably has begun? 1. Assumes the lithotomy position 2. Perspires and has a flushed face 3. Indicates back and perineal pain
Comprehensive Examination 1
Review Questions: Part A
 2. A nurse is assessing a client who is experiencing postmenopausal bleeding. The tentative diagnosis is endometrial cancer. Which findings in the client’s history are risk factors associated with endometrial cancer? Select all that apply.
2. A nurse is assessing a client who is experiencing postmenopausal bleeding. The tentative diagnosis is endometrial cancer. Which findings in the client’s history are risk factors associated with endometrial cancer? Select all that apply.
 14. Oxytocin (Pitocin) augmentation via IV piggyback (IVPB) is prescribed for a client in labor after a period of ineffective uterine contractions. What nursing interventions are most important if strong contractions that last 90 seconds or longer occur? Select all that apply.
14. Oxytocin (Pitocin) augmentation via IV piggyback (IVPB) is prescribed for a client in labor after a period of ineffective uterine contractions. What nursing interventions are most important if strong contractions that last 90 seconds or longer occur? Select all that apply.
 21. A nurse is working with a client who has the diagnosis of borderline personality disorder with antisocial behavior. What personality traits should the nurse expect the client to exhibit? Select all that apply.
21. A nurse is working with a client who has the diagnosis of borderline personality disorder with antisocial behavior. What personality traits should the nurse expect the client to exhibit? Select all that apply.
 33. What clinical findings does a nurse expect when assessing a child with acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Select all that apply.
33. What clinical findings does a nurse expect when assessing a child with acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Select all that apply.
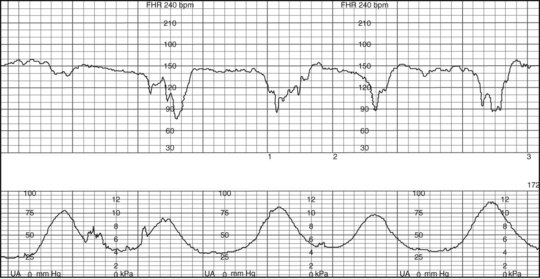
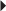 35. A client who is lying in the supine position while in active labor has an IV oxytocin (Pitocin) infusion and external monitors in place. Using the monitoring strips below, identify the appropriate nursing interventions. Select all that apply.
35. A client who is lying in the supine position while in active labor has an IV oxytocin (Pitocin) infusion and external monitors in place. Using the monitoring strips below, identify the appropriate nursing interventions. Select all that apply.
 39. A nurse is caring for an underweight adolescent girl who is diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. What are common characteristic of girls with this disorder that the nurse should identify when obtaining a health history and performing a physical assessment? Select all that apply.
39. A nurse is caring for an underweight adolescent girl who is diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. What are common characteristic of girls with this disorder that the nurse should identify when obtaining a health history and performing a physical assessment? Select all that apply.
 53. Nurses who care for the terminally ill apply the theories of Kübler-Ross in planning care. According to Kübler-Ross, individuals who experience a terminal illness go through a grieving process. Place the stages of this process in the order identified by Kübler-Ross.
53. Nurses who care for the terminally ill apply the theories of Kübler-Ross in planning care. According to Kübler-Ross, individuals who experience a terminal illness go through a grieving process. Place the stages of this process in the order identified by Kübler-Ross.
 56. A client is to receive 125 mL of IV fluid every hour. The drop factor of the IV tubing is 10 gtt/mL. How many drops per minute should the nurse administer? Record your answer using a whole number.
56. A client is to receive 125 mL of IV fluid every hour. The drop factor of the IV tubing is 10 gtt/mL. How many drops per minute should the nurse administer? Record your answer using a whole number.
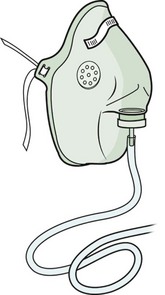
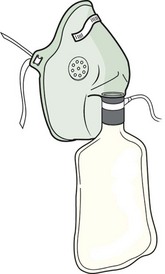
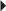 72. A nurse is caring for a client in respiratory distress. The health care provider orders oxygen via a nonrebreather mask. Which mask should the nurse obtain to implement the oxygen order?
72. A nurse is caring for a client in respiratory distress. The health care provider orders oxygen via a nonrebreather mask. Which mask should the nurse obtain to implement the oxygen order?
Review Questions: Part B
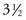 -year-old child is admitted to the hospital for an appendectomy. What should the nurse use to best prepare the child for the hospital experience?
-year-old child is admitted to the hospital for an appendectomy. What should the nurse use to best prepare the child for the hospital experience?
 96. A client receives spinal anesthesia during labor and birth. Twenty-four hours later, she tells a nurse that she has a headache. Which statements indicate to the nurse that the headache is a reaction to the anesthesia? Select all that apply.
96. A client receives spinal anesthesia during labor and birth. Twenty-four hours later, she tells a nurse that she has a headache. Which statements indicate to the nurse that the headache is a reaction to the anesthesia? Select all that apply.
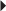 118. Which clinical findings should the nurse expect when assessing a client with hyperthyroidism? Select all that apply.
118. Which clinical findings should the nurse expect when assessing a client with hyperthyroidism? Select all that apply.
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



 Denotes alternate format question.
Denotes alternate format question.