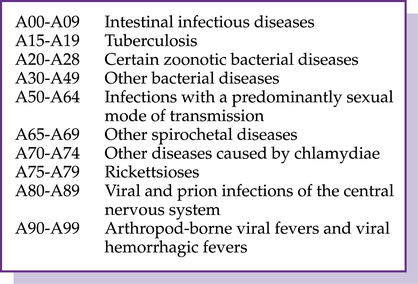
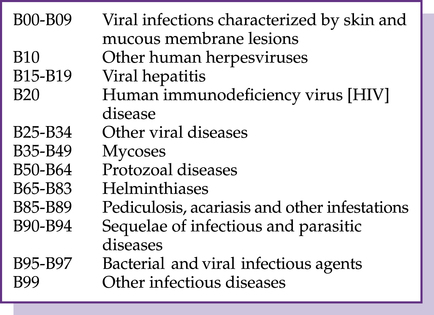
CHAPTER 4 After completing this chapter you should be able to 1. Review certain infectious and parasitic disease codes. 3. Assess the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism codes. 4. Examine the endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases codes. 5. Understand the mental, behavioral and neurodevelopmental disorder codes. 6. Examine the diseases of the nervous system codes. 7. Analyze the diseases of the eye and adnexa codes. 8. Comprehend the organization and reporting of the ear and mastoid process codes. 9. Recognize the diseases of the circulatory system codes. 10. Evaluate the diseases of the respiratory system codes. 11. Demonstrate the ability to report diagnoses with I-10 codes for Chapters 1-10. Chapter 1 in the I-10 Tabular is Certain Infectious and Parasitic Diseases (A00-B99), which classifies diseases according to the etiology (cause) of the disease. Because infectious and parasitic conditions can affect various parts of the body, the chapter contains a wide variety of codes and complex terminology. The A codes include the blocks illustrated in Figure 4–1. B95.61 Methicillin susceptible Staphylococcus aureus infection as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere (MSSA) B95.62 Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere (MRSA) The B codes include viral infections, mycoses (fungi), protozoal (microscopic animals), helminthiases (parasitic worms), pediculosis (louse), acariasis (mites), sequelae of infectious disease, and other infectious agents. The B codes are illustrated in Figure 4–2. Common codes reported with the B codes are herpes (B00), chickenpox (B01), herpes zoster (shingles, B02), measles (B05), and German measles (Rubella, B06).
Chapter-specific guidelines (ICD-10-CM chapters 1-10)
Certain infectious and parasitic diseases
A codes (a00-a99)
B codes (b00-b99)
Viral hepatitis
 Hepatitis A (HAV) was formerly called epidemic, infectious, short-incubation, or acute catarrhal jaundice hepatitis, and the primary transmission mode is the oral–fecal route.
Hepatitis A (HAV) was formerly called epidemic, infectious, short-incubation, or acute catarrhal jaundice hepatitis, and the primary transmission mode is the oral–fecal route.
 Hepatitis B (HBV) was formerly called long-incubation period, serum, or homologous serum hepatitis. Transmission modes are through blood from infected persons and from body fluids of infected mother to neonate.
Hepatitis B (HBV) was formerly called long-incubation period, serum, or homologous serum hepatitis. Transmission modes are through blood from infected persons and from body fluids of infected mother to neonate.
 Hepatitis C (HCV), caused by the hepatitis C virus and is primarily transfusion associated.
Hepatitis C (HCV), caused by the hepatitis C virus and is primarily transfusion associated.
 Hepatitis D (HDV), also called delta hepatitis and is caused by the hepatitis D virus in patients formerly or currently infected with hepatitis B.
Hepatitis D (HDV), also called delta hepatitis and is caused by the hepatitis D virus in patients formerly or currently infected with hepatitis B.
 Hepatitis E (HEV) is also called enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. The primary transmission mode is the oral–fecal route, usually through contaminated water.
Hepatitis E (HEV) is also called enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. The primary transmission mode is the oral–fecal route, usually through contaminated water.
Chapter-specific guidelines (ICD-10-CM chapters 1-10)
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access