Cations and Anions
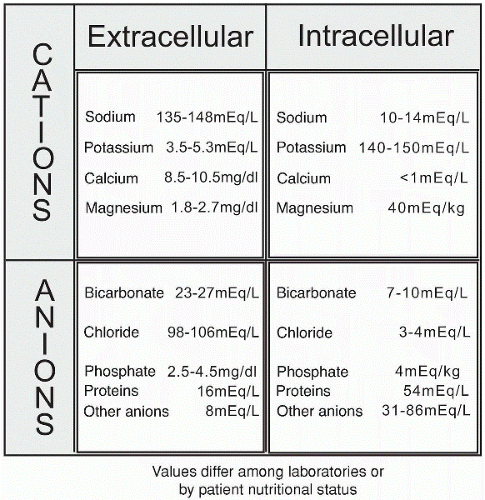
Electrolytes are divided into positively and negatively charged groups called cations (+) and anions (−). Single or multiple charges denote their strength, or valence. Sodium and potassium are the predominant monovalent single-charge cations, whereas chloride represents a major monovalent anion. Calcium and magnesium represent divalent double-charge cations vital in many body functions. These electrolytes are measured in milliequivalents. Divalent ions have a stronger bond than monovalent ions. For example, two monovalent anions attempt to maintain an electrochemical balance by combining with one divalent anion (e.g., Ca++ + 2CL− = CaCl2).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree