Chapter 13 Care of the Late Preterm Infant
1. Late preterm infants (LPIs) are at risk for rehospitalization. Common causes of rehospitalization include sepsis, hyperbilirubinemia, failure to thrive, and feeding difficulties. What is another common cause of rehospitalization of the LPI?
2. A 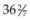 -week gestational age infant of a diabetic mother was delivered vaginally, weighing 3.75 kg. Spontaneous rupture of membranes occurred 2 hours prior to delivery. Fluid was clear and nonodorous. Fetal electrocardiographic monitoring revealed a normal tracing. Immediately after birth, the infant displayed the following symptoms: tachypnea, grunting, retractions, and cyanosis. Continuous positive airway pressure was provided with supplemental oxygen at 50%. Initial arterial blood gas values revealed a respiratory acidosis with hypoxia. Which of the following differential diagnoses most likely correlates with this infant’s presentation?
-week gestational age infant of a diabetic mother was delivered vaginally, weighing 3.75 kg. Spontaneous rupture of membranes occurred 2 hours prior to delivery. Fluid was clear and nonodorous. Fetal electrocardiographic monitoring revealed a normal tracing. Immediately after birth, the infant displayed the following symptoms: tachypnea, grunting, retractions, and cyanosis. Continuous positive airway pressure was provided with supplemental oxygen at 50%. Initial arterial blood gas values revealed a respiratory acidosis with hypoxia. Which of the following differential diagnoses most likely correlates with this infant’s presentation?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


