Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Disorders
1. The nurse notifies the licensed practitioner because this infant most likely has:
2. The infant also is noted to have a webbed neck, epicanthal folds, and lymphedema of the hands and feet. A genetics consult is indicated to evaluate this infant for which of the following?
3. The effectiveness of prostaglandin E1 therapy for a patient with hypoplastic left heart syndrome is best demonstrated by:
4. For an infant with tricuspid atresia, prostaglandin E1 is started at 0.05 mcg/kg/minute. Which of the following should the nurse monitor to assess effectiveness of the prostaglandin E1 therapy?
5. Digoxin is used in the long-term management of supraventricular tachycardia because of which effect?
6. When assessing an infant with hypoplastic left heart syndrome, the nurse should anticipate:
7. The care plan for an infant receiving indomethacin should include monitoring for which of the following?
8. The main goal of preoperative management of an infant with hypoplastic left heart syndrome is to:
9. A 26-week gestation infant has been oliguric for 14 hours. The electrocardiogram (ECG) shows peaked T waves and a widened QRS complex. Serum laboratory values are Na 128 mEq/L, K 6.9 mEq/L, Cl 85 mEq/L, Ca 6.8 mg/dl, glucose 30 mg/dl. What is the most likely cause of the infant’s ECG abnormalities?
10. The rationale for performing a balloon septostomy in transposition of the great vessels is to increase:
11. Supplemental oxygen should be used with caution in infants with single-ventricle anatomy because:
12. The plan of care for an infant of a diabetic mother should include monitoring the infant for signs and symptoms of decreased cardiac output due to hypoglycemia because hypoglycemia:
13. Which of the following statements about cyanosis is correct?
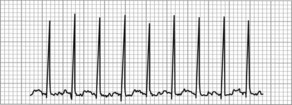
14. Which of the following best describes this rhythm?
After conversion, a 12-lead electrocardiogram is obtained. Lead V2 is shown here.
15. The abnormality in this tracing is best described as:
16. Which long-term drug treatment should the nurse expect for this condition?
17. Which of the following would be most beneficial to the infant with pulmonary atresia?
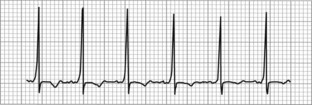
18. A 2-day-old, full-term infant has become moderately ill after a normal postnatal course. Capillary refill is 3 seconds and peripheral pulses are adequate. The cardiac monitor shows a heart rate of 280 beats/minute with a narrow QRS complex. Vagal maneuvers have been unsuccessful. Two doses of adenosine are administered with no resulting change on the electrocardiogram. The next therapeutic intervention of choice is:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>