Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, Adult
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) seeks to restore and maintain the patient’s respirations and circulation after his heartbeat and breathing have stopped. CPR is a basic life support (BLS) procedure performed on victims of cardiac arrest. It should be performed according to the 2010 American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines.1
Studies show that early CPR can improve the patient’s likelihood of survival. Chest compressions are particularly important because perfusion during CPR depends on them. To prevent a delay in chest compressions, the AHA changed the sequence of CPR in the 2010 guidelines from “A-B-C” (airway, breathing, and compressions) to “C-A-B” (compressions, airway, and breathing), which gives the highest priority to chest compressions when resuscitating a patient in cardiac arrest.1
High-quality CPR is important not only at the onset of resuscitation but throughout the entire resuscitation process. Integrating defibrillation and other advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) measures into the resuscitation process minimizes interruptions in CPR.1
Equipment
Backboard or other hard surface ▪ automated external defibrillator (AED) ▪ gloves ▪ Optional: disposable airway equipment.
Implementation
Guidelines for performing CPR vary depending on whether CPR is being performed by one or two rescuers.
One-Person CPR
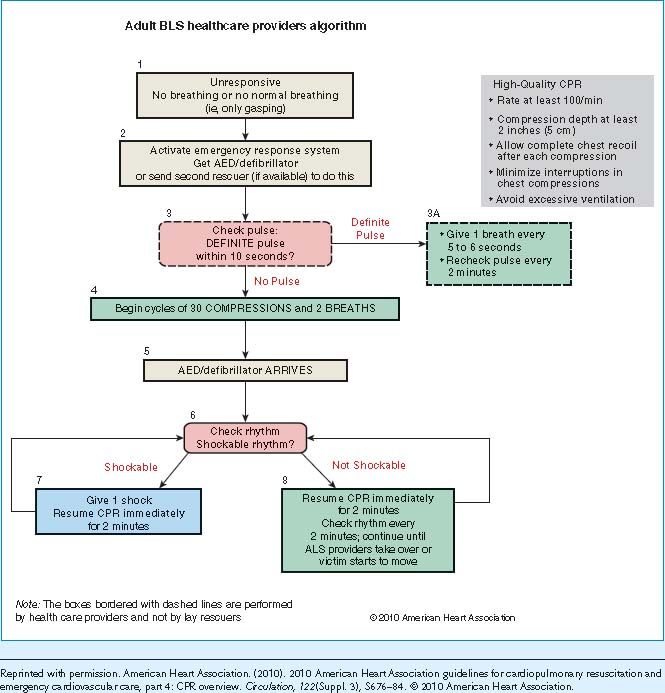
The following illustrated instructions provide a step-by-step guide for CPR as currently recommended by the AHA. (See The AHA BLS algorithm, page 118.)
As a sole rescuer, you will determine unresponsiveness, check for breathing, activate the emergency response system, check for a pulse, and begin chest compressions.1
Assess the patient to determine if he’s unconscious (as shown below). Tap him on the shoulder and shout, “Are you alright?” This helps ensure that you don’t begin CPR on a conscious person. While checking for responsiveness, check to see if the patient is apneic or only gasping. If the patient is unresponsive and apneic or only gasping, assume that he’s in cardiac arrest.1
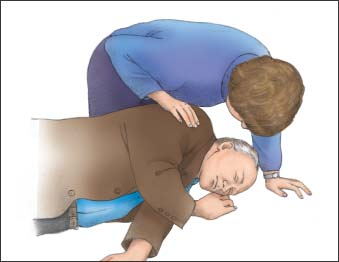
Immediately call out for help and have someone activate the emergency response system or call a code.1
Send someone to get the AED. If no one is available, get the AED and return to the patient.1
Put on gloves, if available, to prevent exposure to potentially infectious blood and body fluids.
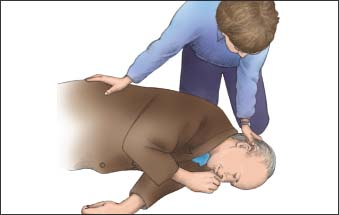
Place the patient supine on a firm surface such as a backboard; if the patient is on an air-filled mattress, deflate the mattress to maximize the effectiveness of chest compressions. When moving him, roll his head and torso as a unit; avoid twisting or pulling his neck, shoulders, or hips (as shown in next column at top). Don’t delay the initiation of CPR to place the patient on a backboard.1
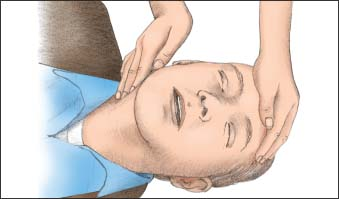
Kneel beside the patient’s chest or stand beside his bed at his chest. Palpate the carotid artery that’s closest to you. To do this, place your index and middle fingers in the groove between the trachea and the sternocleidomastoid muscle (as shown below). Palpate for no longer than 10 seconds.1
If you detect a strong, easily palpable pulse, don’t begin chest compressions. Instead, perform rescue breathing by giving the patient 10 to 12 breaths per minute (1 breath every 5 to 6 seconds). Give each breath over 1 second; each breath should cause visible chest rise.1
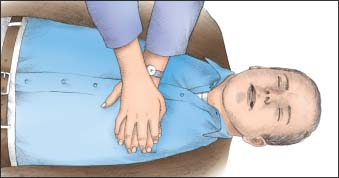
If, within 10 seconds, you don’t feel a pulse or you aren’t sure whether you feel a pulse, start giving chest compressions. Make sure that your knees are apart to provide a wide base of support. Place the heel of one hand on the center of the patient’s chest (over the lower half of the sternum) and the heel of the other hand on top of the first so that your hands are overlapped and parallel (as shown below).1
The AHA BLS Algorithm1
The following algorithm shows the steps to follow when cardiac arrest is suspected in an adult patient.
 |
With your elbows locked, arms straight, and shoulders directly over your hands (as shown below), give compressions. Using the weight of your upper body, compress the patient’s chest at least 2″ (5 cm), keeping chest compression and chest recoil durations equal. Allow the chest to completely recoil after each chest compression so the heart can adequately refill with blood.1
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
